Volume 122
Published on December 2025Volume title: Proceeding of ICSPHS 2026 Symposium: Critical Perspectives on Global Education and Psychological Development
Through the Escape the Corset Movement (ECM), the essay explores the impact of social media on feminist consciousness, discourse, and activism in South Korea. Founded in 2016 and prominent nationwide in 2018, ECM urged women to discard the patriarchal model of beauty and reassert bodily control by cutting their hair, not wearing makeup, and throwing away beauty products. Drawing on concepts from digital activism and feminist media studies, the paper maps the historical transition from conventional to digital media in Korean feminist movements and reveals how online platforms changed modes of participation and communication. With hashtags like #EscapeTheCorset, social media operated as a public sphere where stories, community, and the development of collective identity could take place. The text analyzes how digital narratives and graphical confrontations as forms of protest challenged Confucian gender norms and re-considered femininity in modern Korean culture. Finally, the paper demonstrates how ECM’s discourse played a role in economic and cultural resistance, with efforts to resist the pink tax as well as the #Women_ShortCut_Campaign, demonstrating social media’s potential to reproduce and sustain activism. However, the study does emphasize critical constraints: platform hierarchies, online harassment influenced by gender, and entrenched patriarchal structures that inhibit transformational initiatives. ECM embodies, in the end, the emancipatory and structural possibilities of digital feminism, exposing how social media can become a force behind social change, but also remain rooted in unequal power relations.

 View pdf
View pdf


This article examines the construction of gender identity among African American female bloggers in China, focusing on Rose, an African American blogger on the Xiaohongshu platform. Despite the growing relationship between China and Africa and the increasing number of African immigrants, African women in China still face marginalization on race and gender. The content of these bloggers aligns with China's mainstream policies, such as "Rural Revitalization" and "Belt and Road," but reinforces gender roles under patriarchy, binds women's value to domestic domains, and defaults them to unpaid labor and emotional service roles. In user comments, there are both affirmations of these bloggers' personal traits and attention to their skin color and racial identity. This phenomenon reflects the differences between relevant policy orientations and existing cognitive tendencies among some groups. Despite the formation of certain practical norms at the platform level and the bloggers' active efforts to secure development space, African female bloggers still face dual challenges related to gender and race in their actual development. The process of their identity construction is consistently influenced by multiple external factors such as observation, evaluation, and regulation, and they exist within this complex interactive structure.

 View pdf
View pdf


Semantic ambiguity is a common phenomenon in natural language. In observations of natural language, a sentence or word often has more than one meaning; multiple interpretations are common. After language training, normal individuals can eliminate ambiguity in dialogue by relying on context and prosodic features. Among these cues provided to normal listeners, emotional tone, as a special type of prosodic information, can influence listeners' comprehension preferences when context is insufficient or multiple interpretations exist. The positive or negative impact depends on the expression of emotion in different cultures. This study aims to observe the role of emotional tone in eliminating semantic ambiguity through a behavioral experiment based on eye tracking. Participants in the experiment listened to ambiguous sentences with different emotional tones and were asked to choose the interpretation that best matched their understanding from multiple options. This comprehension was then compared with the original meaning to determine its correctness. The results showed that emotional tone significantly influenced semantic interpretation. In the experiment, a positive tone was more likely to lead listeners to choose positive interpretations, while a negative tone increased the likelihood of choosing negative interpretations. The effect of negative emotion was more significant. These findings suggest that affective intonation not only conveys emotional information in dialogue but also serves as an important auxiliary cue for semantic processing in cognition. This discovery contributes to a deeper understanding of the interaction between emotion and language.

 View pdf
View pdf


The psychological well-being of contemporary adolescents is heavily influenced by social media, particularly via algorithm-driven recommendations and virtual networks. This study explores how aspects of online culture, including misogyny, group polarization, and algorithmic amplification, impact adolescent psychological well-being and their views on gender roles. Through the use of the Netflix series Adolescence as a case study, this analysis applies Social Learning Theory, Objectification Theory, Attachment Theory, and Emotion Regulation Theory to evaluate the relevance of these frameworks in examining the series’ narrative, characters, and symbolic elements. The results indicate that toxic online communities exacerbate identity confusion, emotional regulation difficulties, and adherence to rigid gender norms among adolescents, especially in the absence of secure attachments. As such, these communities are closely linked to negative mental health outcomes. To this end, interventions should prioritize media literacy education, active parental guidance, and platform accountability to promote critical thinking, emotional resilience, and safer digital environments for young people.

