Volume 186
Published on September 2025Volume title: Proceedings of CONF-FMCE 2025 Symposium: Semantic Communication for Media Compression and Transmission
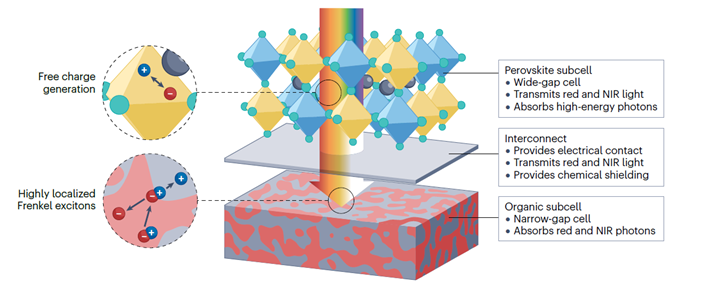
Single-junction perovskite solar cells have a relatively low upper limit of efficiency, making it difficult to develop them into industrialized photovoltaic cells. To improve efficiency, perovskite tandem solar cells have become a research focus. Among them, perovskite tandem solar cells can meet different performance requirements by adjusting organic materials. In this paper, by comparing key performance and other factors between perovskite-organic tandem solar cells and those of other types of tandem solar cells, the advantages, areas for improvement, and development prospects of perovskite-organic solar cells are summarized. Meanwhile, the organic layer materials in perovskite-organic solar cells, especially Indacenodithieno [3,2-b] thiophene-imidazolecore (ITIC), are summarized, aiming to sort out the development status of perovskite-organic solar cells in recent years and provide some basic information and innovative ideas for future research in this field.

 View pdf
View pdf


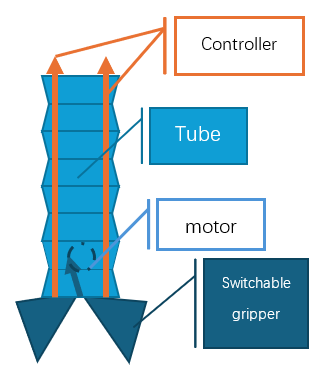
The current field of grippers has been developing for a long time; however, there are still niches that are seldom reached. Grippers for narrow spaces are still uncommon in the family of grippers. This study focuses on designing a portable object retrieval clamp for recovering lost objects from narrow settings, such as drainage grates. The device integrated a modular system with a foldable Yoshimura origami-inspired tubular arm, a motor-powered cable control system, and switchable effectors: one mechanical clamp for flat objects and one origami-based clamp for cylindrical or prismatic objects. There is also structural and mathematical analysis, including degree-of-freedom calculation and folding component relationships. Prototypes were built to test the effectiveness of designs, and control systems have been proven effective, offering a compact, adaptable solution for object recovery in confined spaces. Future work will focus on improving gripper interchangeability, enhancing arm control sensitivity, and optimizing materials for durability and performance.

