Volume 203
Published on August 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICEMGD 2025 Symposium: Resilient Business Strategies in Global Markets
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) plays a crucial role in enhancing the resilience of global supply chains. This paper investigates how SRM strengthens supply chain stability and agility by fostering better coordination, transparency, and responsiveness. It highlights essential factors such as power dynamics, mutual trust, supplier performance monitoring, and long-term strategic collaboration. As global markets face increasing uncertainties—from geopolitical risks to environmental challenges—organizations rely more heavily on robust SRM frameworks to manage supplier risks and ensure continuity. In recent years, companies have also faced growing pressure to comply with ethical standards, labor regulations, and environmental laws, elevating the importance of SRM as a governance mechanism for ethical sourcing and sustainability. The research incorporates a case study of Walmart, demonstrating how structured SRM practices can help mitigate supply risks, increase supplier responsiveness, and maintain cost-effectiveness under dynamic conditions. It further reveals that companies integrating SRM into broader strategic planning not only reduce their vulnerability to disruption but also build competitive advantage by fostering supplier innovation and flexibility. Overall, the paper concludes that SRM has evolved beyond an operational necessity into a key enabler of long-term organizational resilience, sustainability, and strategic alignment in a rapidly changing global business environment.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study aims to compare the performance of the Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) and Simulated Annealing (SA) algorithms in optimizing distribution routes for cold-chain logistics of aquatic products. First, a multi-objective optimization model is constructed with distribution cost, transportation time, and loss rate as core objectives, incorporating temperature control and time window constraints. Constraint integration is achieved through improved algorithm designs, such as the temperature deviation penalty term in ACO and the dynamic penalty function in SA. Second, based on a simulation scenario with 21 nodes (1 distribution center and 20 customer points), systematic comparative experiments are conducted on the two algorithms, focusing on core indicators including total driving distance, time window violation, total cost, and product loss rate. The results show that the SA algorithm performs better in comprehensive optimization indicators: the total cost is 1.87% lower than ACO, the product loss rate is reduced to 3.8%, the time window satisfaction rate is increased to 88%, and the temperature constraint violation rate is only 0.5%, making it more suitable for strict temperature control scenarios of long-distance and high-value aquatic products. The ACO algorithm, however, has an advantage in convergence speed (reaching the optimal solution in 27 iterations) and computational efficiency, suitable for dynamic route adjustment in small-to-medium distribution networks. The study suggests that future research can explore hybrid optimization strategies of the algorithms and validate the model's effectiveness in larger distribution networks, providing a quantitative basis for algorithm selection in cold-chain logistics enterprises.

