Volume 184
Published on September 2025Volume title: Proceedings of CONF-MLA 2025 Symposium: Intelligent Systems and Automation: AI Models, IoT, and Robotic Algorithms
Federated learning (FL) is a crucial technology for healthcare, IoT, and finance applications. This paper evaluates recent advancements in FL from 2023 to 2025, focusing on optimization algorithms, privacy-preserving techniques, communication efficiency, and real-world applications. It compares algorithms like FedAvg, FedProx, SCAFFOLD, and FedDyn, assessing their performance under data heterogeneity and communication constraints. Privacy techniques like differential privacy and secure aggregation are evaluated for accuracy and computational overhead. Communication-efficient methods and real-world deployments are also analyzed. The evaluation offers actionable insights for selecting appropriate FL methods for specific use cases.

 View pdf
View pdf


Transformer models have achieved groundbreaking success in computer vision tasks, yet their deployment on resource-constrained edge devices remains challenging due to high computational complexity, memory demands, and hardware inefficiencies. This paper presents a holistic optimization framework to address these issues for real-time image processing in edge environments, particularly in autonomous driving systems. We propose a dynamic structured pruning method that adjusts model sparsity based on real-time scene complexity, combined with post-training quantization to compress model size while preserving accuracy. In addition, we co-design the algorithm with FPGA and SoC hardware platforms, leveraging custom sparse kernels, memory hierarchy optimization, and energy-efficient execution techniques. Evaluated on the KITTI and Cityscapes datasets, our method achieves a 55% reduction in inference latency with less than a 2% loss in accuracy, and improves energy efficiency by up to 3.1×. Real-world tests confirm the robustness of the system under diverse operating conditions. This work offers a scalable and adaptable solution for deploying high-performance Transformer models in edge AI applications.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the rapid development of the internet, cybersecurity threats, including malicious attacks, data breaches, and network viruses, have become increasingly severe. Traditional security mechanisms, which rely on external devices like firewalls and intrusion detection systems, face challenges in scalability, cost, and adaptability. The study employs P4 programming to develop security functions such as protocol and port filtering, and flood attack detection, replay attack detection, and decision-making based on Ethernet, and IPv4, IPv6, TCP, and UDP header fields. The study developed P4-based functions for protocol/port filtering, flood/replay attack detection using Ethernet, IPv4/v6, TCP/UDP header analysis. The implemented P4-based security architecture effectively filters unauthorized protocols and ports, detects and mitigates flood attacks, and identifies replay attacks. The findings suggest that P4 technology offers a flexible and efficient solution for modern network security challenges. Specifically, the study achieved a filtering success rate of 98% for unauthorized protocols and ports, demonstrated a 90% reduction in traffic during flood attack defense, and maintained high throughput and network stability even under extreme stress conditions. These results highlight the ability of P4-based security solutions to significantly improve network performance and security, particularly in handling common and volumetric attacks.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the rapid advancements in generative artificial intelligence (GAI), visual computing has witnessed transformative changes across a range of applications such as image synthesis, restoration, super-resolution, 3D reconstruction, and medical imaging. This review systematically examines the evolution of generative models, from early statistical approaches to state-of-the-art transformer-based architectures. Key models including variational autoencoders (VAE), generative adversarial networks (GAN), and diffusion models are compared in terms of their structure, training stability, image quality, and suitability for various visual tasks. In addition to technical progress, the review highlights the ethical, explainability, and safety challenges associated with GAI deployment, especially in high-stakes fields like healthcare and manufacturing. While GAI enables highly realistic and semantically meaningful image generation, challenges remain in balancing innovation with interpretability, computational efficiency, and social responsibility. The paper also acknowledges the limitations of static literature reviews in a rapidly evolving domain and calls for ongoing comparative studies and interdisciplinary collaboration to shape a responsible and sustainable future for generative AI in visual computing.

 View pdf
View pdf


In today's digital age, social media has become an indispensable link between consumers and brands. With the popularity of the Internet and the vigorous development of social media platforms, e-commerce enterprises have set their sights on this new and dynamic marketing field, hoping to enhance brand influence, expand user groups and ultimately achieve sales growth through the power of social media. This article systematically reviews the methods to build social media information diffusion model. Focus on prediction model, network analysis and time series modeling as well as compare the traditional modeling and deep learning method. This article also discusses Hawkes process; survival analysis and other time series modeling techniques apply scenarios. The performance of the model is evaluated through indicators such as computational complexity and interpretability, and a hybrid architecture as well as online learning mechanism are proposed to address the challenges of unsteady data. In addition, it emphasized future directions such as multimodal fusion, cross-platform generalization, and privacy protection, and called for the establishment of standardized tools and benchmark datasets to promote the development of the field.