 View pdf
View pdf


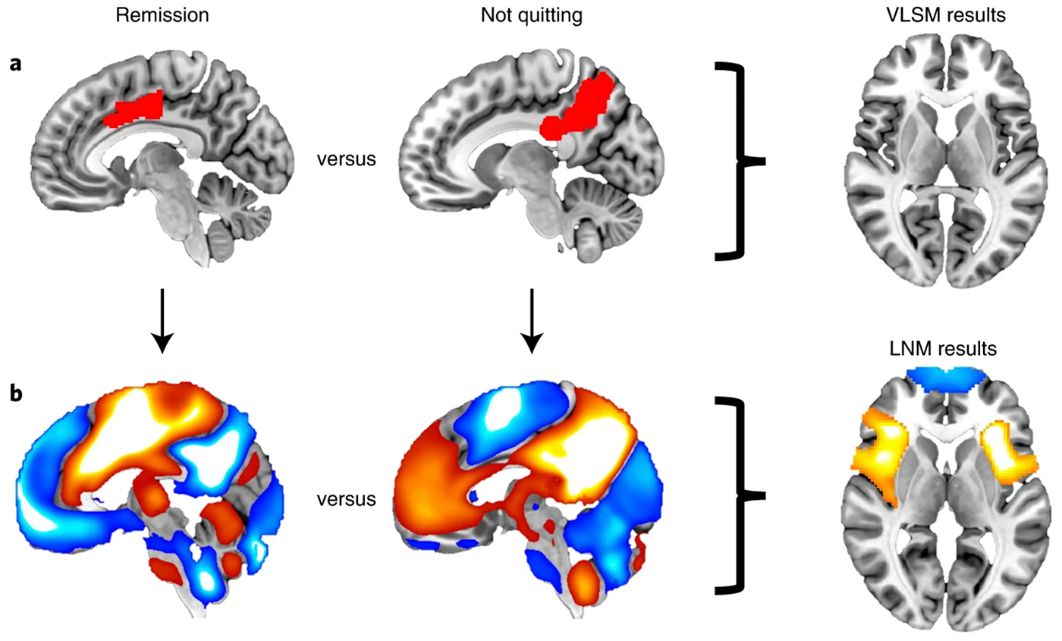
Addiction is considered as a disorder of large-scale brain networks, yet extracting robust biomarkers from high-dimensional connectivity data still remains challenges. With emphasis on attention-based and feature-selection architectures, this paper summarizes recent work applying graph neural networks to addiction-related brain connectivity. This paper introduces the theoretical foundations of brain graphs based on functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), and detail the feature-selected graph spatial attention network (FGSAN) family and related extensions, and compare their merits in the aspects of classification and interpretability. Attention mechanisms empower adaptive weighting of interactions between regions, while a Bayesian feature selector enforces sparsity to highlight potential biomarkers. Across animal and human studies, these methods often improve classification accuracy and identify biologically plausible nodes. However, they face the limits of small cohorts, scanner variability, and model complexity. This paper concludes that graph neural networks, especially when paired with feature selection and temporal modeling, provide a promising framework for discovering addiction-related signatures. This paper also recommends validating these approaches on larger human datasets, and developing explainable, computationally efficient variants in order to improve translational utility.

 View pdf
View pdf


Volumetric Additive Manufacturing (VAM) is a new additive manufacturing (AM) technology. As a layer less manufacturing technique, VAM offers faster printing speeds, no support requirements, and greater design freedom compared to traditional AM. In recent years, VAM has made significant progress in printing equipment improvements and material diversity. This article reviews the technological development of VAM from three perspectives: equipment, manufacturing processes, and materials. It evaluates and analyzes the status of each dimension and compares the technologies and research results in each. VAM's printing equipment and manufacturing processes have been improved in terms of exposure mechanisms and light projection efficiency, resulting in the development of automated exposure AM and full-scale tomography volumetric AM. Regarding printing materials, more biomedical materials are now being used in VAM, and VAM technology can process living cells and cell-laden materials. These advancements not only demonstrate the immense potential of VAM in revolutionizing manufacturing paradigms but also open up new possibilities for applications in regenerative medicine and personalized healthcare.

