Volume 204
Published on November 2025Volume title: Proceedings of CONF-MLA 2025 Symposium: Intelligent Systems and Automation: AI Models, IoT, and Robotic Algorithms
In recent years, algorithms in the field of computer vision have been continuously innovated and promoted, and the progress of small object detection has become a key task in the development of this field. However, compared with the detection of medium and large targets, factors such as background interference can easily interfere with the detection of small targets with smaller pixel coverage areas, making progress more difficult. In recent years, researchers have proposed various methods to address these challenges, and the three most representative frameworks are algorithms developed using YOLO, Transformer, and Diffusion models. This article provides a detailed overview and comparison of three models. The YOLO based method is superior in improving real-time detection through multi-scale feature enhancement, structural optimization, and adjusting the loss function. Based on the Transformer, the accuracy and precision of identifying small targets are improved by adjusting the mechanism, using a hybrid structure and multimodal feature fusion. And researchers will adjust the diffusion process, involving the construction of diffusion bounding boxes and diffusion engines, to enable the application of diffusion model algorithms. Finally, this article summarizes the advantages and limitations of these methods and discusses potential future research directions. The significance of this study lies in providing a unified overview of the three main research paradigms, helping researchers understand current progress, identify existing challenges, and explore new possibilities for advancing small object detection.

 View pdf
View pdf


As the information society enters the era of big data, data has become a crucial production factor driving industrial innovation and upgrading. As a key component of traditional manufacturing and consumer electronics, the camera industry has faced multiple challenges in recent years, including the widespread adoption of smartphones, diversified consumer demand, and global supply chain fluctuations. Against this backdrop, leveraging data science to realize accurate user insights, efficient product iteration, and flexible operational management has become a core concern for both academia and industry. Research indicates that the application of data science in the imaging and camera fields encompasses multiple areas, including analyzing user profiles, upgrading products, and improving resource allocation efficiency in the face of fierce competition. This paper systematically reviews existing research in the camera field using case studies and literature reviews, exploring the value realization mechanisms of data science in the camera industry and providing insights for the industry's intelligent transformation.

 View pdf
View pdf


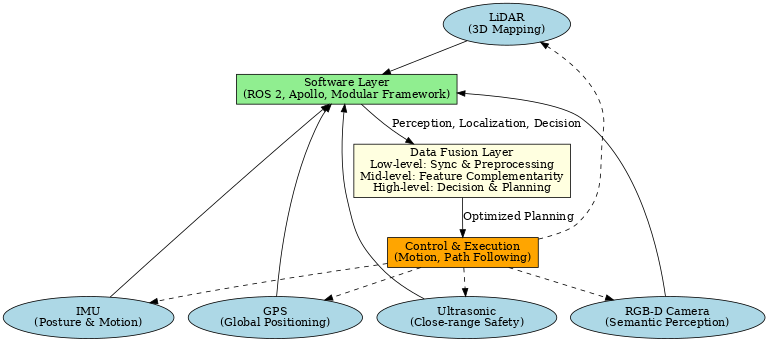
The rapid growth of the food delivery industry has intensified the “last mile” challenge, where efficiency and safety remain bottlenecks. Single-sensor navigation methods, such as GPS, cameras, or LiDAR alone, often fail in dynamic urban environments due to signal drift, poor lighting, or adverse weather. This study proposes a multi-sensor fusion navigation model integrating LiDAR, RGB-D cameras, GPS, IMUs, and ultrasonic sensors to achieve complementary perception. The model employs a layered framework: low-level data fusion for synchronization and correction, mid-level feature fusion for semantic–geometric alignment, and high-level decision fusion for path planning and behavior prediction. The purpose of this research is to evaluate the feasibility of applying multi-sensor fusion to food delivery robots. Nevertheless, the analysis relies heavily on simulations and benchmark datasets, without fully considering long-term costs, hardware durability, or user acceptance. Future research should include large-scale field trials, interdisciplinary cost–benefit evaluations, and advances in lightweight fusion algorithms to enable scalable deployment in real-world delivery environments.

