Volume 208
Published on August 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICFTBA 2025 Symposium: Financial Framework's Role in Economics and Management of Human-Centered Development
Amidst the dual drivers of intensifying globalization and disruptive technological innovation., "Huawei has solidified its position as China's flagship technology multinational with a robust presence in global telecommunications and consumer electronics. Studying Huawei's strategies is crucial due to its significant impact on international technology standards, global market dynamics, and geopolitical relations, especially amid escalating tensions between major economic powers. This article intends to examine Huawei's corporate strategy and competitive tactics, focusing on its strategic adjustments to the obstacles of international expansion and geopolitical uncertainty. Utilizing a detailed case study approach based on existing literature and industry data, the analysis evaluates Huawei's strategic evolution, global market deployment, and competitive responses. The findings indicate that Huawei has successfully leveraged persistent technological innovation, extensive global market penetration, and agile strategic adjustments to establish significant competitive advantages. However, to sustain this momentum, Huawei must prioritize enhancing supply chain resilience, strengthening risk management capabilities, and diversifying its strategic focus to effectively navigate and mitigate escalating political pressures and technological restrictions.

 View pdf
View pdf


Reinforcement learning (RL) has demonstrated significant potential in optimizing sequential decision-making within financial markets' highly dynamic and uncertain environments, offering distinct advantages over traditional trading approaches. This literature review investigates the use of RL in developing and improving trading strategies by integrating the findings of ten recent studies published between 2018 and 2025, selected for their focus on RL applications in different financial domains. These studies employ a range of RL techniques, such as Q-learning, and Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO), across a variety of financial markets, including stocks, Forex, Bitcoin, and derivatives. The review shows that RL-based strategies, which often use innovations such as multi-agent systems, ensemble learning, and sentiment analysis, demonstrate superiority such as better adaptability to non-dynamic stationary market conditions, enhanced risk-adjusted returns, and capability to learn complex relationships directly from market data, thus outperforming conventional methods and market benchmarks. Challenges hindering the practical application of reinforcement learning in trading include sample efficiency, training stability, market complexity, and the necessity for accurate market assumptions. These are areas requiring further examination and enhancement.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper explores the real-world applicability of capital structure theories by comparing two representative Chinese firms: JD.com and Alibaba. Using financial indicators and theoretical alignment, the study examines how the Trade-off Theory and Pecking Order Theory explain each firm’s financial behavior under varying corporate conditions. The comparative analysis focuses on debt structure, interest coverage, cash flow patterns, and governance models. Findings show that JD.com’s stable cash flow, asset intensity, and centralized governance align with the Trade-off Theory, while Alibaba's strong internal cash flow, asset-light operations, and sensitivity to control dilution reflect the logic of the Pecking Order Theory. These results highlight that capital structure decisions are highly context-specific and must correspond to a firm’s financial profile, risk tolerance, and strategic priorities. The study emphasizes that no single capital structure theory is universally applicable; rather, firms should adopt a contextual approach that balances cost efficiency with organizational stability. These insights contribute to a more nuanced understanding of corporate financing strategy and offer practical guidance for companies facing diverse financial and governance environments.

 View pdf
View pdf


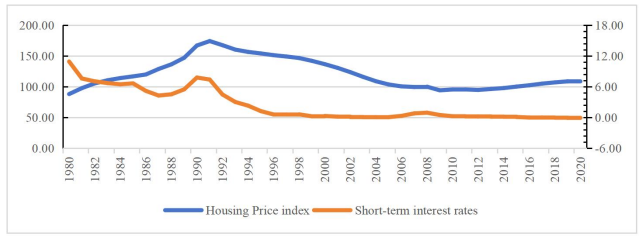
From the 1990s to the 2000s, Japan, the United States, and Spain have all experienced real estate bubbles triggered by prolonged loose monetary policies. Unlike Japan and Spain, which fell into prolonged economic recessions after the bubbles burst, the U.S. economy recovered quickly after a brief decline in asset values. Therefore, this paper finds that whether it was after Japan signed the Plaza Accord or after Spain joined the European Monetary Union, the loose monetary policies and low interest rates implemented by both governments led to excessive investment in the real estate industry. During the asset boom period, both Japan and Spain lacked adequate financial regulation, which resulted in the accumulation of systemic risks. Following the burst of the bubble, the surge in non-performing loan ratios led to credit tightening and significant wealth losses, ultimately plunging both economies into a deep recession. Before the subprime crisis erupted, the Federal Reserve had already assumed the responsibility of regulating financial institutions. The macroprudential management tools it employed, which targeted both the temporal dimension (countercyclical measures) and the structural dimension (risk correlation), effectively curbed the spread of the crisis across markets following the asset bubble burst. This paper suggests that developing countries should begin to establish a “two-pillar” policy before a crisis to smooth economic fluctuations and coordinate the implementation of macroprudential and microprudential policies.