 View pdf
View pdf


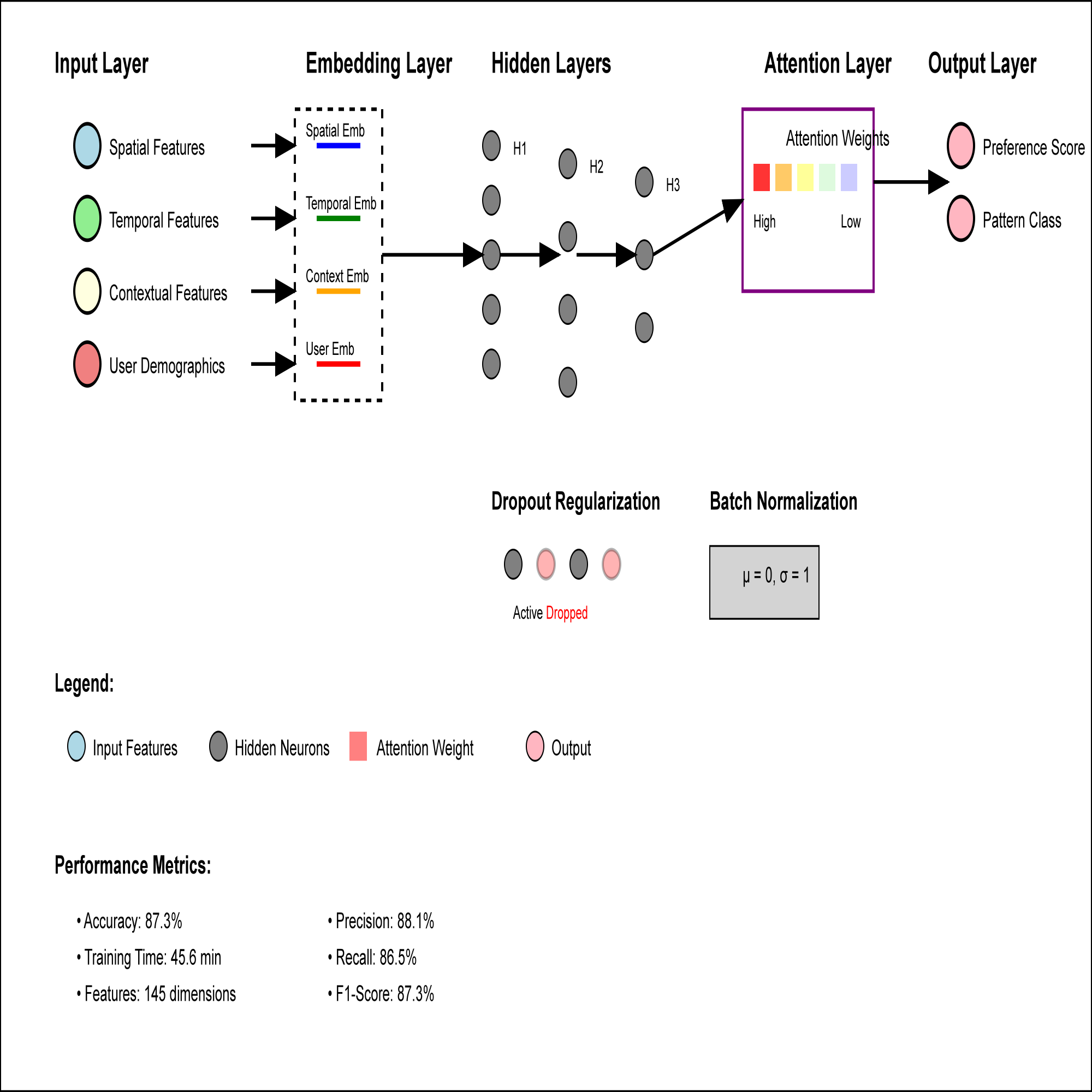
The rapid expansion of ride-hailing services has generated massive amounts of user travel data, presenting both opportunities and challenges for service optimization. This research proposes a comprehensive framework for identifying user travel preferences and developing personalized recommendation strategies using advanced machine learning techniques. Our methodology integrates feature extraction algorithms, pattern recognition models, and recommendation systems to enhance user experience and operational efficiency. Through extensive experiments on real-world datasets, we demonstrate that our approach achieves 87.3% accuracy in preference identification and improves user satisfaction by 23.7% compared to conventional methods. The proposed framework effectively addresses the heterogeneity of user behaviors while maintaining computational efficiency, providing practical solutions for ride-hailing platforms to deliver customized services and optimize resource allocation.

