Volume 187
Published on October 2025Volume title: Proceedings of CONF-FMCE 2025 Symposium: Semantic Communication for Media Compression and Transmission
This paper focuses on the application of conductive polymer in flexible wearable devices. At the start, the importance of flexible wearable devices in daily healthcare and the strengths of flexible wearable devices over traditional wearable devices are introduced. The material to build a flexible wearable device is special; it needs to acquire High Flexibility, High Conductivity, and Biocompatibility. In this case, the paper introduces conductive polymers, and it also lists three kinds of conductive polymers that are mainly applied in flexible devices. Polystyrene Sulfonate (PEDOT: PSS), Polyaniline (PANI), and Polypyrrole (PPy). The properties and strengths of three kinds of materials are introduced, and their applications are also listed. Practical applications include PANI-based electrochemical sensors for real-time sweat pH monitoring (aiding in detecting diabetes, etc.) and PEDOT: PSS-based flexible EEG devices, which replace rigid electrodes and conductive gels to enhance comfort. The paper also mentions the drawbacks of conductive polymers and states the future development of conductive polymers.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the increasing demand for energy in the society, energy storage devices are more widely used. As one of the main energy storage devices in the past, lead-acid batteries are characterized by low cost, relatively long life and relatively simple maintenance. In particular, it is a highly favored, risk-free option for energy storage and vehicle starting due to its mature structural design, controllable reaction mechanism, and flawless recycling system, as well as the chemical stability of its aqueous electrolyte. Nevertheless, when lead-acid batteries are charged at a high rate, large, insoluble lead sulfate particles tend to form on the electrode surfaces. As the cycle progresses, these particles accumulate, preventing the electrolyte from penetrating the plates and reducing the active substance's utilization rate. The lead-acid battery's negative electrode sulfation is permanent and makes it unsuitable for energy storage applications. To make lead-carbon batteries, which are an improvement over lead-acid batteries and a solution to the sulfation problem, carbon materials are added to the negative electrode of the battery. The use of carbon material has the dual benefit of enhancing battery performance and preventing sulfation, but it also introduces the issue of excessive hydrogen precipitation. In this regard, this paper researches and discusses the hydrogen precipitation problem of lead-carbon batteries, analyzes the key role of the hydrogen precipitation inhibitor and its influence on the battery performance, and explores the performance of the battery materials.

 View pdf
View pdf


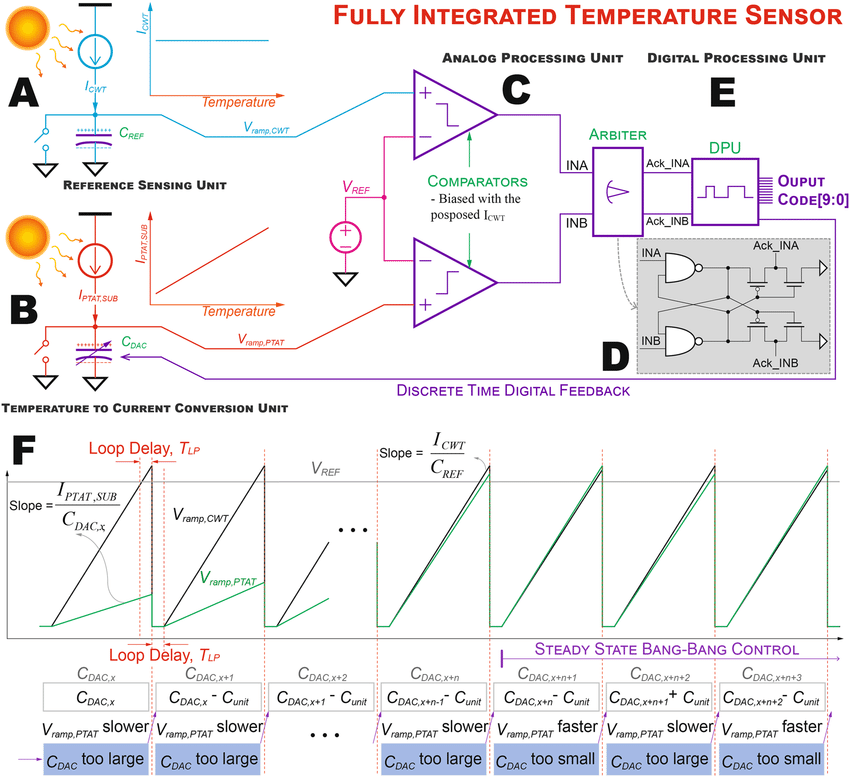
The swift progress of Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies has elevated the significance of temperature monitoring in industrial, environmental, and intelligent systems. However, core issues like measurement accuracy, energy efficiency, and system scalability continue to limit its widespread application. This paper explores recent advances in temperature sensing technologies in WSNs, addressing challenges such as accuracy, energy efficiency, and adaptability, while investigating related optimization methods. Through a review of relevant literature and evaluation of case studies, it examines the advantages and limitations of current technologies, thus highlighting major challenges and possible solutions. The results demonstrate that despite significant progress, challenges persist in adapting to dynamic environments and maintaining long-term stability, with future improvements expected to arise from the incorporation of innovative materials and advanced algorithms.

