Volume 18 Issue 7
Published on August 2025This study systematically explores the inventory cost management system of cross-border e-commerce, with a focus on analyzing key cost components such as procurement, logistics, and warehousing. It identifies critical issues including data silos, demand forecasting deviations, and cross-border operational risks, and proposes targeted solutions. Strategies such as building integrated data platforms, implementing intelligent replenishment algorithms, optimizing warehouse network layouts, and establishing supply chain collaboration mechanisms are proposed. These approaches aim to address the high operational costs and extensive management issues faced by small and medium-sized cross-border e-commerce enterprises, ultimately facilitating inventory efficiency optimization and compliance-oriented development.

 View pdf
View pdf


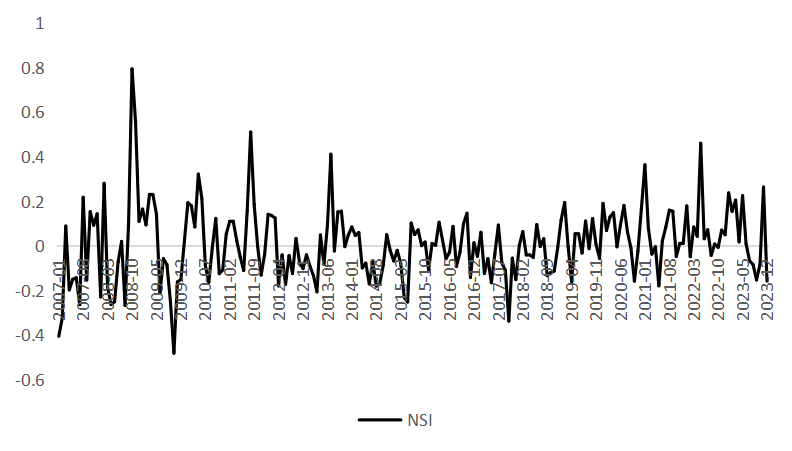
Against the backdrop of deepening global economic integration, capital flows between different markets have accelerated, intensifying the cross-market transmission of financial risks. Starting from the complex linkage mechanisms between financial market risks and macroeconomic conditions, this paper incorporates economic agents' risk perceptions into a unified analytical framework. Using monthly data from January 2007 to December 2024 on indicators related to financial institutions, stocks, currencies, bonds, foreign exchange, and the real estate market, we apply a Quantile XGBoost+SHAP model to characterize tail risk factors across China's financial submarkets. We further employ a QVAR-DY model to analyze, from a static perspective, the spillover effects among different dimensions at various quantiles, and to trace the time-varying characteristics and evolutionary paths of risk transmission from a dynamic perspective. The study provides an in-depth analysis of the dynamic linkage between financial risks and macroeconomic conditions. The findings reveal that: (1) Economic agents’ risk perception exhibits significant synergistic and threshold effects on macroeconomic performance; (2) Static analysis indicates heterogeneity in the main sources of risk spillovers across different quantiles, with the most pronounced effects observed in lower-tail risk spillovers; (3) Dynamic analysis shows that upper-tail risk spillovers spike sharply in response to extreme events over the short term, whereas lower-tail risk spillovers reflect a more passive market response to long-term adverse factors and exhibit a gradual release pattern under negative conditions. Moreover, risk clustering patterns vary across different states.

