Volume 122
Published on August 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICBioMed 2025 Symposium: Computational Modelling and Simulation for Biology and Medicine
Breast cancer is a malignant tumor that originates from the breast tissue. Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) accounts for a certain proportion of all types of breast cancer, and it is a type of breast cancer that is difficult to treat and highly dangerous. Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) lacks three receptors, which leads to its difficulty in treatment. The common treatment methods for triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) mainly include chemotherapy and immunotherapy. Immunotherapy is a treatment approach that targets the tumor's ability to evade the immune system's attack, helping T cells maintain normal activity and stimulating the immune response. Although chemotherapy leads to a relatively good prognosis, it poses significant harm to the human body. In recent years, there have been many advancements in the use of vaccines for treating triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). This review article will mainly discuss the current progress, advantages, and challenges of using vaccines to treat triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).

 View pdf
View pdf


Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine disorder characterized by insulin resistance (IR), affecting 5.61% of reproductive-aged women in China, with over half exhibiting IR. Current treatments focus on individualized management, but optimal therapeutic strategies remain unclear. This article further analyzes the therapeutic effects and impact of low-calorie dietary patterns (LCDs) as adjuvant therapy for PCOS with IR. The findings demonstrate that LCDs exemplified by intermittent fasting (IF) and ketogenic diets (KD) significantly enhance weight management outcomes. By reducing caloric intake and optimizing metabolic status, these dietary approaches improve IR-related parameters, effectively reduce BMI, and increase insulin sensitivity, establishing their value as adjunct strategies within the integrated management of PCOS with IR. However, current applications of LCDs as adjuvant therapy still present limitations and challenges, including compromised patient compliance and a lack of longitudinal data on long-term efficacy. To address these challenges, future research should launch rigorous large-scale longitudinal studies to explore synergistic mechanisms combining LCDs with psychological interventions, with the goal of improving treatment adherence.

 View pdf
View pdf


Over the past decade, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have revolutionized the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) at the systemic level. This review analyzes 210 studies (2015–2024) to trace the progression from initial PD-1 blockade trials to modern multi-agent protocols, emphasizing the transformation of HCC’s immune-excluded milieu into one that fosters sustained antitumor activity. Mechanistically, pathways involving PD-1/PD-L1, CTLA-4, LAG-3, and TIM-3 induce T-cell dysfunction, hinder neoantigen recognition, and attract immunosuppressive macrophages. ICIs counteract these effects, revitalizing cytotoxic T-cell migration and diversifying T-cell receptor profiles. Pooled data from phase II/III trials indicate monotherapy response rates of 14–30%, increasing to 27–46% with combinations such as atezolizumab/bevacizumab or durvalumab/tremelimumab. However, these regimens are accompanied by higher-grade adverse events (25–37%). Challenges such as inconsistent biomarker expression, loss of interferon-γ signaling-induced resistance, and overlapping toxicities persist. To address these, the author suggests: (1) multi-parameter biomarker models combining PD-L1, TMB, and circulating CD8+ Ki-67 levels; (2) staggered dosing to separate ICI initiation from anti-angiogenic therapy; and (3) pharmacovigilance systems to track delayed toxicities and tailor treatment withdrawal.

 View pdf
View pdf


Meniere's disease is a long-term inner ear condition that leads to vertigo, hearing loss, and tinnitus. It affects primarily women between the ages of 40 and 60 years. It is hard to treat due to its numerous causes. Research has indicated that issues like fluid buildup in the inner ear, immune system attacks, and reduced blood flow could all play a role. Diagnostic tests like vascular endothelial function testing (VEMP), electrocorticography (ECoG), and 3T magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can assist, but all have drawbacks and are frequently utilized together. Treatment strategies encompass diuretic therapy, intratympanic injections, vestibular rehabilitation, neuromodulation, and immunomodulatory interventions. However, no single modality has proven universally effective; physicians must therefore implement individualized, combination-based treatment regimens. This review delineates the principal pathogenic mechanisms of Meniere’s disease and critically evaluates a range of therapeutic approaches, highlighting the importance of personalized treatment algorithms and multidisciplinary care models to optimize patient outcomes in Meniere’s disease management.