 View pdf
View pdf
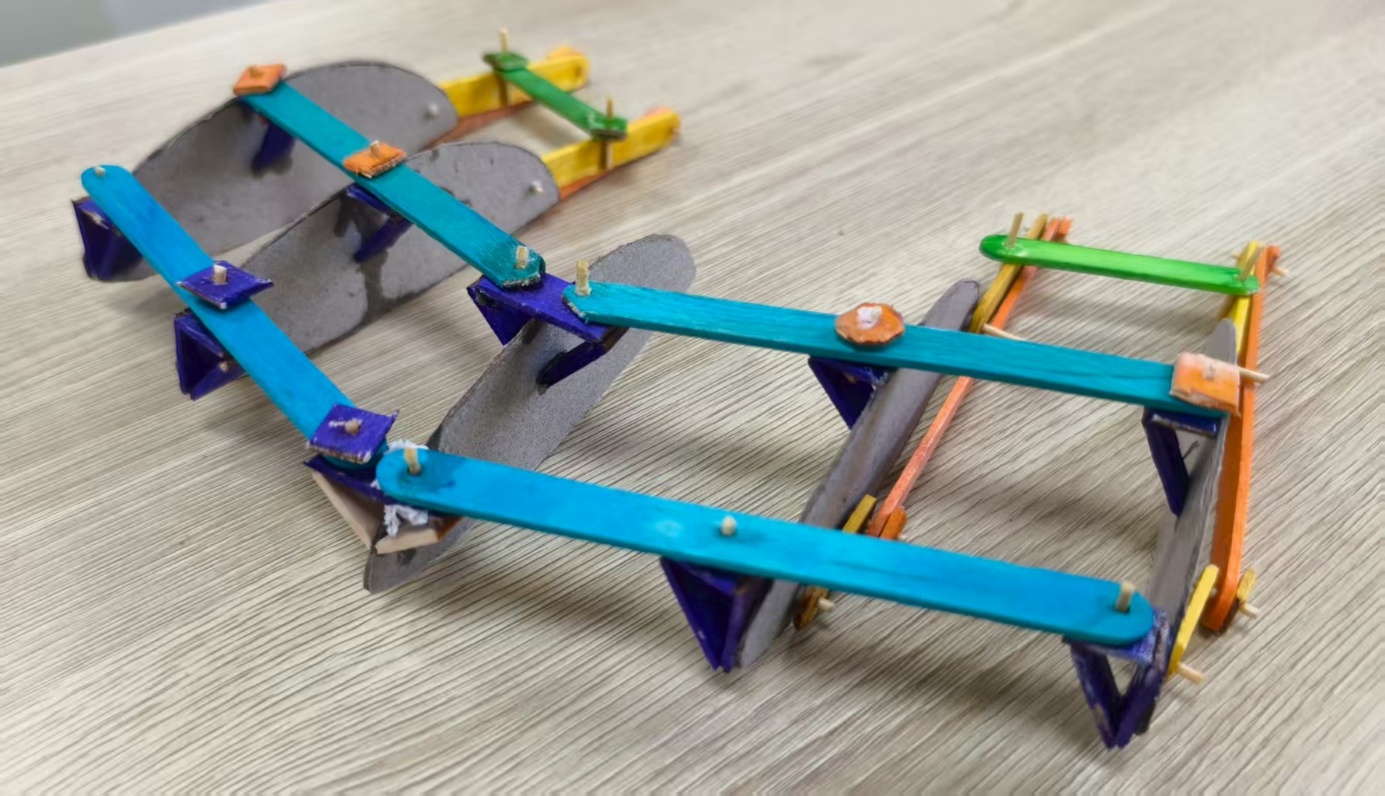



Most of the gliders need to be assembled and disassembled before and after flight. After reviewing the information, we found that there are almost no semi-automatic foldable gliders on the market. Based on the four-bar linkage and slider structure of the umbrella, we designed two umbrella-like structures to fold the glider's wings and its tripod—one on the upper part and one on the bottom part. These two umbrella-like elements are controlled by the same main slider, which is placed in the horizontal direction at the middle part of the entire structure (one on both the left half and the right half). Meanwhile, glider wings may encounter many obstacles and weather conditions, such as wind and rain, during flight. In order to adapt to wind velocity and detour obstacles, we have decided to use another four-bar linkage structure to adjust the elevation angles of the left and right wings separately. There are four such four-bar linkage structures on the wings (two on both the left half and the right half). If the speeds of the left wing and the right wing are not the same, the direction of flight can be changed. Thus, this structure can facilitate takeoff, speed adjustment, and direction change.