 View pdf
View pdf


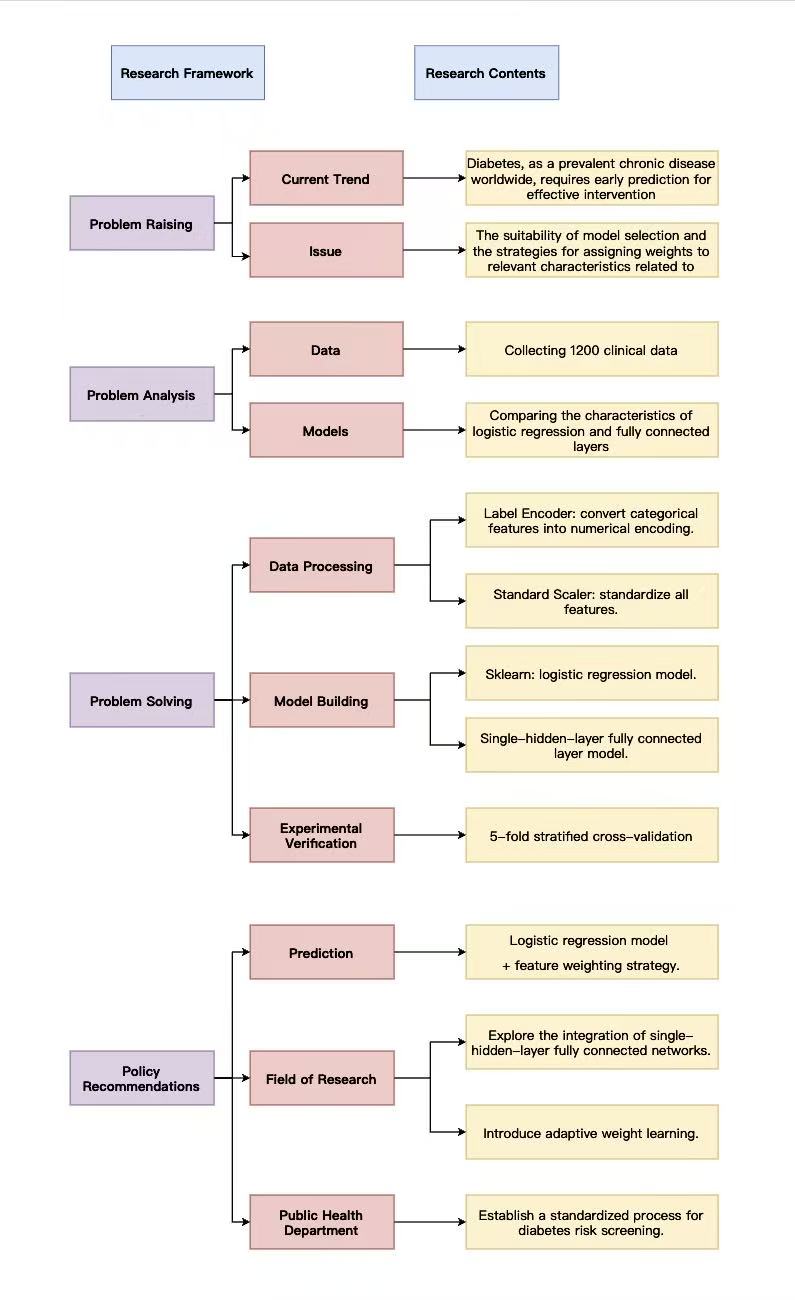
Diabetes is one of the most common diseases that targets the elderly population worldwide. Therefore, early prediction is of crucial significance for intervention treatment. This study focuses on two models: logistic regression and fully connected layers. For the task of predicting diabetes incidence, it compares the impact of having or not having a feature weight strategy on the model's accuracy. The experiment was characterized by clinical physiological indicators, and two types of models were constructed, respectively: a logistic regression model with weights and a model with average weights. The accuracy was evaluated through 5-fold cross-validation. The results show that due to the linear nature of the task, the prediction accuracy of logistic regression is superior to that of the fully connected layer. Moreover, for all model types, the weight strategy can significantly improve the accuracy. This study provides practical references for model selection and feature engineering in diabetes prediction and also offers a theoretical basis for the adaptability of models and weight mechanisms in linear tasks.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the development and progress of science and technology, facial recognition has become an important research direction in the field of computer science and has been widely applied in areas such as identity verification and security. This paper systematically reviews traditional and emerging face recognition methods, covering classic algorithms such as two-dimensional principal component analysis (2DPCA), as well as the rapidly developing deep learning techniques in recent years. Among them, the face recognition method based on deep convolutional neural networks has significantly improved the recognition accuracy and robustness compared with the original two-dimensional principal component analysis algorithm. For complex scenarios such as occlusion, illumination changes and posture differences,this paper introduces an improved method based on attention mechanism, generative adversarial network, and 3D point features. These approaches significantly enhance recognition accuracy in challenging scenarios, particularly in occluded settings such as wearing masks, and under special conditions including weak lighting.In addition, this paper summarizes the bottlenecks in the current research status and points out the future development directions and trends.