 View pdf
View pdf


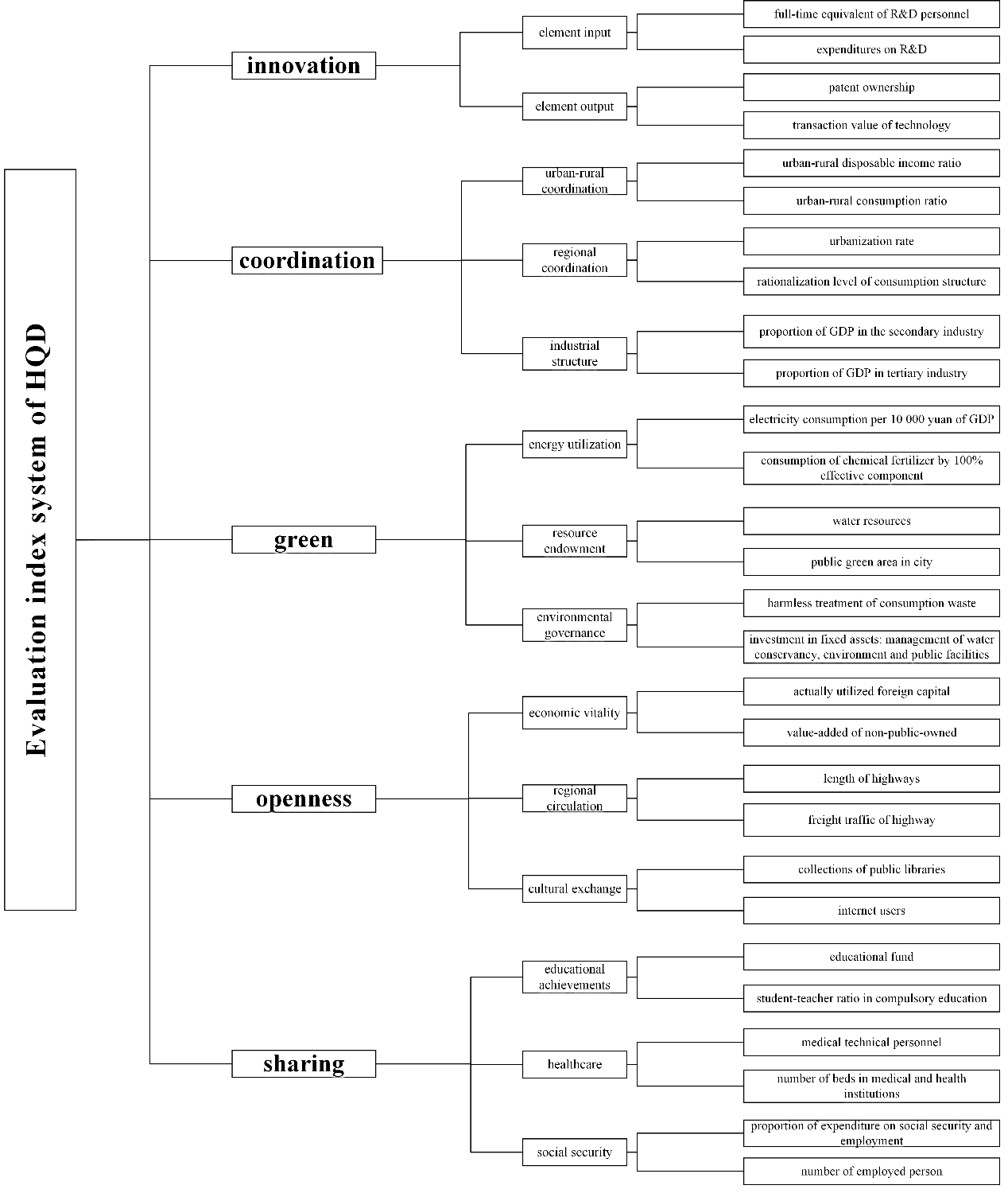
The evaluation index system for high quality development (HQD) in Henan Province of China was constructed and measured based on new development principles. Three-dimensional ecological footprint model was used to evaluate natural capital utilization, and the correlation between natural capital utilization and HQD was deeply explored through correlation analysis and threshold regression model during 2005—2020. The main results were: heterogeneity of HQD and each dimension score in each city was strong, and the northwest Henan was higher than in the southeast. 18 cities had the highest score in coordination dimension (0.09~0.17) and the lowest in innovation dimension (0.00~0.04). The maximum EFsizewas 1.30×106~6.09×106hm2in Zhoukou, and the lowest was 1.34×105~2.33×105hm2in Jiyuan. Cultivated and construction land contributed highly to EFsize. The first lag term of HQD had a positive effect on current HQD, and threshold values for the EFsizeand EFdepthwere 1.487×106hm2, and 9.090 respectively. EFsizeand EFdepthhad a positive effect on the improvement HQD, indicating a nonlinear trend of strong to weak change. The findings provided theoretical and technical support for policies related to optimizing land use patterns, upgrading industrial structures, and ecological compensation among cities in China.

