Volume 201
Published on July 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICEMGD 2025 Symposium: Digital Transformation in Global Human Resource Management
With the continuous development of China.com" she Ritz-Carlton Hotel Nanjing Based on UGC Reviews important in the national economy, with the hotel industry facing fierce competition. Customer perceived service quality has gradually become a core factor in measuring the comprehensive competitiveness of high-end hotels. This study takes The Ritz-Carlton Nanjing as a case, collecting user-generated content (UGC) from major tourism platforms, and applies text mining techniques to systematically analyze customer’s seasoning the comprehensive competitiveness of high-end hotels. This study takes The Ritz-Carlton Nanjing as a case, collecting user-generated content (UGC) from major tourism platforms, and applies text mining techniques to systematically analyze custonse. Based on word frequency analysis, sentiment analysis, and topic identification, this paper constructs a UGC-based service quality perception framework and proposes practical improvement suggestions, including enhancing staff service awareness, optimizing cleaning procedures, and improving dining services. The research enriches theoretical studies on high-end hotel service quality in the Chinese context and provides data-driven insights for managerial practice. It also discusses the application prospects of UGC in service quality evaluation and suggests future research directions.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the context of rapid advancements in the field of intelligent economy, there is an increasing demand for community distribution. This study is firmly rooted in the paradigm of an intelligent economy. Its objective is clear: to explore the contemporary challenges associated with optimising community distribution strategies. This investigation is being conducted in the context of the rapid advancements witnessed in the field of e-commerce, which have resulted in the diversification of consumer demands. This is happening because of inefficiency and high costs in community distribution. The intelligent economic background creates an opportunity for community distribution. This involves analysing the current situation and problems of community distribution, analysing the application of intelligent logistics technology in community distribution, proposing optimisation strategies based on intelligent algorithms for distribution path optimisation, dynamic demand prediction, and customer service quality, and verifying the feasibility of the strategies through case studies. The findings show that using intelligent technology to optimise community distribution is the key to achieving efficient and high-quality results, ensuring both enhanced efficiency and elevated customer satisfaction.

 View pdf
View pdf


Under the background of the global dual carbon (carbon peak and carbon neutrality) goals , the development of new energy enterprises is closely related to ESG (environment, society and governance) investment. As the core force for achieving low-carbon transformation, the valuation system of new energy enterprises is undergoing a profound transformation from the traditional ESG comprehensive value of the index. At the same time, blockchain technology, with its decentralization and data immutability, provides innovative solutions for information disclosure and data management in ESG investment. However, existing research has not explored the mechanism by which blockchain technology empowers ESG investment to affect the valuation of new energy enterprises. This study aims to systematically sort out the impact mechanism and, through a comprehensive analysis of relevant literature, reveal the application value of blockchain technology in ESG investment and its role in improving the valuation of new energy enterprises, in order to fill the research gap. The study found that blockchain technology has shown significant advantages in improving the transparency of ESG data, reducing management costs and optimizing the decision-making process, providing technical support for ESG investment in new energy companies. ESG investment has a positive impact on the valuation of new energy companies through risk mitigation, brand premium and policy dividends, and forms a synergistic effect through multi-dimensional paths.

 View pdf
View pdf


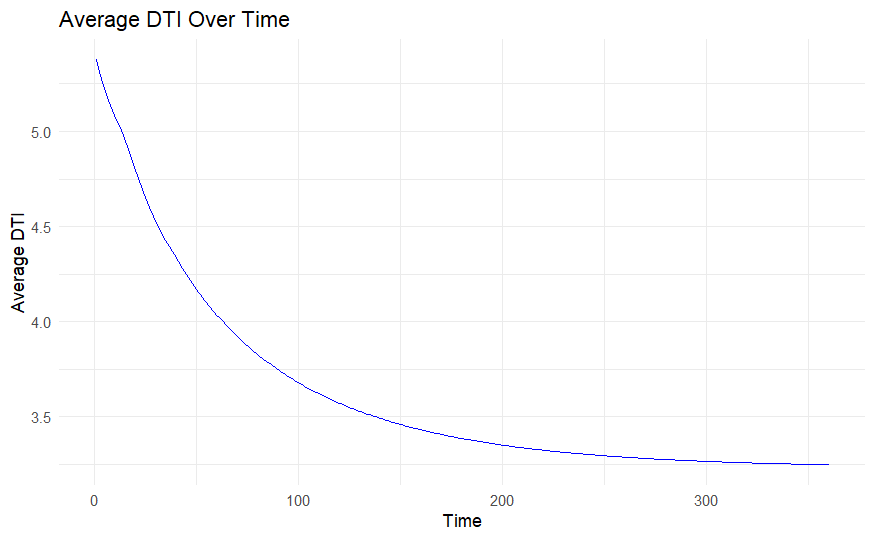
This paper analyzes credit loss under different LTV/DTI settings. By running various macroeconomic variables from current and previous periods, a VAR model simulates 360,000 scenarios with different LTV/DTI pairs over 360 periods. Using a cutoff, the research determines how many scenarios present a high risk of default and examines whether this aligns with theoretical expectations. Comparing the credit analysis results, the study finds that higher LTV significantly increases credit losses. This corresponds with the theoretical understanding that higher LTV indicates lower down payment for borrowers, thereby reducing the cost of default. Borrowers lack strong motivation to maintain repayments and are more likely to default when confronting financial difficulties. The research demonstrates that when LTV reaches a high level, increases in DTI lead to greater credit losses. Conversely, when LTV is low, rising DTI does not substantially impact credit performance.

