Volume 131
Published on August 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICBioMed 2025 Symposium: Interdisciplinary Frontiers in Pharmaceutical Sciences
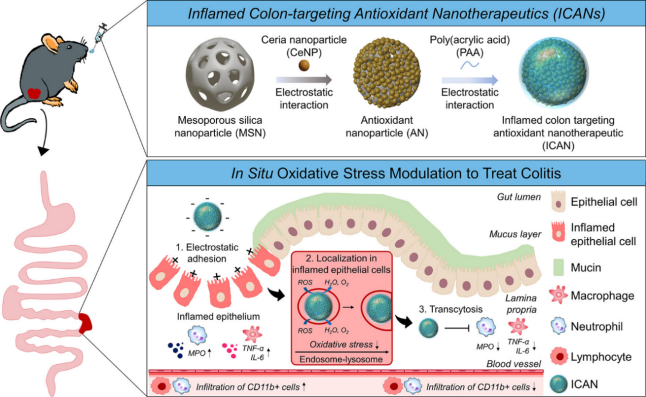
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a global health concern. Existing therapies, including anti-inflammatory drugs and biologics, often suffer from limitations such as insufficient targeting and high cost. In this context, nanoformulations have shown significant potential due to their advantages in drug protection, targeted delivery, and multifunctional synergy. This article reviews the latest progress in the treatment of IBD with nanoparticles. It categorizes nanodelivery systems into two main types: drug delivery systems and plant-related delivery systems. The article also provides examples of each type, detailing their preparation methods, targeted delivery mechanisms, and experimental outcomes. The findings reveal that while studies have confirmed the effectiveness and advantages of nanoformulations for treating IBD, transformation encounters significant challenges. In the future, it is necessary to integrate new technologies to develop more intelligent nano-response systems and accelerate clinical verification, ultimately aiming for precision and universalization of IBD treatment.

 View pdf
View pdf


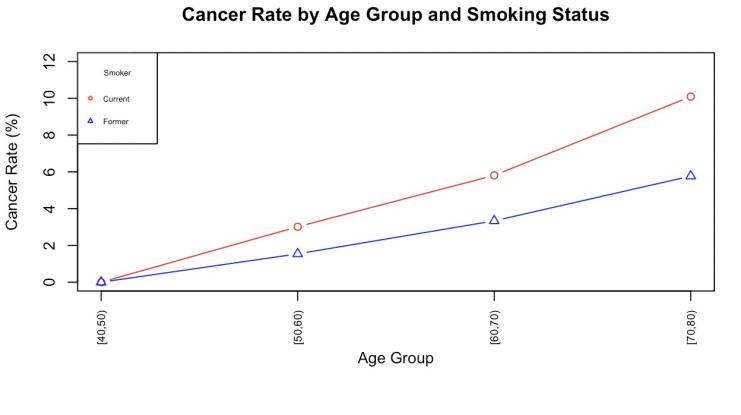
Lung cancer is one of the most deadly effects of tobacco smoking, which continues to be one of the world's top avoidable causes of death. This paper examines the relationship between smoking prevalence and lung cancer incidence from a global public health perspective. By using a literature review approach to summarize and analyze epidemiological studies from several countries and regions, the results show that there is a significant positive correlation between smoking prevalence and lung cancer incidence. Even after taking into account variables such as economic level and educational attainment, smoking remains a major risk factor for lung cancer. The study also suggests that the implementation of comprehensive tobacco control policies (including increasing tobacco tax rates, banning smoking in public places, and health warning labels) could be effective in reducing smoking prevalence and further reducing the incidence of lung cancer cases. This study emphasizes the importance of continuing to promote tobacco control policies and health education globally, and provides strong theoretical support and empirical evidence for future lung cancer prevention and control.

 View pdf
View pdf


Marked by clinical and pathological heterogeneity, Castleman disease (CD) is a lymphoproliferative disorder classified into unicentric (UCD) and multicentric (MCD) types. Distinct subtypes of Castleman disease differ in pathogenesis, pathology, and prognosis, yet diagnosis and treatment remain challenging, requiring standardized approaches. This paper explores the classification, pathological characteristics, diagnostic methods, and treatment strategies of CD, with a focus on the clinical and pathological features of different subtypes. Through analysis of recent literature on clinical presentations, imaging, histopathological diagnostic criteria, and therapeutic outcomes, this study provides evidence-based guidance for clinical practice. The results show that CD can be histologically categorized into hyaline vascular (HV), plasmacytic (PC), and mixed variants. Besides, MCD is further subdivided into HHV-8-associated, POEMS syndrome-associated, and idiopathic (iMCD) subtypes. The diagnostic approach combines clinical presentation, imaging results, and pathological evidence while excluding infectious, autoimmune, and malignant disorders. Treatment for UCD primarily involves surgical excision with favorable prognosis, whereas MCD requires tailored regimens including antiviral therapy, immunosuppression, targeted agents, and chemotherapy. Despite their efficacy in achieving quick symptom relief, corticosteroids are predominantly used as ancillary agents due to the constraints imposed by their long-term adverse effects.

 View pdf
View pdf


Tooth defects can cause severe pain, infection, and impaired daily functions, significantly affecting the quality of life for patients. Although traditional root canal treatment can prolong the lifespan of a damaged tooth, it cannot fully restore the biological activity and tissue integrity of the teeth. Dental tissue engineering, as a cutting-edge regenerative medical strategy, is of great significance for restoring the natural structure and function of teeth. It aims to achieve the regeneration and repair of dental hard and soft tissues through interdisciplinary approaches. It comprises three key elements: seed cells, scaffold materials, and growth factors. This article reviews the current developments in this field, systematically elaborating on the differentiation potential of seed cells in dental regeneration. It evaluates the performance of various scaffold materials in supporting cell adhesion, proliferation, and mineralization. It introduces the crucial role of growth factors in inducing seed cells to differentiate into cementoblasts and osteoblasts. This article aims to promote the translation of dental tissue engineering into clinical practice, providing a more effective treatment plan for patients with tooth defects.

 View pdf
View pdf


Malassezia is a yeast that typically exists as a harmless organism within the host's skin flora. However, under specific microenvironmental conditions, it can transform into a pathogenic form directly linked to seborrheic dermatitis and pityriasis versicolor. These findings highlight the critical need to decipher its phase transition mechanisms, particularly the lipase activation threshold triggering pathogenicity. Within this broader analytical framework, this paper reviews what the evidence appears to reveal regarding the pathogenic factors of Malassezia based on what seems to emerge from existing literature and data. What the analysis tends to support is that the relationship between Malassezia and its human host appears to be complex, seemingly varying by body site, age group, and what appears to be host susceptibility. The pathogenicity of Malassezia is not an inherent attribute but rather a dynamic process triggered by imbalances in the host microenvironment. Future research must employ integrated multi-omics approaches (microbiomics, metabolomics, and immunomics) to dissect strain adaptation mechanisms. This will advance precision intervention strategies targeting host-microbe interactions, thereby facilitating a paradigm shift from "antimicrobial" to "microbiome-preserving" therapeutic approaches.

 View pdf
View pdf