 View pdf
View pdf


The rapid expansion of digital platforms has significantly transformed how information is represented, particularly in the online food delivery industry. On these platforms, consumers make purchasing decisions by browsing images provided by restaurants. Within this evolving landscape, visual imagery plays a crucial yet underexplored role in shaping purchasing decisions on platforms like Uber Eats. This study examines how specific image attributes in food photography impact restaurant sales performance. Leveraging a unique dataset of restaurants from Uber Eats, we employ advanced image-processing techniques to extract 12 key visual features. By applying regression models, we quantify the impact of these visual attributes on restaurant sales. Our findings reveal that texture difference and Saturation positively influence sales, enhancing food appeal and engagement. Conversely, excessive Brightness Contrast has a negative impact, likely due to visual discomfort or diminished product detail. This research contributes to the growing literature on visual marketing and digital commerce by offering empirical evidence on how image design in online food delivery platforms affects purchasing behavior. Our findings provide practical recommendations for food delivery platforms, marketers, and restaurant owners to optimize visual content, ultimately improving consumer engagement, brand perception, and sales performance.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the field of corporate management, the impact of CEO narcissistic traits on corporate strategic decision-making and economic development has attracted increasing attention. However, existing research mainly focuses on routine business operations, leaving an obvious gap in the discussion of business resource allocation. From the perspective of the Upper Echelons Theory, this paper takes Gree Electric Appliances, a leading enterprise in China’s home appliance industry, and its CEO Dong Mingzhu as the research objects to explore the manifestations of CEO narcissistic traits, the decision-making transmission mechanism, and their impact on corporate economy. The study finds that Dong Mingzhu is deeply bound to Gree Electric Appliances, and she enhances the company’s visibility and market attention, making centralized decisions in marketing, product promotion, etc. Dong Mingzhu’s narcissistic traits affect strategic choices through paths such as binding personal brands to the enterprise and high media exposure, which improve the company’s popularity in the short term but lead to inefficient resource allocation for diversified projects in the long term. This research provides theoretical references and practical insights for the governance optimization of strong-leadership enterprises.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the rapid growth of international trade and cross border capital flows, traditional payment systems such as SWIFT are increasingly challenged by inefficiencies, high fees, and a lack of transparency. As a response, blockchain technology, characterized by decentralization, immutability, and traceability, has emerged as a potential solution for modernizing cross border payments. This paper offers a comprehensive analysis of the current state of blockchain technology in this domain, reviewing its applications, key advantages, and limitations. By examining how distributed ledgers and smart contracts can streamline payment processes, reduce intermediary costs, and enhance transparency and compliance, the study highlights blockchain’s transformative potential. However, challenges such as regulatory fragmentation, limited technological maturity, and accessibility barriers remain significant obstacles to large scale adoption. Relying on secondary data and existing literature, this study also emphasizes the need for future empirical research and case based analysis to evaluate performance, security, and scalability of blockchain based systems in real world cross border payment scenarios.

 View pdf
View pdf


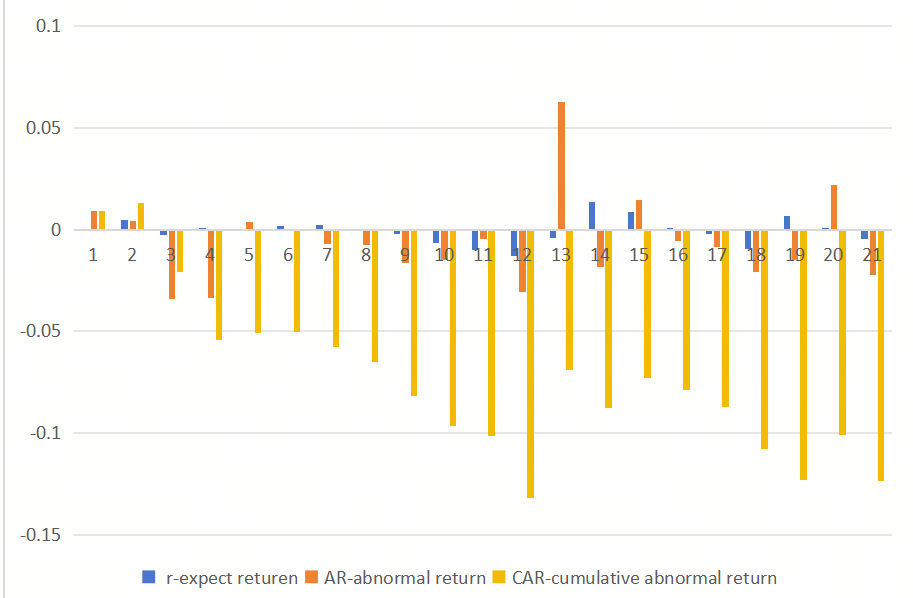
As organizations face pressure from consumers to address ESG issues, sustainable marketing campaigns have become prevalent. Such campaigns can link a brand's public image to environmental sustainability, thereby helping to boost sales. Many companies will be attracted to the huge benefits of an ESG product like green bond. But there are some companies that just love the mere boo-boo of ESG. They want to label their company as ESG as a way to attract users with advertisements. As a matter of fact, they will not do any actions related to green bond. This behaviour is known as “greenwashing”. The aim of this paper is to explore the impact of greenwashing on companies, especially when the public notices. For research, this paper uses an event study to help quantify unusual changes in stock prices when a particular event occurs, such as when a company is exposed for greenwashing practices. The object of study is the bond price of S&P 500 and Volkswagen from June 8th, 2014 to April 9th 2015. Data sources are from Investing.com, which widely used by investors, analysts, researchers and financial practitioners worldwide. Finally, this study finds that the abnormal returns (AR) show significant fluctuations during the event window, especially around the event date, August 21, 2015, this demonstrates the adverse effect that greenwashing has on a company.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the era of globalization, the scale of international talent mobility is enormous. However, this flow remains uneven, with developing countries often facing the challenge of brain drain. This article analyzes a number of studies on the phenomenon of brain drain and its impact on national human capital and innovation capacity in developing countries in the context of globalization. This article first summarizes the basic connotation and definition of brain drain and examines the drivers of brain drain in developing countries with the help of the two aspects of push and pull in the push-pull theory. This article analyzes how human capital and innovation capacity in developing countries have changed in the context of brain drain, summarizing research on both positive and negative impacts. Finally, this article summarizes the limitations of existing research and offers recommendations. First, cross-national comparative research and analysis of net population outflows should be strengthened. Secondly, research on non-linear relationships should be deepened.