 View pdf
View pdf


The role of the directors' remuneration system in the corporate governance structure has become increasingly prominent as companies focus on long-term strategic development and sustainable governance. Using McDonald's Corporation as a case study, this paper examines the reflection of its director compensation system in incentive and constraint mechanisms, strategic goal alignment and ESG (environmental, social and governance) performance orientation. The results of the study show that McDonald's director compensation system is mainly characterised by a clear structure and long-term incentives, with approximately 70% of the compensation in restricted stock units, reinforcing the binding relationship between directors and the long-term interests of the company. The company has gradually introduced ESG performance indicators in recent years, linking 20 per cent of equity incentives to non-financial targets, demonstrating a high awareness of sustainable governance. At the same time, it outperforms its peers in terms of pay transparency, director shareholding requirements and strategic alignment. However, there are still problems such as insufficient quantification of ESG objectives, subjectivity in performance assessment and lack of flexibility in shareholding rules. The study concludes that the McDonald's director compensation system is effective in strengthening corporate governance and raising directors' awareness of their responsibilities, but it needs to further improve the system's scientificity and adaptability to adapt to the changes in the external environment and the diversified demands of investors.

 View pdf
View pdf


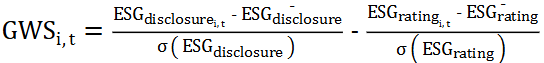
As China’s economic development transitions from rapid growth to high-quality development, reducing environmental pollution has become an unavoidable proposition for enterprise sustainability. With the accelerated growth of China’s digital economy in recent years, the impact of enterprises’ digital transformation on “greenwashing” behavior needs to be studied in depth. This paper analyzes all A-share listed firms during the 2012-2022 period to investigate the association between digital transformation and corporate “greenwashing” behavior through empirical testing. The study finds that digital transformation exerts an inhibitory effect on corporate “greenwashing” behavior, with strategic green innovation weakens the effect. Heterogeneity analysis reveals that the inhibitory effect of digital transformation is particularly pronounced among enterprises in heavily polluted industries or non-state-owned enterprises. These findings offer theoretical support and policy inspiration for governmental initiatives to encourage the corporate digital transformation, ultimately promoting sustainable and high-quality economic growth.

 View pdf
View pdf


While growing competition in the tech industry and increasing societal focus on pay equity and corporate social responsibility, Adobe faces new challenges. The executive compensation system is the key tool to attract, motivate, and retain top talent. This paper explores Adobe’s executive pay system to uncover its potential problems and offer practical suggestions for improvement. The goal is to help balance corporate goals and social expectations. The study uses literature review, case study, and comparative analysis to examine Adobe’s executive pay structure, how it works, and its strengths and weaknesses. The findings show that Adobe links executive pay closely to company performance, which helps ensure leaders take responsibility for revenue growth and shareholder returns. The heavy reliance of stock-based rewards boosts performance incentives, but it also leads to high volatility and fairness concerns. The current system focuses more on financial outcomes and less on broader employee satisfaction or social goals. The pay gap between top executives and regular employees remains wide, which is common in the tech industry, but may hurt team cohesion and public image as society grows more sensitive to fairness. In conclusion, Adobe’s pay system shows clear strengths in performance alignment but needs improvement in terms of stability, fairness, and balancing multiple goals. Based on the literature and case analysis, this paper suggests using more non-financial performance metrics, increasing pay transparency, and giving employees a stronger voice in pay-related matters to support more sustainable corporate governance.

