Volume 236
Published on November 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICFTBA 2025 Symposium: Financial Framework's Role in Economics and Management of Human-Centered Development
In modern financial markets, the matching efficiency among market participants is crucial to market stability and efficiency. Bilateral matching theory, as an important theoretical framework, provides scientific methods and tools for solving complex matching problems. This article aims to systematically review the development process of the bilateral matching theory, analyze its current application and challenges in the financial market, and explore future research directions. Through a comprehensive literature review, this study finds that although the bilateral matching theory has been widely applied in financial fields such as venture capital, bank loans, and the securities market, it still faces major challenges in practice, such as data privacy, model adaptability, and regulatory constraints. Research shows that the application of big data analysis, artificial intelligence and international cooperation can enhance the application efficiency of this theory, thereby strengthening market efficiency and competitiveness. Future research should focus on overcoming these challenges to fully unleash the potential of bilateral matching theory in financial markets.

 View pdf
View pdf


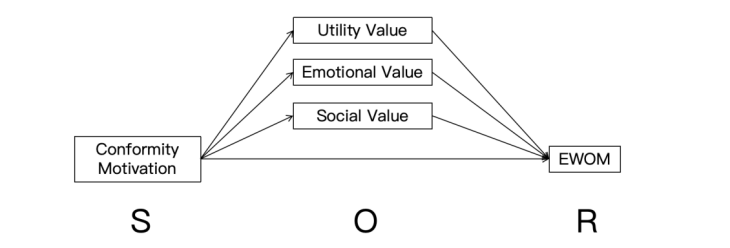
In the era of social media, consumers’ purchase decisions are often influenced by external factors, leading to conformity in shopping behavior. Such conformity motivation may further shape their electronic word-of-mouth (eWOM) behavior. This paper examines the mechanism through which conformity shopping behavior influences eWOM and tests the mediating effects of functional value, emotional value, and social value. The study aims to enrich eWOM theory by integrating the roles of social motivation and perceived value, while also providing practical insights for brands seeking to leverage conformity effects in social media communication. Data were collected from 200 social media users via an online survey about their most recent shopping experiences. The results indicate that conformity motivation significantly promotes eWOM behavior, primarily through the perception of functional value. Emotional value did not exhibit a mediating effect, while social value showed a potential but insignificant mediating role.

 View pdf
View pdf


Multinational corporations (MNCs) have significant social impacts through their profit-driven strategies, which vary based on market structure. In competitive markets, MNCs promote innovation and consumer welfare, while in monopolistic environments, they often harm societal well-being by limiting choice and efficiency. This study examines the social impact of MNCs’ profit-driven strategies, distinguishing between outcomes in competitive versus monopolistic markets. It explores how MNCs generate and spend money, and evaluates whether their activities contribute positively or negatively to society under different market conditions. The paper adopts a qualitative case analysis approach, drawing on examples from industries such as retail opticians, artificial intelligence, and technology. The findings indicate that in competitive markets, MNCs generally enhance societal welfare through innovation and efficiency. However, in monopolistic settings, their profit-seeking behavior often leads to consumer harm, reduced competition, and inefficient resource allocation. While philanthropic efforts by MNCs are noted, they are insufficient to offset structural harms. The study concludes that robust regulatory frameworks are essential to align corporate profit motives with broader social welfare.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper examines the implications of the UK government's introduction of a 20% Value Added Tax (VAT) on private school fees. The analysis is framed within the theoretical contexts of the commodification of education, Bourdieu's theory of social reproduction, and the concept of social mobility. The paper argues that while the policy is ostensibly aimed at reducing educational disparities, it is likely to exacerbate social inequalities. The increased cost of private education will likely make it inaccessible for many middle-income families, reinforcing the position of private schools as enclaves for the elite. This, in turn, will hinder social mobility and perpetuate the cycle of social reproduction, as access to the cultural and social capital offered by these institutions becomes even more restricted. The paper concludes that the VAT policy, without other mitigating measures, may unintentionally deepen the very social divides it seeks to address.

 View pdf
View pdf


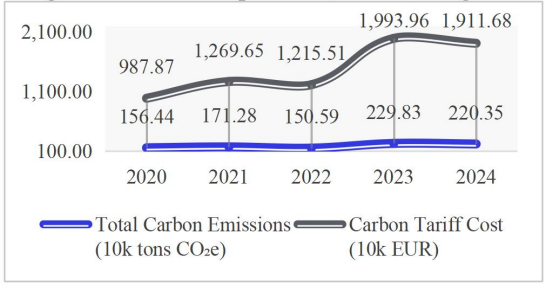
With the advancement of global climate governance and carbon reduction policies, carbon tariffs, as a critical regulatory tool in international trade, are increasingly influencing companies’ cost structures, market competitiveness, and supply chain arrangements. This paper investigates the impact mechanism of carbon tariffs on corporate value and related valuation methods. In the context of reshaping global low-carbon trade rules, it explores the profound influences of carbon tariffs on corporate value through cost transmission, market competition, and supply chain restructuring. In addition, it also analyzes the limitations of traditional valuation methods, which overlook carbon costs and green assets, and provides relevant research suggestions. The study reveals that under carbon constraints, changes in corporate value drivers occur, and that carbon tariffs increase cost pressures on companies while creating long-term value through low-carbon transformation and green innovation.