 View pdf
View pdf


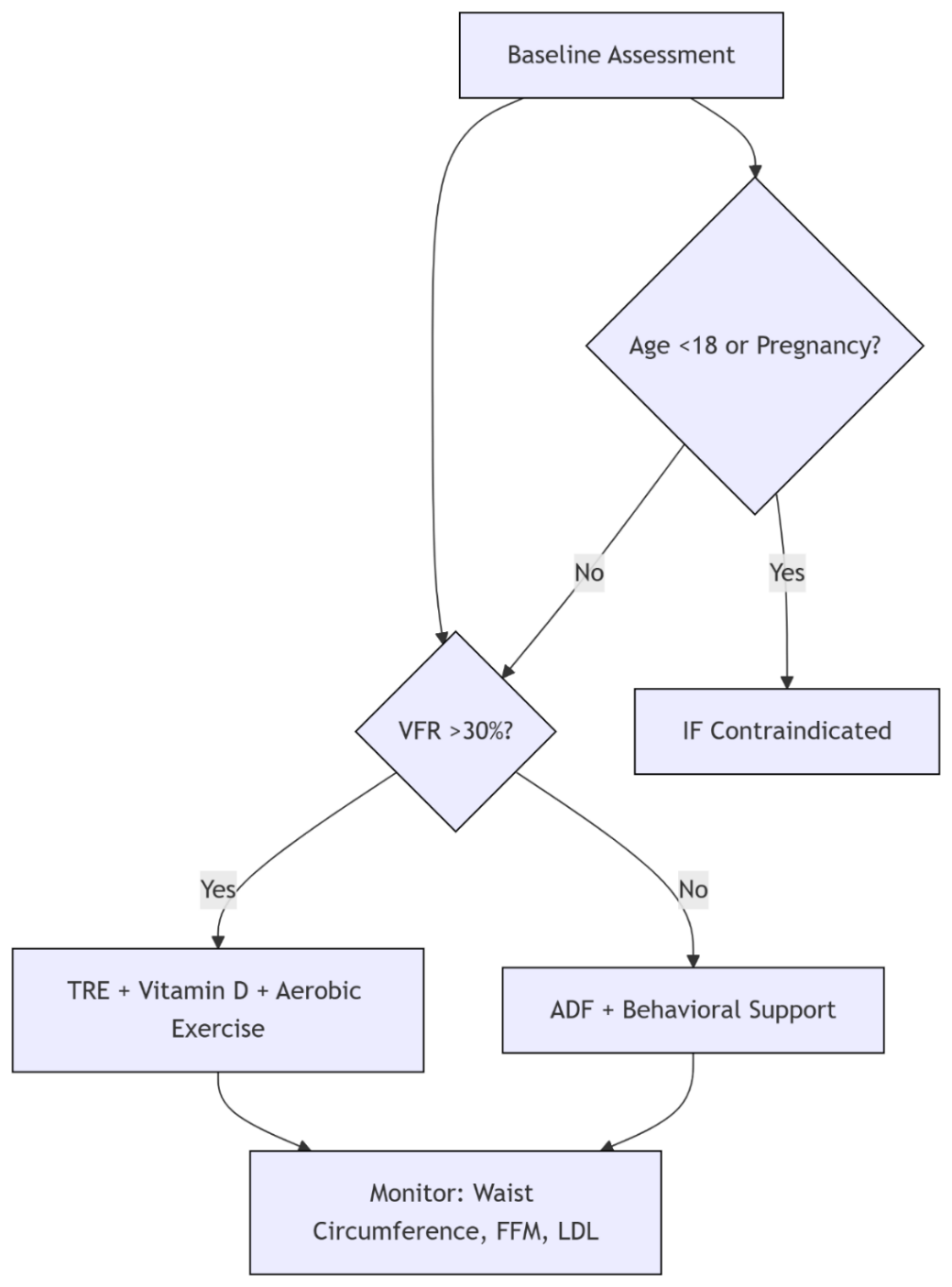
Adipose tissue heterogeneity, particularly the pathogenic role of visceral adipose tissue (VAT) in metabolic diseases, poses significant clinical challenges. Current research confirms that intermittent fasting (IF) induces depot-specific adaptations: VAT exhibits lipid conservation mechanisms while subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) demonstrates thermogenic plasticity through microbiota crosstalk. The gut-liver axis further mediates systemic metabolic synchronization during IF. However, precise frameworks for stratifying IF protocols based on adipose biology remain underdeveloped. This review synthesizes molecular mechanisms driving VAT/SAT differential responses to IF, evaluates depot-specific efficacy of major regimens, and establishes a visceral fat ratio (VFR)-based precision framework. Key findings indicate that early time-restricted eating (eTRE) preferentially reduces VAT with glycemic stability, whereas alternate-day fasting (ADF) carries long-term rebound risks. Integration of circadian-aligned exercise and behavioral support significantly enhances intervention sustainability. This analysis provides clinically actionable stratification: high-VFR individuals benefit maximally from eTRE-exercise synergy, while moderate-VFR phenotypes require vigilant cardiometabolic monitoring during ADF. The framework addresses critical implementation barriers including lean mass preservation and adolescent contraindications. Future research should prioritize digital adherence platforms and biomarker-defined feeding windows to optimize personalization. This work establishes a mechanism-informed foundation for translating adipose-specific IF benefits while highlighting unresolved questions regarding long-term vascular impacts and tissue-specific circadian reprogramming.