 View pdf
View pdf


Drawing on a twelve-month concurrent mixed-methods design that combined a cross-sectional survey (N = 1,240), 14.8 million platform-level digital-trace observations, and a randomized field intervention, this study examines the extent to which international student mobility reshapes civic participation and public-governance dynamics. The analysis identifies three major patterns. First, multilevel regression models show that every additional year spent abroad is associated with a 0.27-point increase (SE = 0.04) in a five-point hybrid-engagement index, controlling for socioeconomic background, language proficiency, and prior civic exposure. Second, difference-in-differences estimation reveals that a policy-literacy workshop raised the odds of formal volunteering by 42 % (OR = 1.42, 95 % CI 1.28–1.57) and boosted perceived municipal responsiveness by 0.34 SD. Finally, network analytics demonstrate that workshop participants expanded the transnational density of their online governance networks by 18.9 % while simultaneously reinforcing local bridging ties, suggesting a dual anchoring of engagement. The findings illuminate how cross-border education catalyzes novel, layered forms of civic involvement and exposes blind spots in representation and service delivery, offering concrete design principles for host-city institutions intent on leveraging student voices for participatory governance reforms.

 View pdf
View pdf


This report critically evaluates the contribution of Transnational Corporations (TNCs) to achieving the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), using The Coca-Cola Company as a case study. TNCs possess significant resources and global reach, positioning them as crucial actors in advancing the 2030 Agenda. The analysis examines Coca-Cola's strategic Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives, finding proactive alignment with several SDGs. Notable contributions include water replenishment and stewardship (SDG 6), the 5by20 women's economic empowerment program (SDGs 5 & 8), climate action through emission reductions (SDG 13), and product reformulation for health (SDG 3). These efforts, embedded within Coca-Cola's business model and driven by stakeholder engagement and a circular economy approach (e.g., "World Without Waste"), yield benefits such as enhanced reputation, market positioning, risk mitigation, and innovation. However, the report identifies significant critical challenges, particularly concerning the health implications of sugary beverages and the persistent issue of plastic pollution, which contradict the company's sustainability claims. The analysis concludes that while Coca-Cola demonstrates the potential for TNCs to positively impact the SDGs through proactive CSR, substantial gaps remain. Recommendations include accelerating sugar reduction, enhancing climate ambition, strengthening supply chain labor practices, innovating beyond plastic, deepening water stewardship, and fostering broader stakeholder collaboration to achieve more systemic and impactful contributions to global sustainable development.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper examines the profound impact of the Long Depression (1873–1896) on the economic structure, colonial policy, and ideology of Britain during the late Victorian era. By tracing the decline of domestic industries, the agricultural crisis, and fiscal austerity in Britain, the study first reveals the effects of the depression on the domestic economy. It then focuses on the cases of India and Egypt to analyze how Britain transferred capital from the metropole to the colonies, employing infrastructure investment, fiscal control, and resource extraction as strategies for economic self-repair. The paper further points out that this period witnessed the rapid rise of imperialist ideology, as the doctrine of free trade gradually gave way to nationalism and the narrative of a "civilizing mission," thereby promoting the institutionalization and cultural legitimation of British policy. Ultimately, the study proposes a "crisis-driven model of British transformation," emphasizing that the Long Depression was not merely an economic crisis, but a historical juncture at which Britain achieved systemic upgrading. This research contributes to a deeper understanding of the complex relationship between global capitalism and British expansion at the end of the nineteenth century.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper explores the algorithmic transformation of financial risk identification methods, tracing the shift from traditional statistical approaches to advanced data-intelligent frameworks. Traditional models such as logistic regression and expert systems, while foundational, often struggle with nonlinear relationships, high-dimensional data, as well as real-time responsiveness and adaptive capacity. In contrast, a novel multimodal framework integrating graph neural networks (GNN) and temporal deep learning (LSTM) based on machine learning, deep learning, and graph-based models offers superior predictive accuracy, adaptability, and scalability. The study examines the application of these algorithms in credit risk assessment, fraud detection, and systemic risk forecasting, while also integrating quantitative tools such as dynamic VaR, Monte Carlo simulations and performance metrics like AUC and F1-score. Key challenges—including model interpretability, regulatory transparency, data bias, and privacy concerns—are assessed and mitigated by Shapley-value-based XAI and federated learning techniques. The paper concludes by outlining future directions such as explainable AI(XAI), causal inference, AutoML, and multimodal data integration toward real-time resilient risk governance systems. These innovations signal a move toward more intelligent, transparent, and resilient financial risk management systems.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the context of an increasingly complex competitive landscape, the enhancement of innovation capabilities through the implementation of effective incentive mechanisms has emerged as a pivotal concern for enterprises. This study utilizes a sample of U.S. publicly listed companies from 1992 to 2021 to empirically investigate the influence of Chief Executive Officer (CEO) option incentives on corporate innovation capacity. The findings reveal that an increased proportion of CEO option compensation relative to total compensation significantly correlates with a rise in the number of patent applications filed by firms, thereby indicating that option incentives can effectively stimulate corporate innovation. Moreover, the impact of option incentives demonstrates heterogeneity. In growth-stage enterprises, characterized by high sales growth rates, option incentives exhibit a more pronounced facilitative effect on innovation. This observation aligns with the resource constraints, elevated growth expectations, and strategic imperatives inherent to growth-stage firms. Additionally, firms led by male CEOs experience a stronger innovation-promoting effect from option incentives, which is consistent with the generally higher risk-taking propensity observed among male executives. The risk compensation mechanism inherent in option incentives is more efficacious in amplifying the innovation drive of such managers. This study provides empirical evidence that can inform the design of effective incentive mechanisms, thereby assisting enterprises in optimizing incentive strategies, enhancing innovation capabilities, and sustaining competitive advantages across varying developmental stages and managerial backgrounds in a dynamic market environment.