 View pdf
View pdf


Social media use (SMU) has become a popular topic in the field of examining its inner properties in social interactions and exploring people’s perceived happiness. Existing literature suggested a clear correlation between different types of social media use (SMU) and mental health status, with passive SMU being negatively correlated with mental well-being. The study aimed to research this relationship with the potential related factors of social comparison and gender differences. The study was conducted in online survey questionnaires, and 150 participants were recruited. The survey consisted of parts of social media activities, social comparison orientation, and DASS-21 to measure participants’ mental well-being. In the results, active SMU was negatively related to social comparison and positively related to mental health status, and passive SMU was opposite. The study also reported gender as a small but significant factor for passive SMU and anxiety level, that female participants were more closely correlated with passive use of social media and were more inclined to show symptoms of anxiety.

 View pdf
View pdf


Artificial intelligence (AI) is profoundly reshaping the global education landscape, yet the distribution of its benefits remains highly inequitable. Students in high-income regions adopt AI tools at much higher rates, while learners in low-resource areas encounter barriers related to infrastructure, affordability, and cultural adaptation. This paper analyzes how inclusive and affordable AI-driven practices can advance educational equity. Using a three-dimensional framework of opportunity, process, and outcomes, it compares initiatives including offline learning devices in Africa, synchronous classrooms in rural China, and adaptive education platforms in Brazil and India. Employing a multi-case comparative approach, this study integrates outcome tracking, cost-effectiveness analysis, and cross-regional datasets. Findings indicate that low-cost devices and solar-powered solutions expand access, while resource-sharing platforms and open educational resources foster fairness of process and outcomes. However, challenges such as algorithmic bias in speech recognition and unequal access to generative AI persist. The paper concludes by proposing recommendations to establish open-course repositories, strengthen teacher collaboration networks, and develop sustainable governance models to maximize inclusion.

 View pdf
View pdf


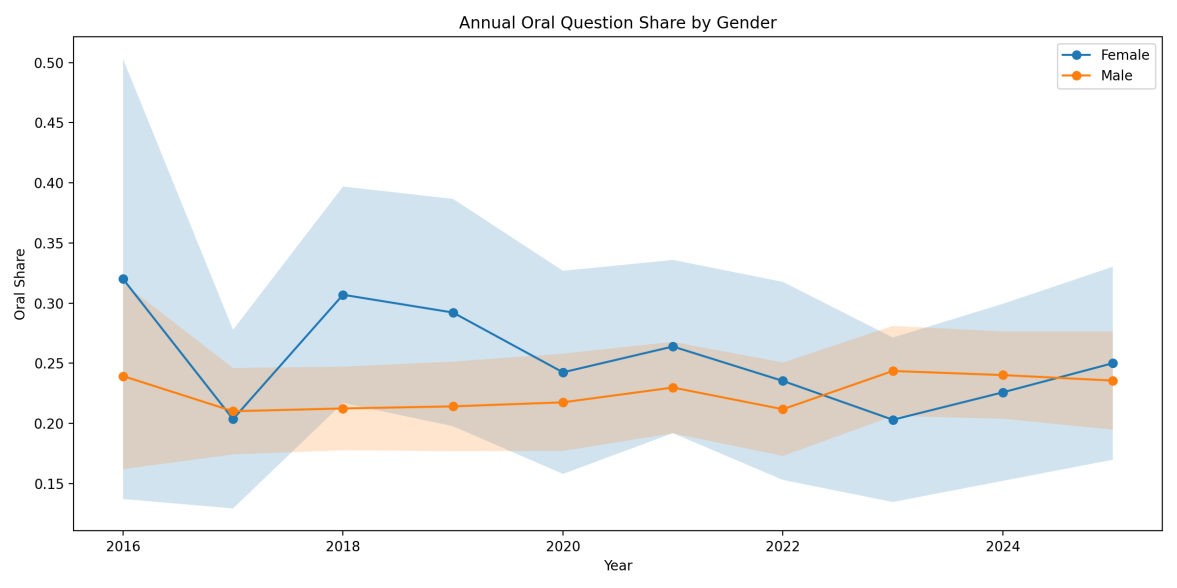
This paper investigates gender differences in questioning behavior within the Legislative Council of Hong Kong, China. Drawing from parliamentary transcripts, it analyzes how male and female legislators engage in scrutiny and representation. Based on an original dataset of 5,402 questions from 2016 to 2025, this study examines whether female legislators differ from male legislators in question format, policy focus, attention to women’s issues, and breadth of topics. This research employ a mixed-method approach that integrates a Chinese large language model (LLM) with machine learning to classify question content by policy domain, framing, and gender-related topics, combined with statistical modeling to test gender effects. The results show that female LegCo members are more inclined to raise questions orally on the legislative floor and disproportionately focus on social and community welfare issues, whereas male members prioritize finance, economy, and infrastructure. Female legislators are also more than twice as likely to bring up issues of gender equality and women’s rights. Moreover, women’s questions span a broader range of policy areas, countering the stereotype of female legislators being confined to “women’s issues.” At the same time, women’s questioning style (e.g. professionalism, directness) is largely equivalent to that of their male colleagues. These findings provide evidence of substantive impacts of female representation even in Hong Kong, China’s semi-authoritarian legislature, and suggest strategies to support and amplify women’s legislative voice.

