Volume 18 Issue 9
Published on September 2025Herd behavior refers to the tendency of individuals to imitate others' behaviors or opinions rather than engaging in independent thinking when facing uncertainty or ambiguity. This phenomenon is extremely common in the fields of finance and economics. In view of the severe volatility exhibited by the real estate market in the post-pandemic period, this study focuses on the real estate market—particularly the herd behavior in China’s real estate market, which has experienced drastic fluctuations in recent years. The aim is to empirically verify the existence of such herd behavior and explore its influencing factors through empirical analysis. A Spatial Autoregressive Model (SAR) is employed, with variables including housing prices, personal disposable income, and one-year personal housing loan interest rates incorporated for modeling. The results indicate that significant herd behavior exists in the real estate market, and various factors exert influences on it to varying degrees. This study provides empirical evidence for understanding the operational mechanism of the real estate market and formulating reasonable policies.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study examines the impact of the Sino-US tariff war and exchange rate fluctuations on China’s soybean import prices during 2018-2019, addressing a critical research gap in understanding how these two factors jointly affect agricultural commodity markets. Using a static price decomposition method with high-frequency data from the US Department of Agriculture, IMF, and China Customs, the research isolates and quantifies the individual and interactive effects of tariffs and exchange rates on import costs. The results demonstrate that tariffs were the primary driver of cost increases in June-July 2018, with a 25% tariff hike raising import costs by 1,379 yuan/ton (100% contribution rate). Subsequently, from July to December 2018, exchange rate fluctuations became the dominant factor, with RMB depreciation contributing to a 527 yuan/ton increase (98.5% contribution rate). When both factors acted together from June to December 2018, they caused a total cost increase of 1,906 yuan/ton, with tariffs accounting for 72.4% and exchange rates for 27.6% of the increase. This study enriches theoretical understanding of agricultural price mechanisms and provides practical insights for policymakers and enterprises in managing trade-related price risks.