 View pdf
View pdf


Investment management in venture capital underscores the significance of post-investment management (PIM) as a core mechanism for fostering startups’ sustainable development through non-financial value-added services. Such PIM activities typically include monitoring, strategic support, resource provision, and exit planning. This paper aims to analyze how the sustainability of starups reflects a balance between survivability and scalability. The study focuses on startups funded by venture capital (VC) firms globally. Specifically, methods involve qualitative synthesis of theoretical frameworks and quantitative analysis of survival rates, revenue growth, and innovation metrics. Research findings reveal that PIM enhances startups’ survival rates and accelerates revenue growth. However, excessive intervention is correlated with a reduction in research and development investment. Moreover, governance quality is positively linked to long-term performance. Findings validate that a balanced portfolio investment management approach, which prioritizes resource empowerment rather than stringent control, maximizes sustainable development outcomes. Future research should further examine ESG integration mechanisms and cultural dynamics within emerging-market contexts.

 View pdf
View pdf


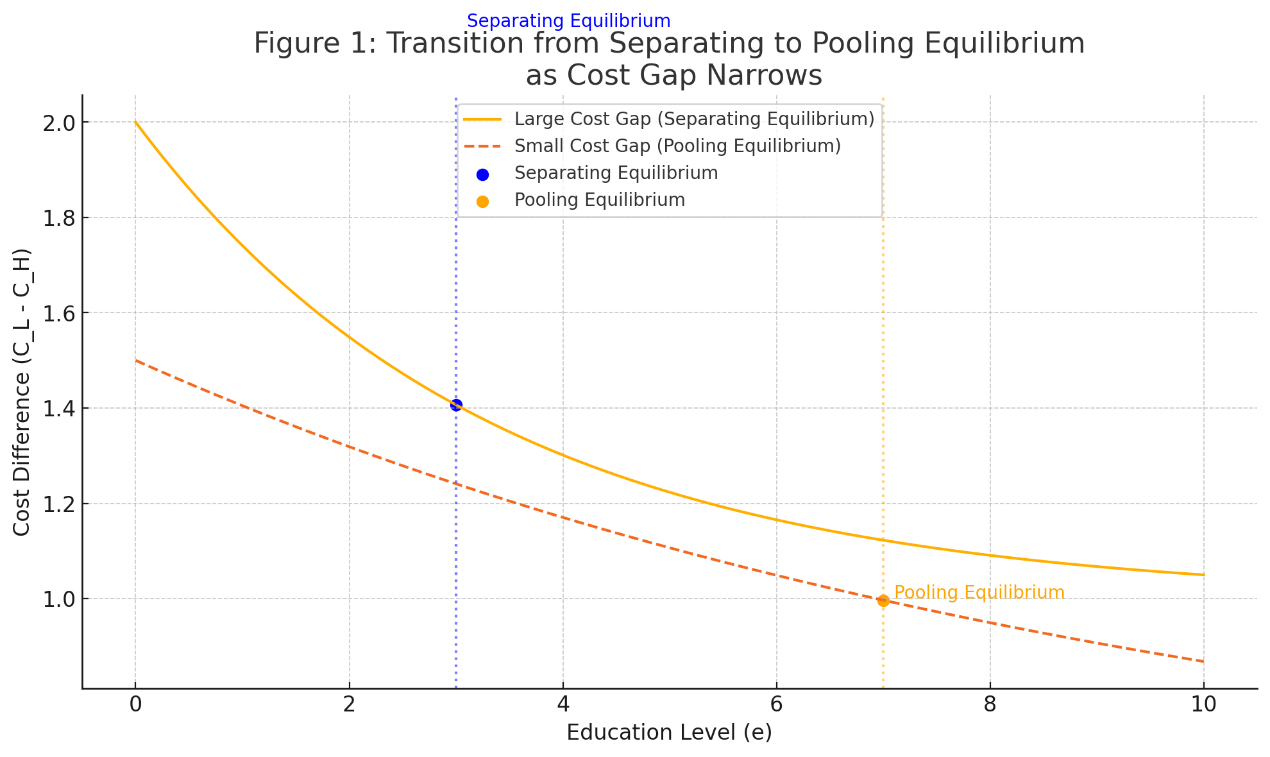
In modern labor markets, rising educational attainment among job applicants often fails to translate into corresponding productivity differences. This phenomenon, commonly referred to as “credential inflation,” raises concerns about the signaling power of education. This paper explores credential inflation through the lens of signaling games in microeconomic theory and investigates how changing cost structures and labor market screening contribute to inefficient signaling. Specifically, a Perfect Bayesian Equilibrium (PBE) model is used, where job applicants privately know their ability level and choose their education level to signal productivity to employers. When the cost of education becomes less sensitive to ability, pooling equilibria emerge, where both high- and low-ability workers choose the same level of education. As a result, education loses its signaling power and inflation of educational requirements occurs. This paper concludes that credential inflation is a rational outcome under certain market conditions and propose policy responses to mitigate its effects on labor market sorting.