 View pdf
View pdf


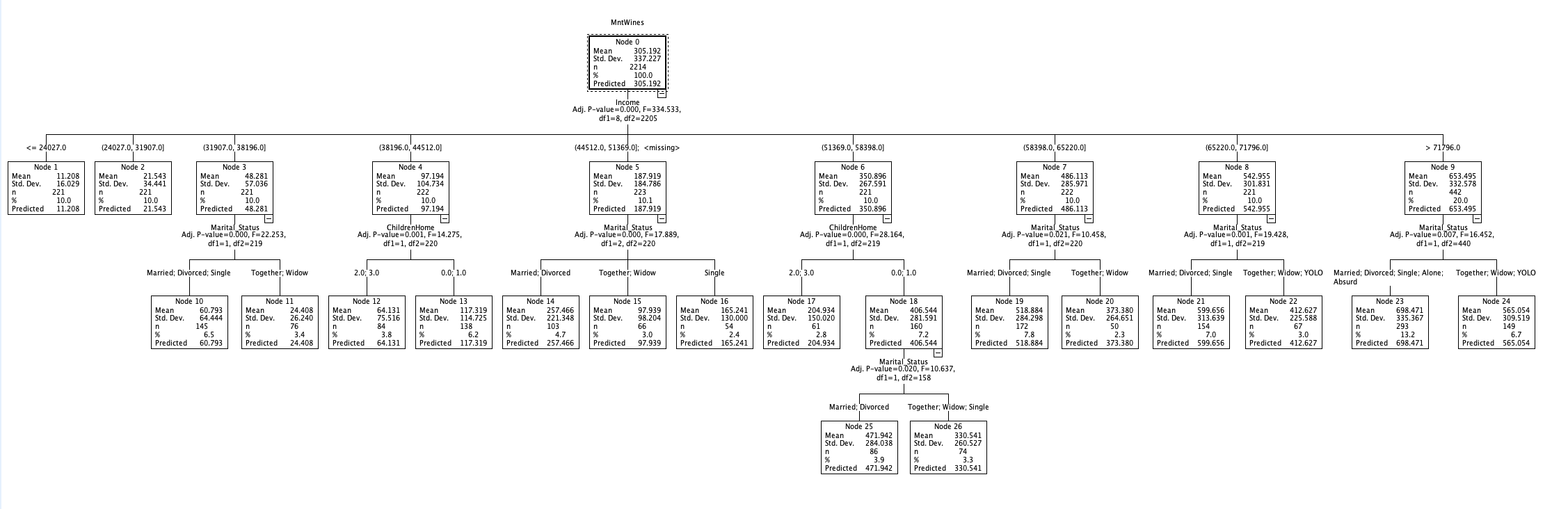
With the rapid development of data-driven marketing, personalized and precision strategies have become essential tools for enterprises to enhance competitiveness. However, the deep mining of multidimensional consumer data in offline superstore scenarios still faces significant challenges. This study applies a decision tree algorithm to analyze consumer behavior patterns in four product categories—wine, candy, meat, and gold—based on customer consumption data from a supermarket. The findings indicate that income level is the core factor influencing consumption. Family structure also plays a differentiating role: childless families prefer wine; families with children spend more on confectionery; meat consumption is influenced by both income and number of children; and gold consumption is primarily driven by income. Accordingly, the study proposes precision marketing strategies such as promoting high-end wines to high-income childless families, recommending healthy candy options to families with children, and tailoring meat and gold promotions based on family structure. By shifting from single-variable to multifactor joint modeling, this study emphasizes the importance of family structure in consumer profiling and offers a cost-effective precision marketing solution using interpretable decision trees for traditional retail.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study explores the paradox where elevated data element utilization level intensifies green innovation bubbles (GIB) in Chinese A-share listed firms from 2012 to 2023. Employing time-fixed effect regression on 36,229 firm-year panel observations, this paper finds a significant positive association between data element utilization level (DEUL) and GIB (β=0.161, p<0.01), indicating that data-driven strategies may unexpectedly widen innovation quantity-quality gaps. Moreover, mechanism analysis reveals DEUL worsens GIB through dual pathways: (1) worsening information asymmetry via selective environmental disclosure (EID coefficient: -0.382, p<0.01), and (2) reinforcing technological path dependence (IID coefficient: 0.090, p<0.05). Notably, superstar inventors positively moderate this effect (β=0.162, p<0.05), speeding up bubble formation on grounds of overreliance on models. These findings challenge "data-driven efficiency," demonstrating that digital tools may cause strategic rigidity and resource misallocation. In terms of this issue, three solutions are proposed: policy-driven algorithm transparency as well as diversified R&D investment, corporate long-term evaluation reforms, and financial bubble-warning systems.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the digital economy era, economic activities increasingly rely on data. With deepening globalization, cross-border data flows have become a vital element of international trade. However, the growing emphasis on digital security has led to rising restrictions on such flows, affecting trade dynamics. Using the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) as a policy case, this study utilizes OECD panel data from 2005 to 2021 to analyze the regulation’s impact on China’s digital service trade exports and the underlying mechanisms. Empirical findings suggest that the GDPR exerts a statistically significant positive influence on China’s digital service exports. Robustness is validated through parallel trend tests, placebo tests, and country-sample variation. A dynamic effects model further reveals that the long-term benefits of GDPR implementation on export efficiency exceed the short-term effects. Heterogeneity analysis indicates that the regulation’s impact varies with the development level of destination countries. Moderating effect analysis shows that institutional variables—such as rule of law, regulatory quality, government effectiveness, and corruption control—and final consumption expenditure enhance the regulation’s export-promoting effect. In contrast, stronger trade competitiveness in destination countries weakens this positive influence. These findings offer empirical insights into the complex relationship between data regulation and digital trade, providing references for optimizing China’s digital service trade policy framework.

 View pdf
View pdf



