Volume 183
Published on September 2025Volume title: Proceedings of CONF-MLA 2025 Symposium: Applied Artificial Intelligence Research
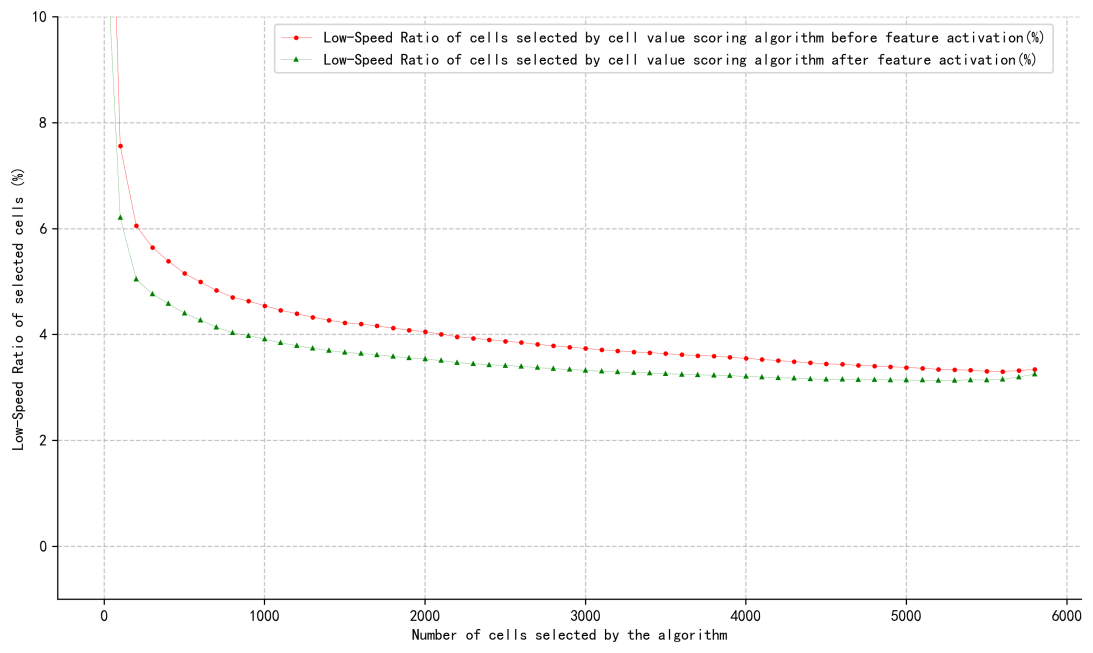
With the increasingly strict assessment of regional mobile operators’ wireless indicator by the wireless communication group, and the need for corresponding licenses and activation fees for the advanced feature algorithms provided by the vendor, regional mobile operators are in urgent need of optimizing a cost - controllable and scenario - based rapid deployment plan for the above - mentioned advanced feature algorithms due to cost control. This paper uses the methods of data analysis and comparative experiments to analyze and study the Key Performance Index (KPI) data of cells provided by regional mobile operators, and proposes an optimal algorithm for feature activation based on cell value scoring. This algorithm aims to solve the problem of how to select cells for deployment when mobile operators deploy specific feature algorithms. The algorithm can balance operating costs and network performance, and help mobile operators make optimal deployment decisions based on data. Based on the experimental KPI data, this algorithm can achieve an approximately optimal effect in terms of improving the Low-Speed network performance, and has a lower time complexity compared with the traditional combination algorithm.

 View pdf
View pdf


Speech recognition technology, a pivotal element in human-computer interaction, has witnessed substantial advancements in recent years, propelled by the synergies of deep learning and big data. This paper provides a systematic review of the evolution of speech recognition algorithms, delineating the principal characteristics and application contexts of traditional speech recognition algorithms, such as Hidden Markov Models (HMM), deep learning-based algorithms, including Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), and end-to-end speech recognition algorithms. Furthermore, this study delves into the multifaceted applications of these algorithms in domains such as voice assistants (e.g., Siri and Alexa), machine translation, and meeting transcription, elucidating their transformative impact. The paper also synthesizes the prevailing speech recognition technologies and the challenges they confront, with a particular emphasis on the limitations of commonly used language recognition algorithms, such as susceptibility to noise, accent variability, and data dependency. Through this comprehensive analysis, the paper aims to illuminate the current state and future trajectories of speech recognition technology. This paper identifies and summarizes the shortcomings of commonly used language recognition algorithms.