 View pdf
View pdf


This empirical investigation evaluates how corporate digital initiatives affect sustainable technological advancements, utilizing a comprehensive dataset comprising authenticated financial records from Chinese A-share market entities spanning the decade from 2013 through 2023. Empirical findings demonstrate a quantitatively measurable constructive linkage connecting organizational technological transformation with environmental innovation strategies. Furthermore, this causal relationship remained robust when implementing alternative proxy variables during methodological validation procedures covering multiple robustness check scenarios. Building upon this analytical framework, the study incorporates R&D expenditure as a mediator to systematically investigate the transmission pathways through which organizational digitalization strategies influence sustainable innovation practices. Empirical findings demonstrate that technological modernization enhances eco-innovation outcomes via their stimulating effects on research capital allocation; statistical validation procedures confirm the hypothesized mediation mechanism exhibits statistically robust explanatory power (p<0.01).This research advances existing literature on determinants of R&D capital allocation while establishing a theoretical framework for corporate strategic prioritization of digital ecosystems and sustainable innovation. The developed model demonstrates how optimizing technological adoption pathways and eco-innovation capabilities synergistically drives enterprise value creation, offering empirical guidance for achieving sustainable growth through innovation-driven transformation.

 View pdf
View pdf


Innovation is a vital factor driving the development of core competitiveness and the upgrade of economic structure., and its dynamic evolution mechanism has always been the research focus in the field of industrial economics and international trade. As complex international dynamics emerge in a globalized world, negative economic shocks can leave long-lasting impacts on firms’ innovation capabilities. This study utilizes the 2018 US-China trade war as a quasi-natural experiment, and a multi-dimensional econometric analysis framework are constructed to examine how trade frictions influence firm-level innovation in China. Constructing a difference-in-differences model, analysis of 2013-2023 firm data indicate that the US-China trade conflict causes a significant decline in innovation activity, but high industry competition and government subsidies mitigate its impact. This study further clarifies the effects of trade friction on firm innovation by contributing to the existing literature and providing empirical evidence as well as policy implications for fostering innovation capacity and resilience.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the accelerated advancement of the economy, financial accounting information has assumed a pivotal role in corporate decision-making processes by providing fundamental benchmarks for managerial personnel. This study endeavors to investigate the underlying mechanisms through which financial accounting information influences operational decision-making in enterprises. Through comprehensive statistical analysis of historical data, it has been demonstrated that financial accounting information serves as an indispensable instrument for monitoring and evaluating corporate performance. The accuracy, timeliness, and completeness of such information directly affect an enterprise's judgment of the market environment and its strategic decisions. Furthermore, empirical research show that when high information quality is high, business operational decisions are significantly more effective compared to scenarios involving lower-quality information. Therefore, improving the quality of financial accounting information is of great significance for enhancing the effectiveness of business operation decisions.

 View pdf
View pdf