 View pdf
View pdf


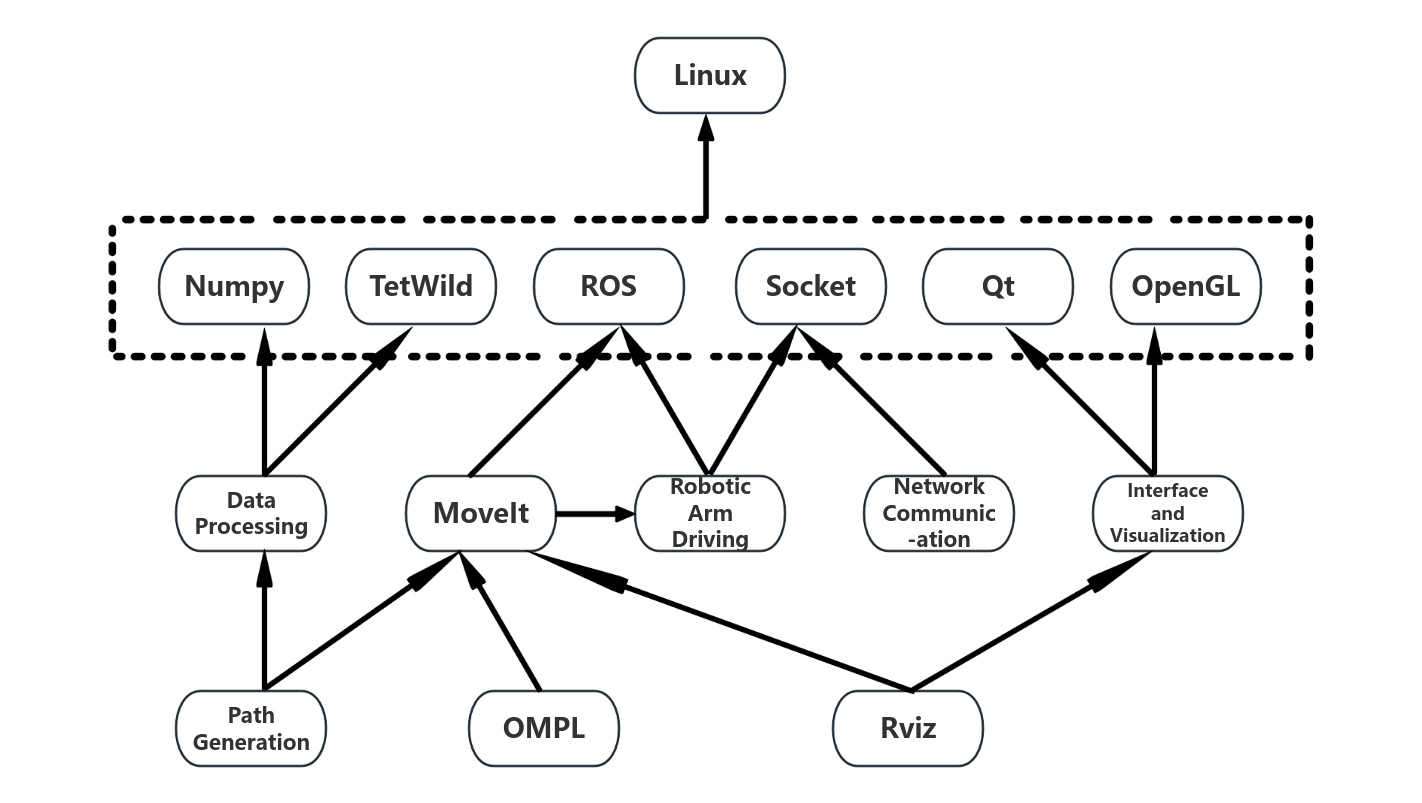
Robot 3D printing technology is a cutting-edge field that has developed rapidly in recent years.Using robots for 3D printing is an innovative combination of robots and 3D printing.This article elaborates on the precision enhancement of 3D printing based on robots from three aspects: the robot motion system, 3D printing technology, and 3D printing materials.This technology combines the multi-degree-of-freedom movement capability of industrial robots with the additive manufacturing principle of 3D printing, and the enhancement of its precision is of great significance for manufacturing complex components and promoting the development of high-end manufacturing.When the robotic arm performs multi-axis linkage, the cumulative error is more obvious than that of traditional 3D printers, which affects the forming quality.Poor stability, generating inertia or vibration when stopping and starting, causing the nozzle to deviate from the set position. At the same time, it is more difficult to extrude and control printing materials with high viscosity and high hardness,and the matching issues of the robot load capacity or the extrusion system also affect the printing precision.The future of 3D printing technology for robots is not only an innovation in manufacturing methods, but also a new starting point for the integration of human creativity and technology. It shows excellent application prospects in the manufacturing of complex components and provides technical support for the development of the intelligent manufacturing field.With the advancement of technology, the reduction of costs and policy support, robot 3D printing technology is expected to become a core pillar of global manufacturing.