 View pdf
View pdf


Sarcopenia, a progressive condition marked by the gradual decline in skeletal muscle mass, strength, and function, is increasingly prevalent among older adults. While resistance training remains an established intervention, dietary strategies have gained attention as feasible and complementary approaches to mitigate muscle decline. This paper summarizes recent studies from the past few years on the potential benefits of natural bioactive compounds commonly found in culinary spices, with a focus on curcumin (in turmeric), piperine (in black pepper), cinnamaldehyde and Cinnamic Acid (in cinnamon) and rosmarinic acid (in rosemary, RosA). For each compound, representative studies were selected to illustrate current evidence. Clinical trials investigating curcumin supplementation have reported modest improvements in muscle strength and endurance. Preclinical studies using animal models have revealed that piperine possesses both anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities, along with its capacity to enhance curcumin bioavailability in humans. In vitro studies on cinnamaldehyde and RosA have shown protective effects against inflammation-induced muscle atrophy. Although these findings highlight promising mechanisms through which dietary bioactive compounds may contribute to the prevention and management of sarcopenia, most evidence to date is derived from animal models, cell culture experiments, or small pilot trials in healthy individuals. Large-scale, well-designed clinical studies targeting older adults with clinically diagnosed sarcopenia are warranted to confirm the efficacy and safety of these interventions.

 View pdf
View pdf


Precise long-range axon guidance is essential for neural-circuit assembly, and its failure underlies disorders ranging from corpus-callosum agenesis to epilepsy and autism. Four ligand families, including netrins, slits, semaphorins and ephrins, provide combinatorial attract-repel signals that growth cones decode via receptor repertoires and cytoskeletal dynamics. Recent studies show how co-receptors, stoichiometry and second messengers pivot single cues between attraction and repulsion, yielding context-specific trajectories. Guidance programmes re-emerge in the adult brain during learning and after injury, supplying intrinsic blueprints for regeneration, yet their aberrant reactivation can drive maladaptive sprouting and network hyperexcitability. Therapeutic concepts now in pre-clinical testing include Eph inhibitors, exosome-delivered netrin-1 or Sonic Hedgehog, gene editing of guidance receptors and AI-assisted multi-cue scaffolds. This review integrates molecular and translational advances, linking defined wiring errors to clinical phenotypes and proposing how programmable guidance signals could achieve targeted and patient specific repair of damaged neural circuits, thereby laying a conceptual foundation for next generation regenerative neurology that unites developmental biology, biomaterials engineering, and data driven modelling.