 View pdf
View pdf


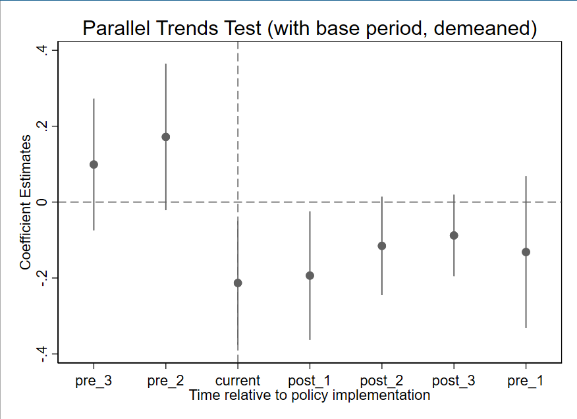
As ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) issues draw increasing attention, Directors and Officers (D&O) liability insurance has emerged as a critical tool in corporate risk management, playing a positive role in enhancing corporate governance and reducing operational risks. Against this backdrop, preventing ESG decoupling is essential for achieving sustainable and high-quality development. Based on data from A-share listed companies between 2007 and 2023, this study investigates the impact of D&O insurance on corporate ESG decoupling. The empirical results indicate that D&O insurance significantly mitigates ESG decoupling, with the effect being statistically significant at the 1% level. Specifically, D&O insurance alleviates ESG decoupling primarily by easing firms’ financing constraints, curbing managerial short-termism, and increasing R&D investment. These findings provide robust empirical evidence for the role of D&O insurance in promoting sound and high-quality corporate development and offer valuable insights for policy formulation and corporate management practices.

 View pdf
View pdf


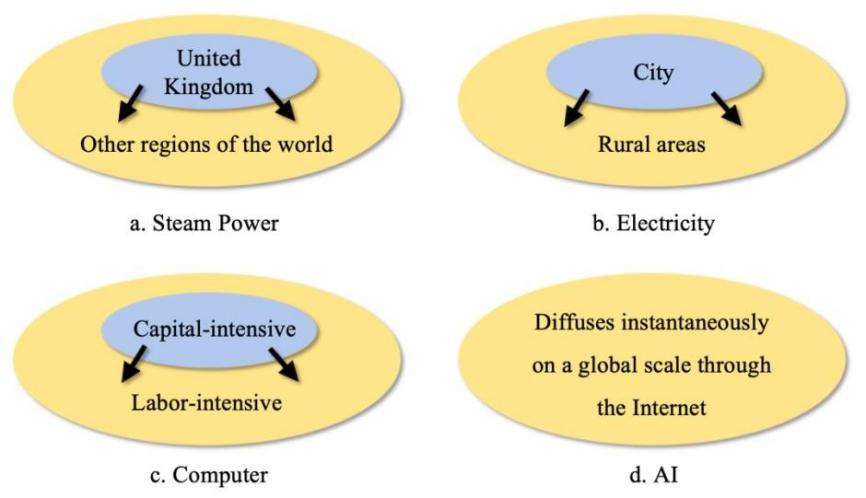
In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) and large language models have rapidly transformed production processes and social structures, whereas traditional general-purpose technologies (GPTs) such as steam power, electricity, and computers have historically had profound effects on productivity and employment. However, current studies provide limited comparisons of AI and traditional GPTs in diffusion, productivity, and employment, and systematic analysis of diffusion bottlenecks, labor adaptation, skill needs, and social costs remains scarce. This study investigates the features and mechanisms of AI and traditional GPTs in diffusion, productivity, and employment, thus examining differences in spatial and industry diffusion, long-term productivity effects, and substitution, compensation, as well as creation impacts on employment. The results reveal that traditional GPTs diffuse slowly with notable regional and industry differences, while AI achieves faster, more synchronized diffusion. Consequently, by driving a shift from scale- to quality-driven productivity growth, GPTs combine substitution, compensation, and creation effects to keep overall employment relatively stable in the short term.