 View pdf
View pdf


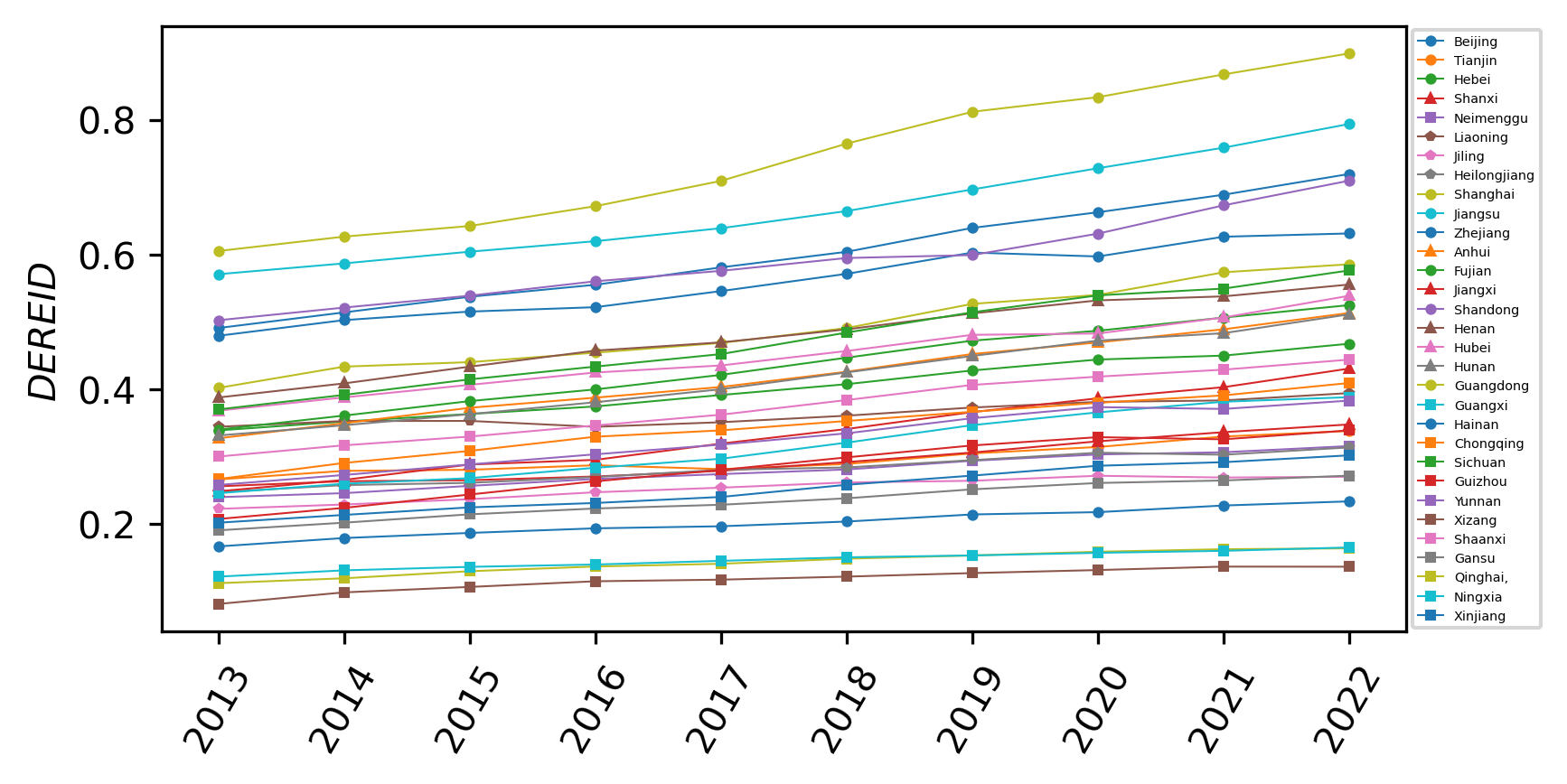
With the sustained advancement of China's digital economy and real economy, their integration has emerged as a prominent area of academic inquiry. This study employs the entropy weight method to assess the developmental levels of China's digital economy and real economy, evaluating their integrated development status. Subsequently, panel regression analysis is conducted to elucidate the direction and magnitude of factors influencing this integration. Furthermore, a threshold model is constructed to investigate the nonlinear threshold effects of these determinants. The empirical findings yield several key insights. First, from 2013 to 2022, China witnessed a consistent upward trajectory in the integration of its digital and real economies, albeit with pronounced regional disparities. Second, the developmental levels of both the digital economy and the real economy exhibit statistically significant positive effects on integration, a result robust across all four regions. Third, threshold regression analysis reveals the presence of nonlinear effects when the following variables serve as threshold parameters, digital economy development level, real economy development level, regional economic development, demographic structure, government support, foreign investment, and environmental conditions. Notably, as these threshold variables optimize, both sectors demonstrate promotional effects on integration—however, the marginal contribution of the digital economy exhibits diminishing returns, whereas that of the real economy displays increasing returns. Based on these findings, this study proposes the following policy recommendations: (1) prioritize coordinated development between the digital and real economies, (2) align talent cultivation strategies with contemporary developmental paradigms, (3) strengthen governmental support for economic transformation, and (4) incorporate environmental sustainability into digital economy development initiatives.

 View pdf
View pdf


Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a key theoretical and practical focus in public policy, yet its specific applications and impacts in empirical public policy research still require in-depth exploration. Adopting a systematic literature review approach, this study collects recent literatures on the application of AI methods in empirical public policy research from the Web of Science Core Collection, as well as academic platforms such as CNKI and Wanfang Data. Through sorting and analyzing these literatures, this paper systematically combs the theoretical foundations of AI in the field of public policy and the practical applications of AI in empirical public policy research, aiming to reveal the current status of theoretical foundations and practical applications of AI methods in empirical public policy research.

 View pdf
View pdf


This article aims to discuss the impact of clothing design on China's economy, focusing on analyzing its contribution to GDP, employment, regional economy, international exchanges, scientific and technological applications and sustainable development in many aspects. The study found that the clothing design industry occupies an important position in the GDP of China and regions, which has significantly promoted economic growth by providing a large number of employment opportunities and promoting the development of related industries. At the same time, cultural integration and consumption upgrading provide new market opportunities for the clothing design industry, but they also face challenges such as international competition and market uncertainty. As an emerging economic model, shopping tourism has shown a strong economic pull effect. However, industrial development also needs to overcome problems such as infrastructure and market saturation. The introduction of modern technology has improved the productivity, innovation ability and market competitiveness of the clothing design industry, but the problem of high R&D investment and technical adaptability still needs to be solved. Finally, this article also discusses the role of sustainable development in improving brand competitivenes.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper focuses on the effect on socio-economic mobility of the UK government’s plan to impose value added tax on school fees, offering a comprehensive review of academic literature and the latest authoritative news. This policy has both positive and negative impacts on socio-economic mobility. Intended outcomes can be achieved when expected tax revenue is reinvested in state education, reducing the gap in education quality and career outcomes between state and private schools, while certain groups may not benefit from the policy and may even see their mobility reduced. There is also uncertainty about the overall impact of the VAT on the UK government budget and the education attainment of the UK society.