 View pdf
View pdf


Epilepsy is a prevalent neurological condition impacting nearly fifty million individuals around the world. Traditional diagnosis based on clinical symptoms and neural monitoring can be inefficient or inaccurate. Pharmacotherapy is the first-line treatment, but about one-third of patients are drug-resistant and may experience adverse effects. Surgical resection is another option but is not suitable for all patients. Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) create a direct communication link between neural activity and external systems, enabling more effective automated seizure detection, forecasting, and individualized therapeutic interventions. Among the various BCI modalities, ranging from implanted electrodes to external sensors, non-invasive, EEG-based systems remain the most widely adopted due to their safety, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use. AI algorithms are used in BCI to process data and detect biomarkers like recently discovered high frequency oscillations (HFOs), brain connectivity, and microstates automatically before sending targeted stimulations or keeping track of the patients’ status remotely. Responsive neurostimulation (RNS) is a neuromodulation system that allows adaptive stimulation, meaning that it is closed-loop, which has the potential of minimizing side effects. This review aims at discussing and evaluating the effectiveness of BCI in seizure detection, prediction, and patient-specific treatments while providing enlightenment on future trends.

 View pdf
View pdf


The incidence rate of type 2 diabetes (T2DM) is on the rise all over the world, and has become an increasingly serious global health problem. At present, people are actively seeking solutions to T2DM and have made many breakthroughs, such as the reversal management model. The role of diet in the treatment of TM2D is also gradually highlighted. There are studies on the impact of various dietary patterns on TM2D. This paper mainly studies the impact of MD on TM2D and explores the impact of the Mediterranean diet (MD) on the special population of T2DM patients and different focus areas. Exploring the relationship between the intervention duration is positively correlated with TM2D. Long-term adherence to TM2D can reduce blood sugar levels, effectively control blood sugar, and prevent various cardiovascular complications by anti-inflammatory, lipid-lowering, and improving insulin sensitivity. This study provides a reference for the preventive treatment and lifestyle intervention the duration of MD intervention and the improvement effect of TM2D. It was found that if TM2D, as well as improving the compliance of TM2D patients with MD, can resolve the limitations of MD that have not yet been resolved. In the future, research can focus on addressing the difficulty of calorie control and the risk of nutrient imbalance in MD, as well as the salt content of some traditional MD, which may lead to high sodium problems.

 View pdf
View pdf


Tinnitus, the perception of phantom sound in the absence of an external stimulus, is increasingly understood to arise from a complex interplay of inflammatory and neuroimmune processes as well as maladaptive neural plasticity. In the periphery, cochlear insult, whether due to age‐related hearing loss, acoustic trauma, ototoxic drugs, or chronic noise exposure, triggers the release of pro‐inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. These mediators can disrupt tight junctions in the blood–brain barrier, permitting peripheral immune factors to infiltrate central auditory pathways. Within the CNS, activated microglia adopt an M1‐proinflammatory phenotype, releasing additional cytokines and reactive oxygen species, while astrocytes lose their homeostatic regulation of glutamate and calcium signaling, further promoting hyperexcitability. These glial changes drive synaptic remodeling and neuronal hyperactivity in key auditory nuclei, consolidating tinnitus percepts through aberrant cortical reorganization. Therapeutic efforts have therefore focused on attenuating inflammation with localized interventions, such as intrathecal corticosteroid injections, and systemic agents like minocycline or anti-TNF biologics. Concurrently, neuromodulation strategies (repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, transcranial direct‐current stimulation, and vagus nerve stimulation) aim to recalibrate cortical excitability and foster adaptive plasticity. Together, these approaches represent a multi‐faceted framework for targeting both the immunological and electrophysiological underpinnings of tinnitus.

 View pdf
View pdf