 View pdf
View pdf


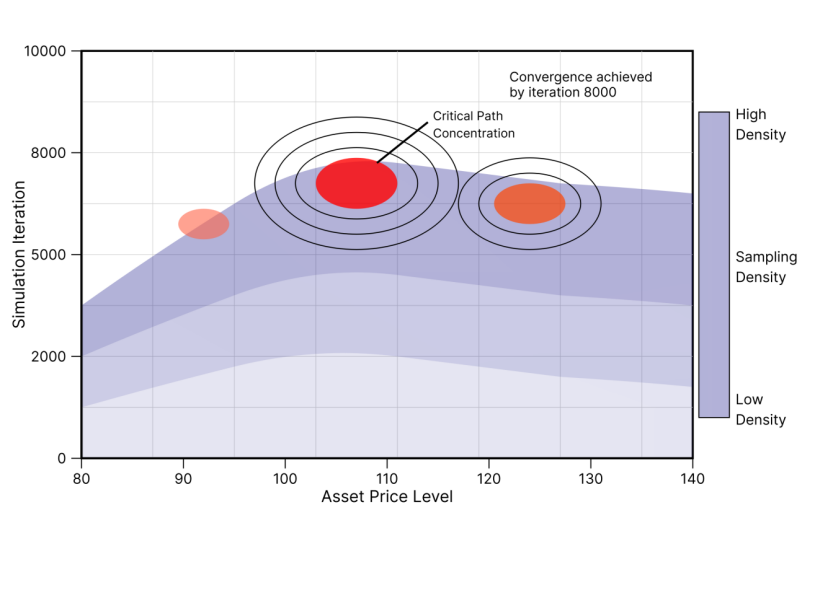
Credit Valuation Adjustment computation encounters substantial computational challenges under jump-diffusion asset dynamics, particularly regarding convergence rates in Monte Carlo simulations. Traditional sampling methods require excessive simulation paths for acceptable confidence intervals, creating operational bottlenecks in real-time risk management systems. This research develops an adaptive importance sampling framework specifically designed for high-dimensional jump-diffusion processes in CVA calculations. The methodology dynamically adjusts sampling densities to account for jump risk while maintaining unbiased estimation properties. A self-adaptive algorithm identifies and oversamples critical paths contributing disproportionately to CVA variance. Experimental results demonstrate variance reduction ratios exceeding 85% compared to standard Monte Carlo methods, with computational efficiency improvements of approximately 400% for portfolios containing European and barrier options under Merton jump-diffusion dynamics. The framework achieves significant variance reduction without sacrificing numerical accuracy, enabling faster risk reporting and more responsive counterparty risk management.

 View pdf
View pdf


As the society and technology advanced these years, the concern about Earth's energy and climate warming rose up. Meanwhile, the appearance of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) promotes the development of many fields, like transportation and aerospace. However, PEMFC is limited by the performance and cost of oxygen reduction reaction (ORR), and relies on Platinum-based catalyst to improve the reaction efficiency, which is scarce, expensive, and may result in catalyst activity decrease under complex reaction environment. That greatly increases the production cost of PEMFC and encourage scientists to develop some non-Platinum catalysts that are friendly environmental, low-priced and abundant. Thus, carbon-based materials stand out due to their high conductivity, good stability and structural designability, including Asphalt-Derived Carbon, which can converse to porous carbon materials with excellent conductivity and adjustable structure. Consequently, this article aims to illustrate the advantages of asphalt-derived carbon, compare several designs of controlled carbonization process for asphalt-derived carbon and the future of asphalt-derived carbon.