 View pdf
View pdf


Depression is a significant global health concern, affecting individuals across all age groups, including adolescents. It can have severe consequences, including physical health problems, mental health issues, social and relationship difficulties, and functional impairment in various aspects of life. In its most extreme form, depression can lead to self-harm or suicide. Given its far-reaching impacts, identifying factors contributing to its onset is critical, as is exploring preventive measures. One such factor is parenting styles and their influence on adolescents' mental health. This study investigates the impact of distinct parenting styles on adolescent depression. A literature review was conducted to analyze existing research on the effects of parenting styles on adolescent depressive symptoms. The literature review indicates that authoritative parenting is associated with fewer depressive symptoms in adolescents, while authoritarian, permissive, and uninvolved parenting styles are linked to higher levels of depressive symptoms. These findings highlight the importance of authoritative parenting in promoting adolescent mental health.

 View pdf
View pdf


Under the trend of digitalization of education, multimedia spatial visualization has become a key driving force for geographical education innovation. Based on twelve core studies and two representative teaching cases, this article discusses how multimedia-based visualization can cultivate geographical thinking in Chinese high school classrooms. The research results show that tools such as GIS, animation and interactive models effectively reduce the cognitive load, enable students to participate in the construction of spatial characterization through visual interaction, and promote the transformation from vision and memory to vision and reasoning. Its core mechanism lies in the cognitive support provided by multimedia, which supports students to understand the spatial relationship and systematic connection between geographical phenomena through visualization, situational and inquiry-based learning. However, challenges still exist, including the limited digital capacity of teachers, regional differences in resources, and the lack of vertical empirical data. The study concludes that multimedia spatial visualization is not only a technological enhancement, but also a teaching bridge connecting cognitive development and geographical thinking cultivation, which provides valuable inspiration for high school geographical innovation and educational modernization.

 View pdf
View pdf


To explore creative cognition in depth, the perspective that Jazz improvisation brings about turns out to be unique and interesting. Jazz improvisation implies real-time generation, instant evaluation, and immediate execution of novel musical creativity. In this review, the most updated neuroscientific research findings in three core sub-fields, intrinsic neural mechanisms, experience-driven neural plasticity, and interpersonal collaboration, are intensively discussed. Improvisations always involve complex brain networking rather than single reaction in an isolated region, where correlations of dynamic interactions among default modes, executive control, attention, sensory-motor, and reward systems occur at the same time. Interactions among these networks and schemes support the generation of spontaneous creativity, predictive motor planning, and sustained immersive experiences. It has also been discovered that long-term jazz training could lead to the enhancement of structural and functional neural plasticity, which strengthens the white matter pathways, like the arcuate fasciculus, and enhances connections between the prefrontal cortex and the premotor area, enabling professionals to convert internal intentions into smooth musical output. Brain synchronization scanning studies show that ensemble improvisation heavily relies on brain synchronization and error monitoring of predictions as well as emotional resonance, which implies that creativity could be an outcome derived from social processes. Despite of various ways of study have been applied in this area and a lack of long-term data, more and more evidence shows that improvisation is the result of adaptive neural cooperation formed through practice and interaction. This review puts forward a comprehensive framework for the understanding of neural mechanism of jazz improvisation and proposes that multi-model and ecologically valid methods should be applied in further research.

 View pdf
View pdf