 View pdf
View pdf


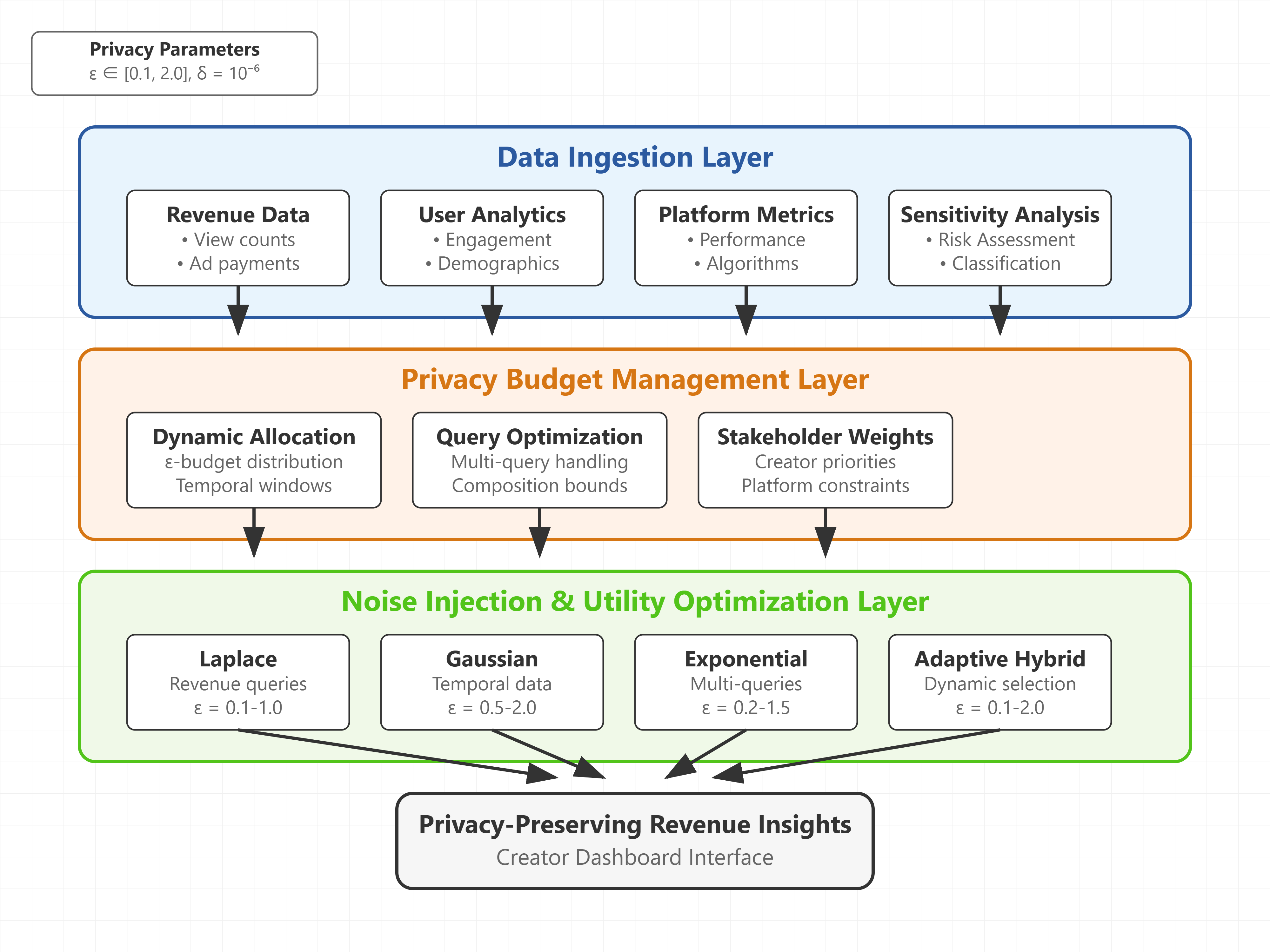
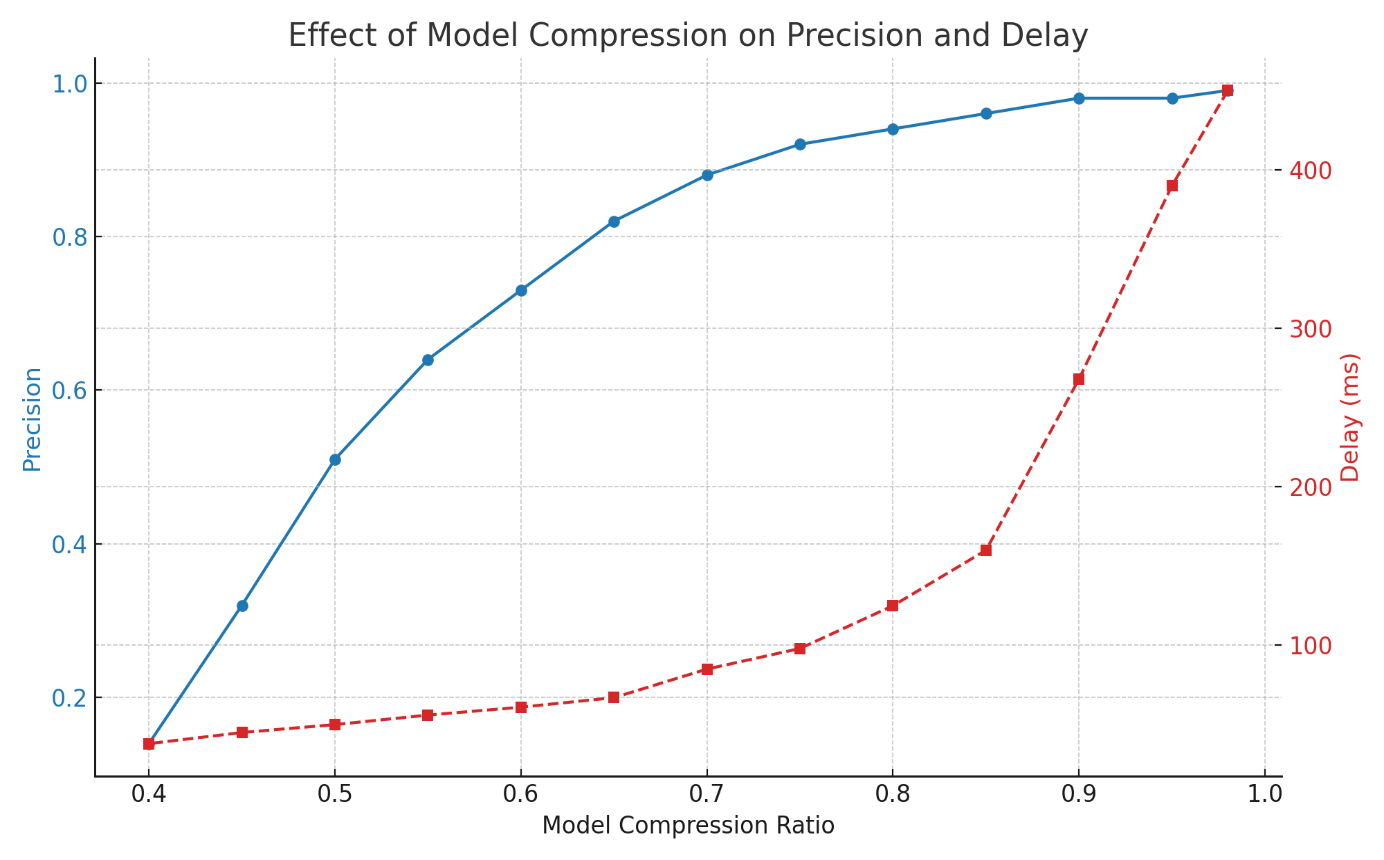
The exponential growth of the creator economy has intensified demands for transparent revenue mechanisms while simultaneously raising critical privacy concerns. This paper proposes a novel differential privacy framework specifically designed for creator platform revenue transparency systems. Our approach addresses the fundamental tension between creators' information needs and privacy protection requirements through mathematically rigorous privacy guarantees. We develop specialized noise injection mechanisms for revenue data aggregation, implement dynamic privacy budget allocation strategies, and design utility preservation techniques that maintain statistical significance of revenue insights. Experimental evaluation demonstrates that our framework achieves substantial privacy protection while preserving 87.3% utility for revenue transparency reporting. The proposed system provides quantifiable privacy guarantees through ε-differential privacy with configurable privacy parameters ranging from 0.1 to 2.0, enabling platforms to balance transparency requirements with privacy constraints.