 View pdf
View pdf


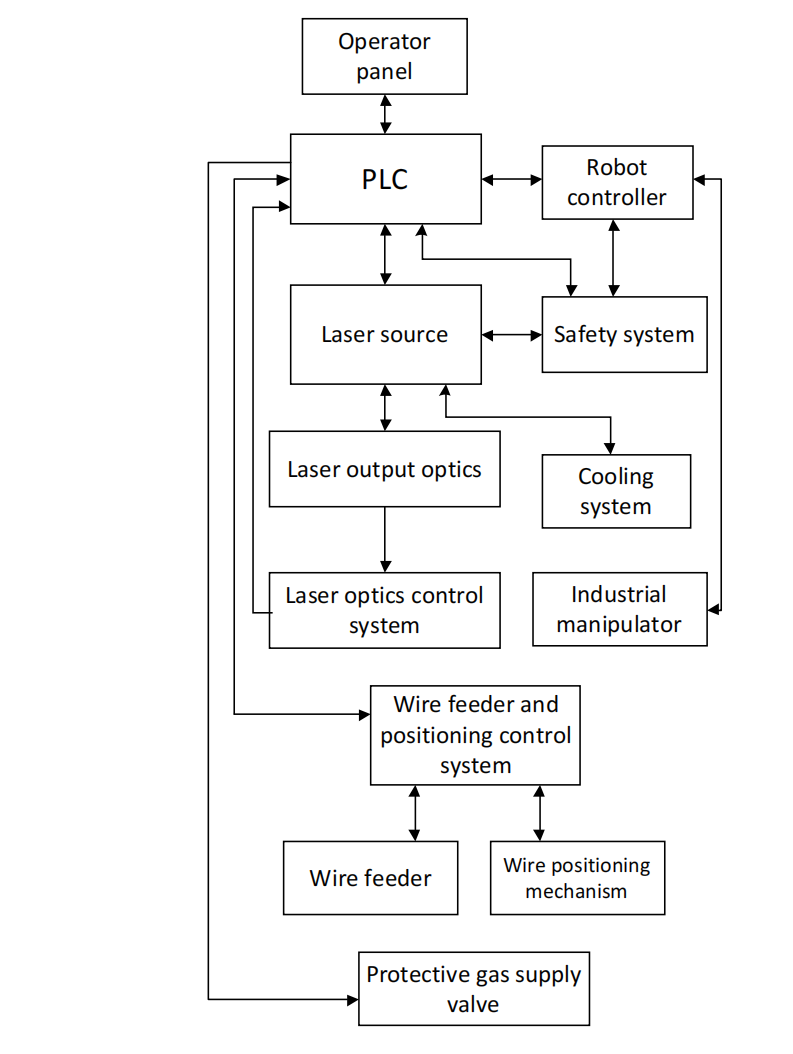
In the aerospace field, the requirements for high precision, lightweight and geometric complexity of complex structural parts are becoming increasingly stringent. Additive manufacturing,especially directed energy deposition(DED) technology has become the core means to achieve this goal. However, traditional additive manufacturing processes suffer from geometric deviations (such as the staircase effect) and low efficiency due to fixed slice layer thickness and unreasonable path planning. Moreover, the existing adaptive slicing algorithms and path planning technologies have not been deeply coordinated with advanced processes such as DED. This paper systematically reviews the research progress of adaptive slicing algorithms based on curvature, slope and features, and path planning technologies such as LSPB, MTT and robot instruction systems. It focuses on analyzing the application of the mechanism of matching path trajectories through dynamic layer thickness adjustment, combined with real-time monitoring of the molten pool image and synchronous control of robot motion in the manufacturing of aerospace parts. It also presents the achievements of high-precision manufacturing in aero-engine turbine blades and titanium alloy components with thin walls and holes. Finally, the existing challenges such as real-time optimization barriers, the compatibility problems of DED processes, and the contradiction between efficiency and precision under complex models, are put forward.

 View pdf
View pdf


Research on the electrolyte of lithium-ion batteries can enhance battery performance, reduce production costs, and make battery application scenarios more extensive. At the same time, better electrolytes can promote the development of industries, such as the new energy industry and the chemical industry, enabling batteries to provide more convenience for human society and offer more benefits to the development of science and technology. However, the current electrolytes still have significant drawbacks, such as poor stability at high voltages, flammability and volatility. This has led to lithium-ion batteries being prone to explosion and combustion accidents, with insufficient safety and stability, and their application environments being relatively limited. This article focuses on enhancing the properties of electrolytes from three aspects: solution, electrolyte, and additive. Summarized ether and sulfone solutions; LiPF6, LiFSI and LiDFOB substances are mixed as electrolytes. The advantages and disadvantages of film-forming additives and flame-retardant additives in improving the performance of electrolytes. It has reference significance for the application of electrolyte components under different conditions.

 View pdf
View pdf