 View pdf
View pdf


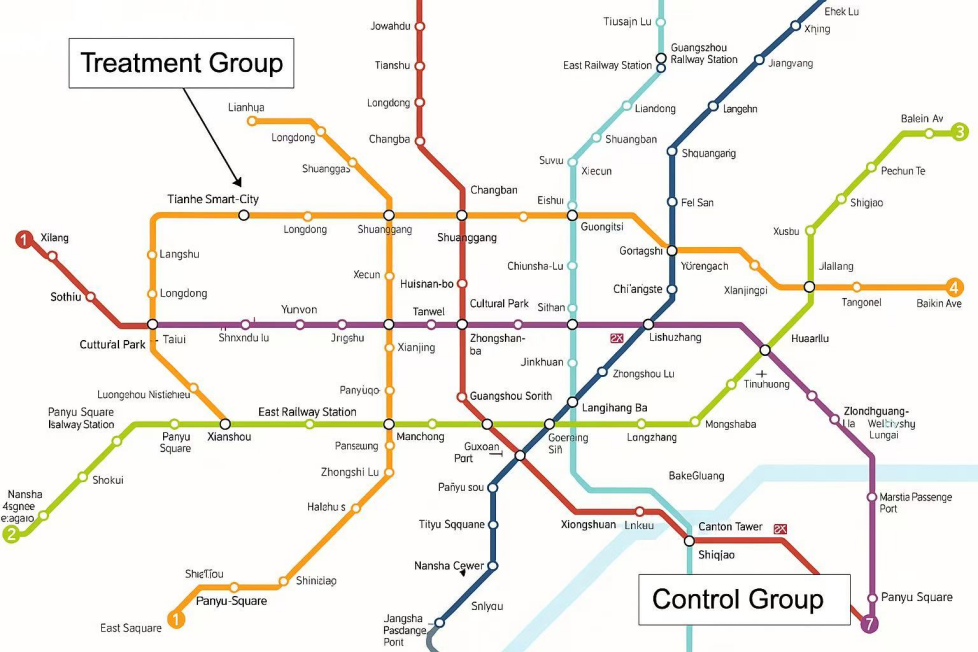
The relationship between urban transit infrastructure and labor market dynamics has gained increasing attention globally, yet significant gaps remain in understanding its impact on youth populations in rapidly urbanizing contexts. Guangzhou presents a compelling case study, where rapid urban rail transit (URT) expansion has outpaced systematic evaluation of its socioeconomic effects, particularly for young workers aged 18-35 who constitute a vital segment of the city's labor force. This research investigates how URT development influences youth employment patterns by examining three interconnected dimensions: spatial accessibility to job opportunities, commuting behavior modifications, and the trade-offs between improved mobility and environmental externalities. The study employs a mixed-methods approach, combining geospatial analysis of transit networks with longitudinal labor market data and environmental impact assessments. Special attention is given to how transit-induced reductions in commuting costs may expand effective job search radii for youth while simultaneously altering urban air quality patterns. By analyzing these dynamics in Guangzhou's context of explosive urban growth and transportation infrastructure investment, the research aims to provide policymakers with evidence-based insights for balancing mobility gains with sustainable development goals, ultimately contributing to broader discussions about equitable transit-oriented development in emerging economies.

 View pdf
View pdf