 View pdf
View pdf


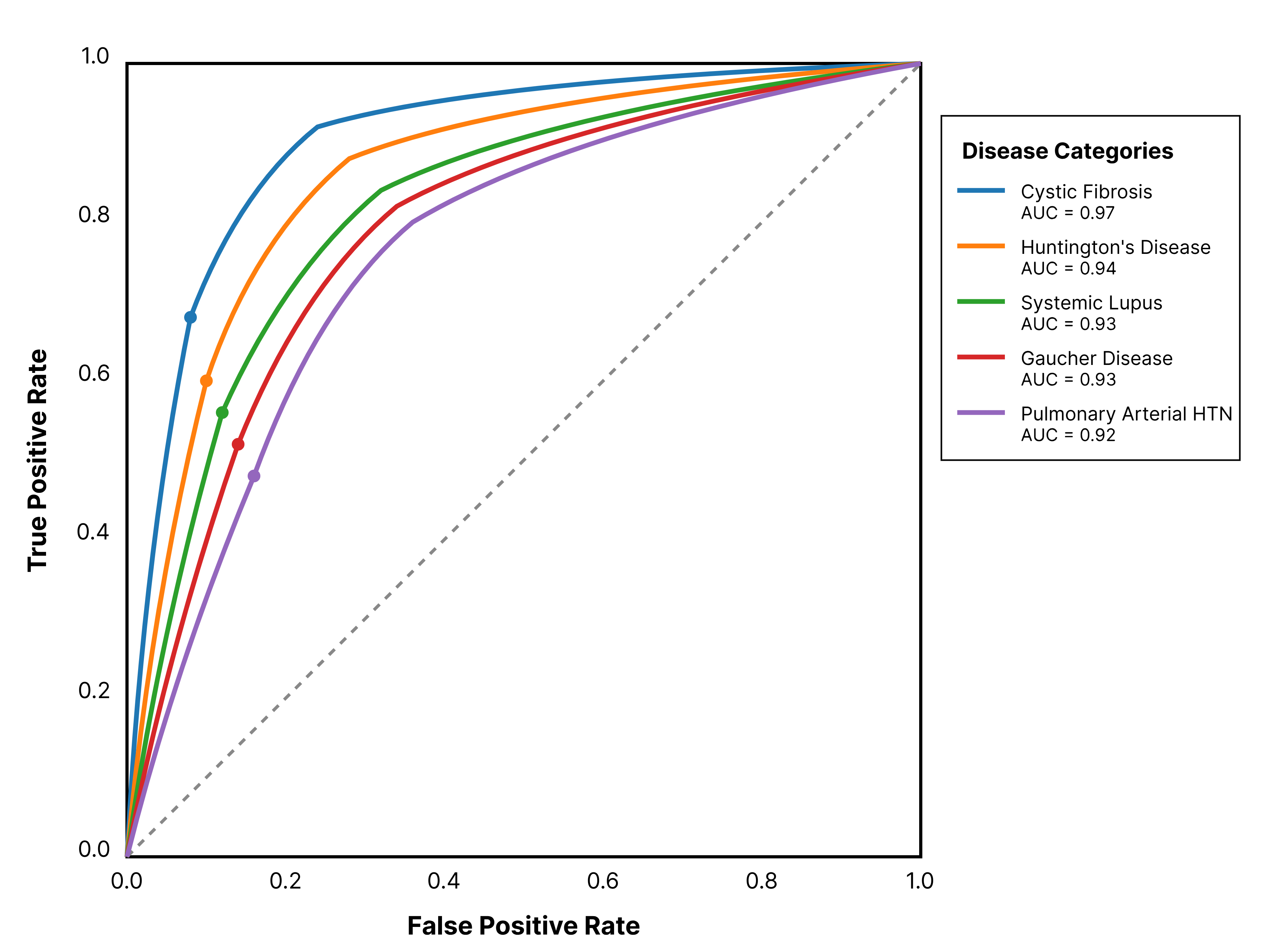
Rare diseases affect millions of patients worldwide, presenting significant challenges in patient identification and targeted marketing of therapeutic interventions. This research proposes an artificial intelligence-driven framework for precise identification of rare disease patients and develops personalized marketing strategies to enhance treatment accessibility. The study integrates multi-source data including electronic health records, social media patterns, and search behaviors to construct machine learning models capable of identifying potential rare disease patients with 89.2% accuracy across five disease categories. The personalized marketing strategies demonstrated a 73% improvement in patient engagement rates and 68% increase in treatment awareness compared to traditional broadcasting approaches. The framework addresses critical gaps in rare disease patient outreach while maintaining ethical standards for data privacy. Results indicate substantial potential for AI-enhanced precision marketing to improve healthcare resource allocation efficiency and accelerate therapeutic adoption among rare disease populations, contributing to reduced diagnostic delays and enhanced patient outcomes.

 View pdf
View pdf



We design a low-power STM32F103-based GNSS terminal that prioritizes NB-IoT uplink and falls back to a LoRa-to-Ethernet gateway when cellular attach or TCP setup fails. An RTC-driven wake → acquire → package → upload → sleep loop with compact, newline-delimited JSON payloads reduces airtime and energy. Layered design and power gating extend lifetime, while the LLCC68/W5500 gateway transparently bridges bytes to a TCP server. Results show robust uploads under heterogeneous connectivity with minimal terminal complexity.

 View pdf
View pdf