 View pdf
View pdf


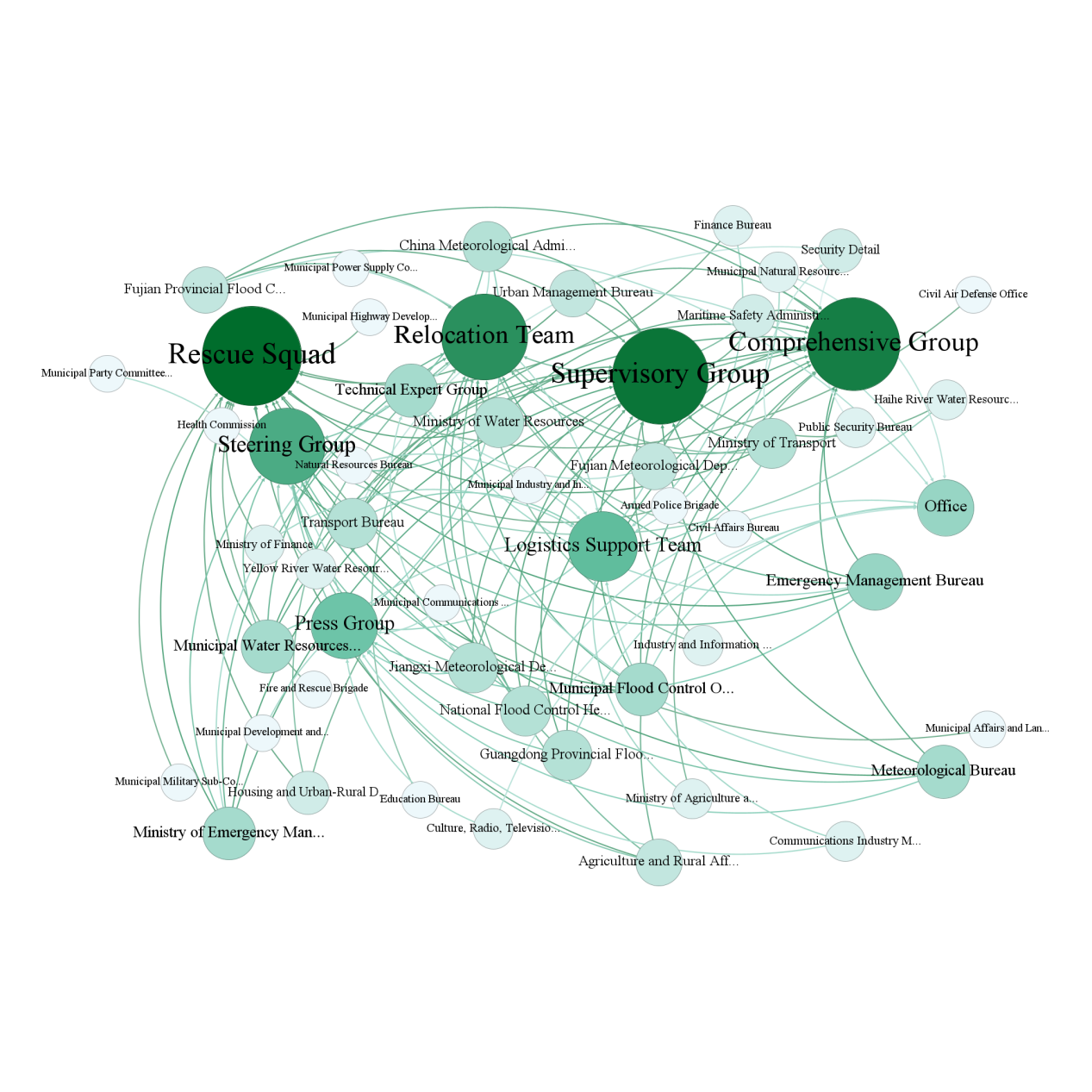
In the context of global climate change intensifying typhoon disaster risks, this paper adopts a social-network analysis perspective and uses Typhoon Doksuri (2023) as a typical case to examine the structural characteristics and operating mechanisms of government emergency coordination networks. By collecting publicly available government documents and media reports and applying UCINET and Gephi, we constructed a coordination network model containing 44 departments and 10 working groups. We then carried out an empirical analysis combining centrality analysis, the core–periphery model, and matrix analysis methods. The results indicate: (1) the Inspection Group, the Integrated Group, and the Relocation & Resettlement Group occupy core positions in the network and undertake cross-departmental coordination and supervisory functions; (2) the Ministry of Emergency Management, water resources departments, and the Flood Control and Drought Relief Command act as core hub nodes, with centrality measures significantly higher than those of other departments; (3) the Safety Alert Group and the Logistics Support Group are located at the network’s periphery and their coordination efficiency needs urgent improvement; (4) the network displays a marked core–periphery structure: coreness (Coreness = 5.429) is significantly higher than periphery (Periphery = 2.000). Based on these findings, we propose a three-dimensional pathway to optimize the coordination network: improve cross-departmental linkage mechanisms, strengthen the emergency capacities of key nodes, and establish a long-term support (guarantee) mechanism — providing theoretical basis and practical reference for improving the effectiveness of typhoon disaster emergency governance.