 View pdf
View pdf


Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) comprise one of the most basic mathematical frameworks for describing phenomena occurring in both space and time. From classical equations for heat and waves to recent applications in physics, engineering, and computer science, PDEs provide the framework for describing dynamics often modeled as heat conduction, fluid flow, electromagnetic fields, and image analysis. Although they date back a number of centuries, they remain entirely relevant today, especially as numerical methods and computational tools have enabled the study of complex, real-world systems. This paper will review PDEs in a number of ways. First, the paper reviews the fundamentals of theory and classification in PDEs, specifically by distinguishing PDEs into elliptic, parabolic and hyperbolic types. Second, applications, particularly privileging the use of PDEs in image processing, particularly spatial denoising, edge detection and reconstruction, as well as the physical sciences, like quantum mechanics and fluid dynamics. Finally, this paper will highlight limitations and future directions of PDEs, highlighting how PDE-based models may be improved through machine learning, or more generally, data-driven approaches. This paper seeks to combine the theoretical aspects of PDEs with practical application to demonstrate both the mathematical richness of the field as well as the interdisciplinary purpose in terms of furthering both scientific understanding and technological innovations.

 View pdf
View pdf


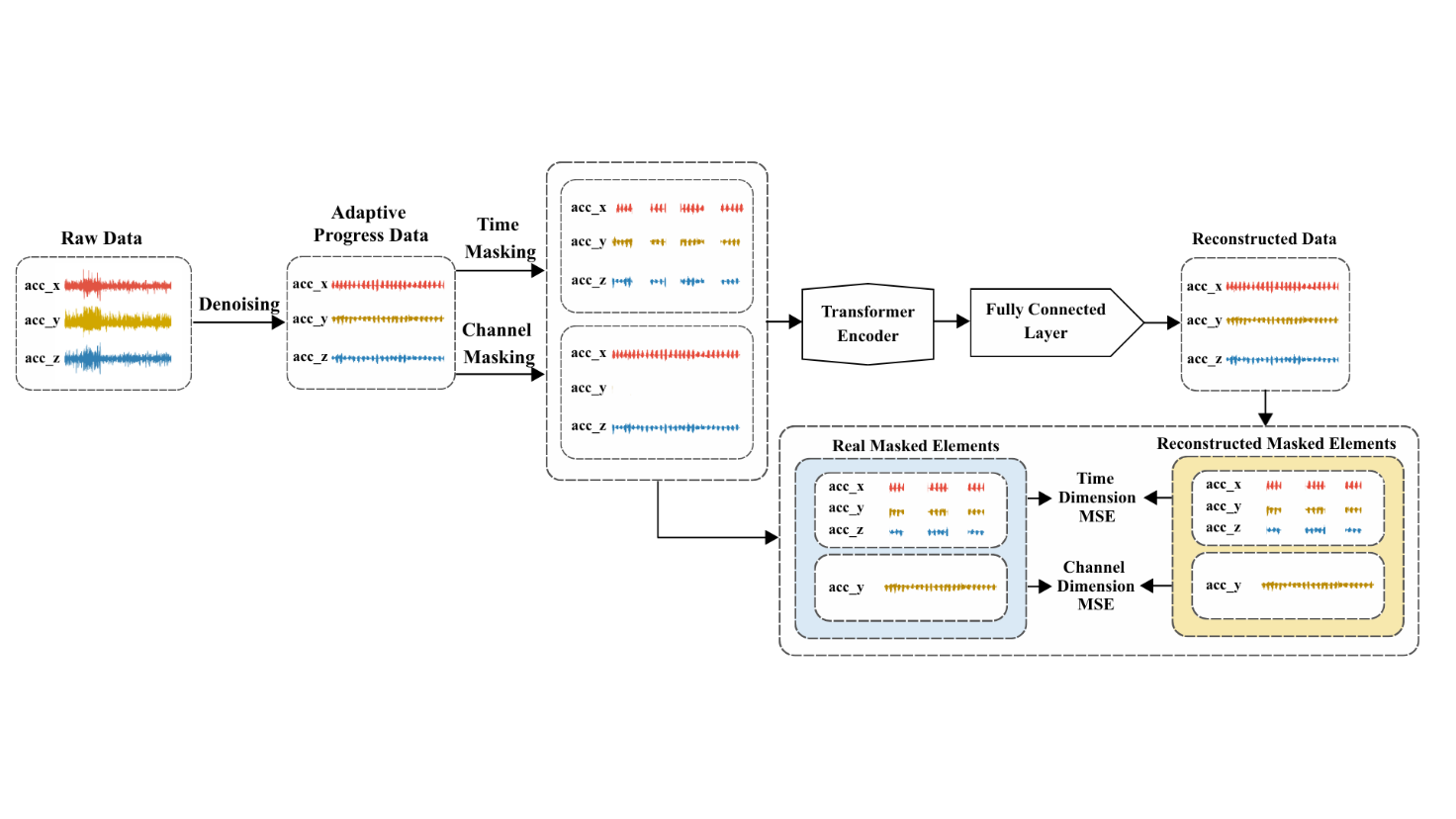
Human Activity Recognition (HAR) using wearable sensors is essential for healthcare and smart home applications, yet real-world deployment remains challenging due to sensor noise. Current self-supervised methods apply uniform architectures regardless of signal quality, leading to poor performance on noisy data. This paper presents SNAP-HAR, a framework implementing Signal-Neural Adaptive Processing that jointly optimizes signal preprocessing and neural architectures based on dataset-specific noise characteristics. Power spectral density analyses quantify orders-of-magnitude differences between laboratory-preprocessed (UCI-HAR) and real-world (USC-HAD, MotionSense) datasets. Our adaptive processing achieves consistent improvements across all configurations, with gains up to 17.0% on clean data and 24.6% on noisy conditions. Most significantly, SNAP-HAR elevates real-world performance to 0.9121 F1-score, matching the 0.9276 laboratory baseline. This convergence validates that robust HAR is achievable through adaptive signal-neural processing, eliminating the deployment gap that historically limited practical applications. Universal improvements confirm our approach provides architecture-agnostic enhancements applicable to self-supervised paradigms.