 View pdf
View pdf


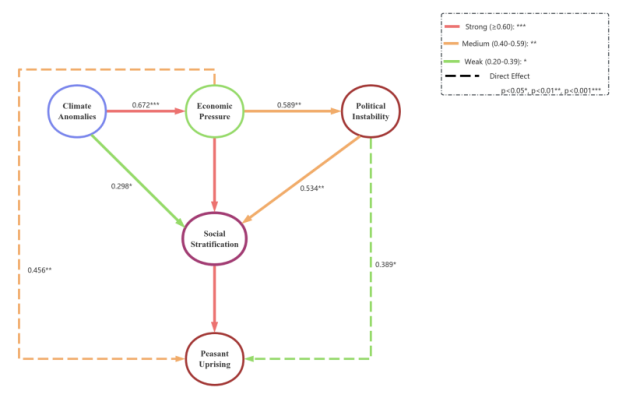
Since ancient times, Chinese peasant uprisings have played a pivotal role in driving social structural transformation and regime changes. From the Chen Sheng and Wu Guang uprising at the end of the Qin dynasty to the Taiping Rebellion in the late Qing, these movements demonstrate distinct periodic and patterned characteristics. However, traditional historiographical research often remains confined to macro-level narratives, lacking systematic modeling and causal inference of triggering mechanisms, particularly underperforming in cross-period and cross-regional explanatory power. With the rise of digital humanities and advancements in artificial intelligence, deep causal graph models offer new methodological tools for historical inquiry. This study constructs a multi-level feature system encompassing climate, economic, political, and social dimensions, and applies a deep causal graph neural network architecture to systematically model and analyze the triggering mechanisms of peasant uprisings across the 2,414-year span from the Pre-Qin to the Qing dynasty. By integrating graph attention networks, bidirectional LSTM temporal modeling, and enhanced PC algorithms, the study successfully identifies core causal paths and critical nodes of peasant uprisings, validates the significant periodic patterns of 60, 120, and 180 years, and reveals the evolving importance of various structural dimensions across different historical periods.