 View pdf
View pdf


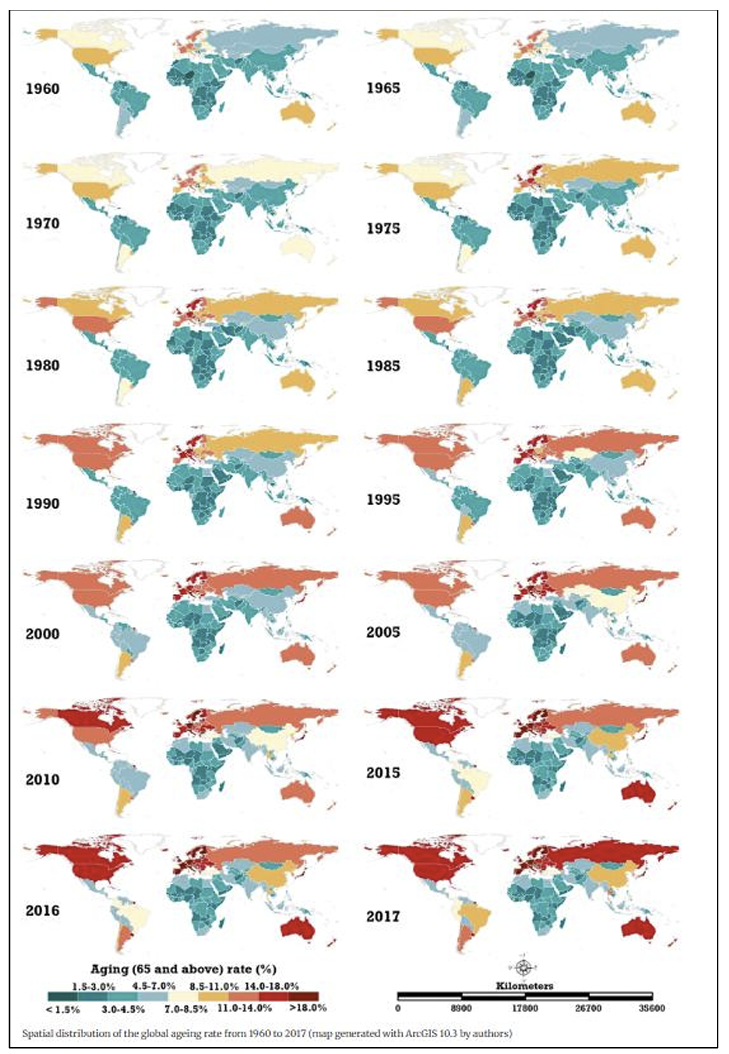
This project will answer the question “To what extent does an ageing population impact a country’s economy?”. The global population has been ageing, and life expectancies are increasing globally. This could bring issues to the economy, such as decreased productivity and GDP. However, it would also provide some opportunities for the global and domestic economy. The research method in this paper would include literature analysis related to the topic and a case study method. The areas mentioned in the topic include the labor force, government implications on the issue, and some opportunities created.

 View pdf
View pdf