 View pdf
View pdf


In recent years, robotics navigation has become a core component of autonomous navigation, enabling robots to sense their environments, localise themselves, and plan safe and efficient paths autonomously. This paper explores the core and fundamental technologies, including LiDAR, computer vision, infrared sensors, Simultaneous Localisation and Mapping (SLAM), GPS with RTK, path planning algorithms, vehicle-to-everything communication, and Direct Memory Access (DMA). It also introduces some typical applications of robotics navigation and its core technologies. Despite the widespread use of robotics navigation and its significant improvement, numerous challenges and difficulties are faced. These include the difficulty of navigation, especially in unknown or dynamic environments. The heavy load of dealing with multiple data streams from sensors is also a problem that should be overcome. Moreover, the social and ethical considerations, such as safety and trust in a human-shared area, remain unsolved. The future development of robotics navigation will focus on Artificial Intelligence combined with 6G communication and edge-cloud computing. Establishing ethical standards will also be essential for the future development of robotics navigation.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study investigates the relationship between Apple's product design and user experience by analyzing Apple's official documents and data related to experiential and emotional design. The following result has been shown: (1) Biologically, utilizing a 72° titanium alloy bezel on the iPhone is used to awaken alpha wave. Combined with the interactive stimulation of dopamine that is secreted, it also brings about a sense of rise in the secretion of dopamine by 23% for the sensory dominant system. (2) On the level of human behavior, the cooperative use across platforms improves the user experience, and the cooperation with AppleOne improves the user experience (ARPU average +47.8%) Establishing a behavior pattern of high dependence. (3) At the value-symbol level, post-purchase hierarchical encoding of personal value symbols—enabled by Apple Watch, premium products, and enhanced privacy and security strategies—increases user satisfaction by 83% and ultimately shapes cultural dynamics. The M3 chip leverages the coevolutionary theory and the sunk-cost trap (its migration costs are 2.3 times the original value of the equipment) to form a system of technological colonialism, which ultimately reveals the inherent contradictions in the "neural conditioning-ecological control" model contained within digital capitalism.

 View pdf
View pdf


Because of the rapid development of digital media and the extended reality (XR) area, the concept of architectural space has gradually shifted from physical reality to narrative spaces in virtual and augmented reality. Moreover, game scenes serve not only as entertainment vehicles but also as important experimental platforms, constructing player behaviour and feelings through architectural language (including spatial order, scale, light and shadow, materials, landmarks, and so on). Starting from three psychological experiences: "horror space," "pleasure space," and "real space", this article explores the impact of gamified architectural language on human emotional perception and behavioural control, drawing on games such as Dead Space and Monument Valley, and some XR practical examples. This article aims to discuss how architectural elements in virtual space influence users’ behaviour by using different spatial strategies. Then explore the possibility and potential value of using these design logics in real spaces and XR interactive environments. Finally aims to provide reference and inspiration for the design of future immersive narrative spaces and interactive spaces.

 View pdf
View pdf