 View pdf
View pdf


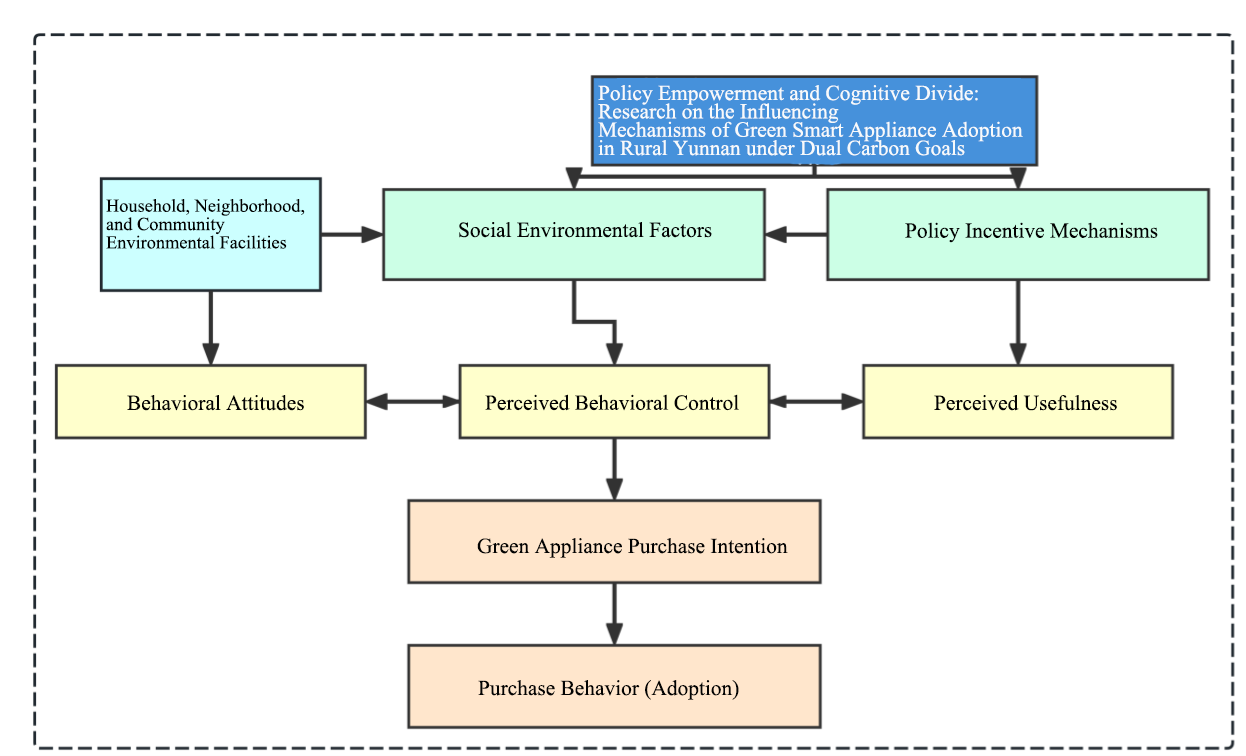
In the context of China's "dual carbon" goals, promoting green and low-carbon transitions in rural areas is of vital importance. Studying the mechanisms behind the adoption of green home appliances can provide empirical support for policy refinement and help drive the transition toward green consumption. Based on 283 rural survey responses from Yunnan Province, this study employs a structural equation model to explore the mechanisms influencing the diffusion of green smart home appliances. The empirical results show that policy subsidies significantly promote adoption by enhancing consumers' policy awareness (path coefficient = 0.68), with policy awareness playing a critical mediating role. Consumer cognition also has a significant positive impact on purchasing behavior (path coefficient = 0.65). Household income level is positively correlated with purchasing decisions, and the presence of adequate infrastructure (such as electricity and internet access) positively moderates the policy effect (moderation coefficient = 0.55). The model exhibits good fit (CFI = 0.96, TLI = 0.94, RMSEA = 0.05). The study reveals that limited policy awareness among low-income groups constitutes a major bottleneck. It is recommended to improve policy transparency and targeting, strengthen localized policy outreach, and enhance supporting infrastructure to bridge the cognitive gap and advance the realization of the dual carbon goals.

 View pdf
View pdf