 View pdf
View pdf


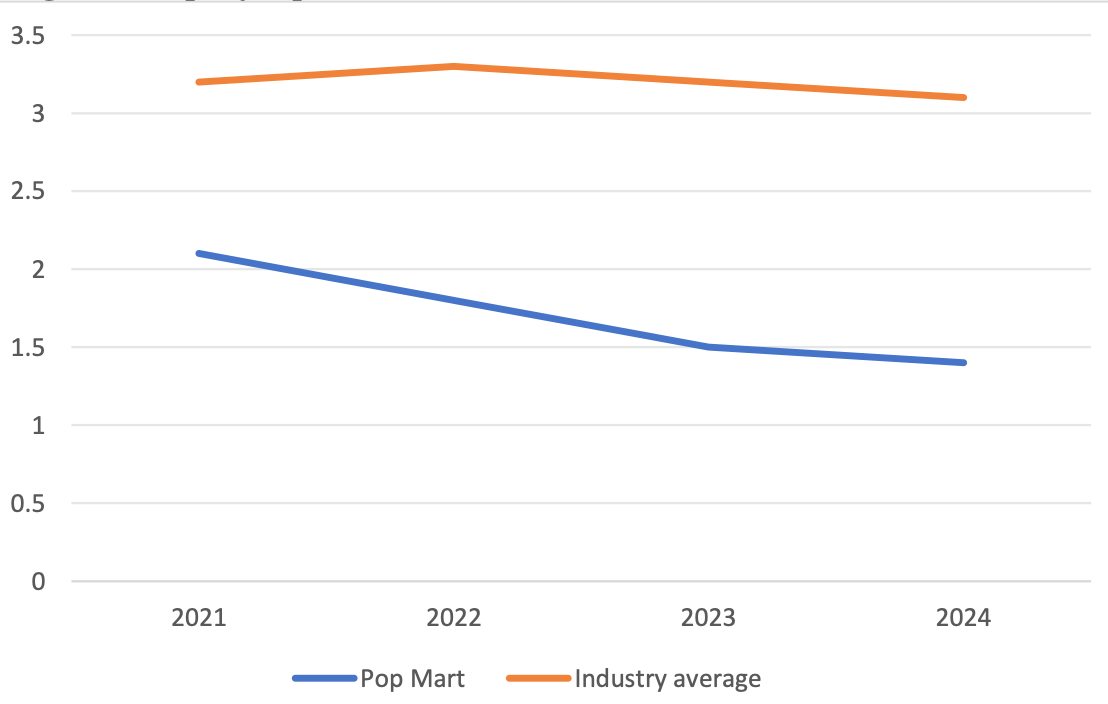
The perfect combination of internet technology and the cultural and creative industry has created a new trend in the “pop culture economy”. Beijing Pop Mart Cultural and Creative Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Pop Mart) as a typical enterprise of “IP + e-commerce” has rapidly expanded. Its unique business model has created huge value while also facing financial risks such as fluctuations in IP value, high inventory, rapid market expansion, and a single profit model. This paper takes Pop Mart as the research object and employs case analysis method, financial ratio analysis method. Based on the financial data of the past 3 to 5 years, it systematically identifies the three major types of main financial risks, namely, its business operations, investment and financing, and capital flow. It also analyzed the management issues and causes of its main risks during the operation process. And based on the comprehensive risk perspective and financial early warning theory, it proposed countermeasures such as improving inventory levels, enriching IP operations, and dynamically constructing financial early warning models. The aim of this paper is to provide decision support for Pop Mart to avoid financial risks and offer references for the future better development of cultural and creative enterprises.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the globalization of Green Trade Barriers (GTBs) and the continuous tightening of green technical standards, exploring the impact of GTBs on the financialization of China’s export-oriented manufacturing enterprises and its underlying mechanism has become a critical research focus.This research selects Chinese A-share listed export-oriented manufacturing enterprises covering the period from 2009 to 2024 as its research samples. It incorporates multi-source datasets—specifically the WTO Environmental Database, CSMAR Database, and annual reports of listed companies—and adopts a two-way fixed effects model along with a mediation effect model to carry out empirical analysis. The results show that: (1) GTBs significantly increase the level of corporate financialization, which supports Hypothesis H1; (2) GTBs elevate firms’ short-term financialization by reducing the current asset ratio, thereby verifying Hypothesis H2. A set of robustness tests—for instance, sensitivity analysis of fixed effect specifications, replacement of industry fixed effects, adjustment of clustered standard errors, and modification of variable functional forms—further confirm the reliability of the baseline conclusions. Theoretically, this study enriches the research framework linking international trade policy, environmental regulation, and corporate financialization, addressing the gap in existing studies that mostly focus on macroeconomic fluctuations or general trade policy uncertainty. Practically, it provides insights for export-oriented manufacturing enterprises to balance short-term financialization and core business development, and suggests policymakers introduce measures to alleviate enterprises’ compliance pressures and prevent the "hollowing-out" of the real economy. Limitations include a sample restricted to A-share listed enterprises; future research may expand the sample scope and explore firm heterogeneity.

 View pdf
View pdf


As a core precious metal with dual commodity and financial attributes, gold price fluctuations are profoundly influenced by macroeconomic policies, monetary conditions, and market supply-demand dynamics. As the global benchmark for gold pricing, the COMEX gold futures market generates price signals that hold significant reference value for investors’ asset allocation decisions, central banks’ reserve management practices, and the stability of the global bulk commodity market. Against this backdrop, this study focuses on the dynamic linkage between COMEX gold futures prices and key macroeconomic variables, aiming to quantitatively analyze the short-term impact effects and long-term equilibrium relationships of the U.S. dollar exchange rate, real interest rates, and inflation rates on gold prices. Methodologically, the Vector Autoregression (VAR) model, this research uses monthly data of COMEX gold futures prices, U.S. Dollar Index (DXY), U.S. 10-year Treasury real yields, and U.S. core PCE inflation rate from 2015 to 2024 as the research sample.

 View pdf
View pdf