 View pdf
View pdf


Deepfake technology, empowered by breakthroughs in deep learning-based image synthesis, is profoundly reshaping identity verification systems, finding extensive application in security, finance, and social media with enhanced convenience. However, its capacity to generate hyper-realistic facial forgeries presents a dual impact: while driving innovation, it simultaneously introduces unprecedented security threats, including privacy violations, identity spoofing, and data poisoning attacks. This paper systematically reviews and assesses current research progress on the security risks and defense strategies associated with Deepfake technology. Through synthesis of existing literature, this paper constructs a multidimensional analytical framework examining three core dimensions: first, the core technological principles underpinning Deepfakes and their evolution; second, the diverse spectrum of security risks arising from their misuse and their underlying mechanisms; and third, the effectiveness and inherent limitations of prevailing defense mechanisms, encompassing detection techniques and legal regulations. This study concludes that although Deepfakes advance facial recognition, mitigating their inherent security threats necessitates a multidimensional synergistic approach. This approach must integrate continuous technological advancements, robust legal oversight, and strengthened public awareness initiatives. Future efforts must prioritize establishing cross-disciplinary collaborative governance mechanisms to achieve a dynamic equilibrium between technological innovation and security assurance.

 View pdf
View pdf


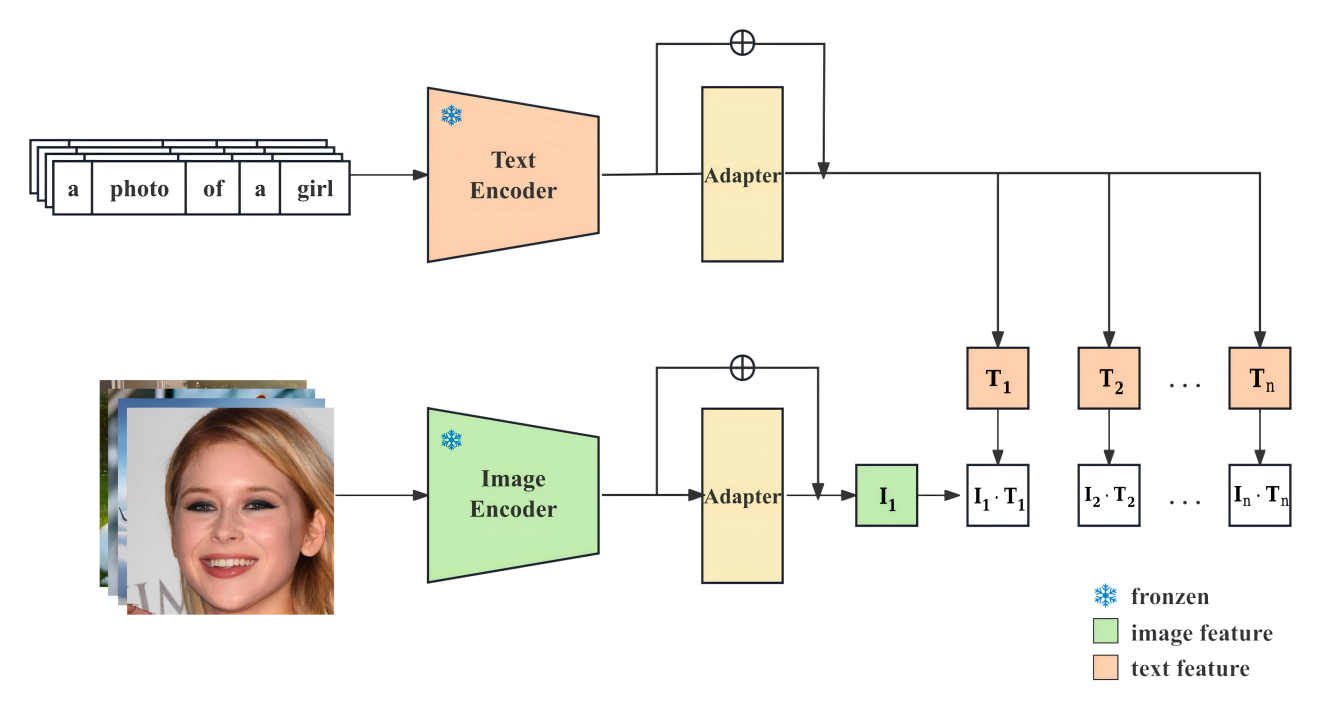
In recent years, with the rapid development of cross-modal learning, pretrained models such as CLIP have demonstrated powerful zero-shot capabilities in image-text alignment tasks, making them central to multimodal research. However, a key challenge remains: how to effectively transfer these capabilities while preserving the strengths of CLIP. To address this, we propose a parameter-efficient multi-task fine-tuning framework—Multi-Task CLIP-Adapter. By inserting lightweight Adapter modules after the frozen CLIP encoder, our method enables unified adaptation across multiple tasks, including classification, image-text retrieval, and regression. Experimental results show that our approach achieves an 8%–12% performance improvement with less than 0.2% additional parameters, while maintaining the original model’s zero-shot capability. Compared to the original CLIP and conventional transfer strategies, the Multi-Task CLIP-Adapter offers significant advantages in parameter efficiency and task generalization, paving a new path for scalable applications of large multimodal models.

 View pdf
View pdf