 View pdf
View pdf


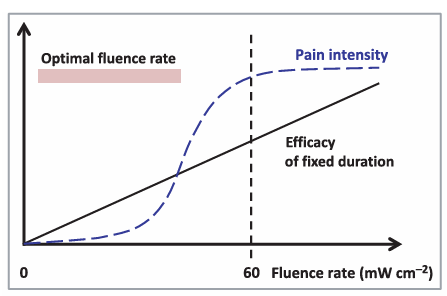
This paper mainly discusses the use of Organic Light-Emitting Diodes (OLEDs) in photodynamic therapy (PDT) and photobiomodulation (PBM) for curing typical basal cell carcinoma, Bowen disease, actinic keratosis. The innovative PDT method has several advantages than the traditional ones—OLEDs plays an essential role in reducing the pain for patients according to case studies and patients can barely experience uncomfortable feelings during the therapeutic process than before. It is also much more light-weighted and can be more closely attached to skin. Therefore, this device can also be applied to the elderly and infants at any location and at any time without going to the hospital. However, there are still some remaining issues such as the chronic pain, which is hard to be eliminated due to the conflict situation since reactive oxygen species (ROS) will cause major pain, however, if completely removing ROS will decrease the effect of PDT. Therefore, more researches need to be done in this field.

 View pdf
View pdf


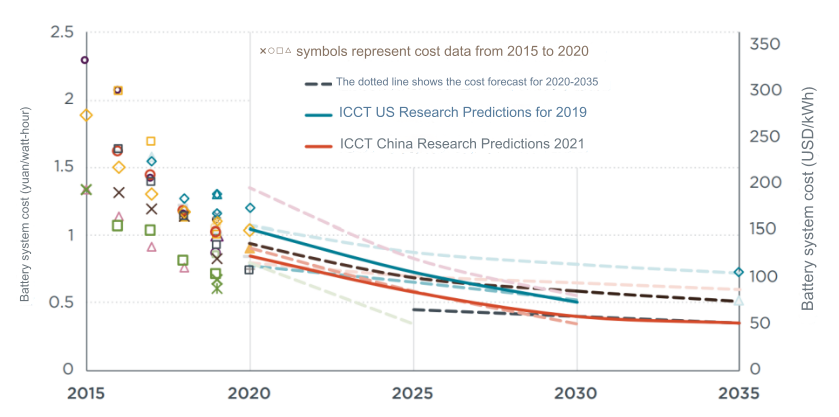
Due to the issue of environmental pollution and the development of transportation, countries around the world have vigorously advocated new energy vehicles in recent years, such as electric vehicles and hybrid vehicles[1]. However, traditional fuel vehicles, electric vehicles and hybrid vehicles have different advantages and disadvantages[2], and there is a lack of objective and accurate comparison of the three types of vehicles. When buying cars, consumers are hard to decide which type of cars they should buy since they don’t know the specific difference between them.Therefore, this paper first starts with the driving device and operation principle, and then compares the driving range, cost and environmental impact, aiming to let readers intuitively understand the differences between the three models. By referring to a large number of relevant literature, and collecting the endurance mileage and other data, this paper makes a comparative analysis, and at the same time makes a prediction analysis of the cost. The research results are as follows: due to the difference in the basic drive device, the three models have different ranking order from high to low in three aspects. For the endurance mileage, the three models are ranked from highest to lowest: hybrid, fuel, electric; In terms of cost, the order is: hybrid, electric, fuel, electric vehicles are expected to be cheaper than fuel in the next decade; For environmental impact, the order of carbon emissions from most to least is: fuel, hybrid, electric. Therefore, combining the three factors and the future direction of automobile development, consumers buy electric vehicles most cost-effective.

 View pdf
View pdf


Solid-state batteries, utilizing solid electrolytes, are emerging as a promising next-generation energy storage technology due to their superior safety, energy density, and lifespan. This study investigates key performance bottlenecks in solid-state electrolytes, with a focus on enhancing ionic conductivity, interfacial stability, and maneuverability for large-scale industrial applications. We conduct a comparative analysis of ion conduction mechanisms, structural characteristics, and interfacial behaviors across different types of solid-state electrolytes—oxide, sulfide, polymer, and hairslide systems. Current solid electrolyte systems exhibit diverse properties and limitations. Polymer electrolytes show ionic conductivity in the range of ~10⁻⁷–10⁻⁵ S·cm⁻¹, while sulfide electrolytes range from ~10⁻³–10⁻² S·cm⁻¹. However, interface resistances often exceed 100 Ω·cm² without surface modifications. Significant progress has been made in hybrid and interface engineering, such as LLZO polymer composites and sulfide@oxide coatings, which reduce contact resistance by 40–70%. An ideal electrolyte system capable of balancing high ionic conductivity, chemical stability, and maneuverability remains elusive. To facilitate industrialization, critical challenges such as processing temperature limits, air sensitivity, and cost-effective material handling must be addressed.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the deepening of the concept of sustainable development, recycled plastics play an increasingly important role in environmental protection and resource utilization. However, in the past, the recycling of recycled materials has faced many challenges in practical applications, which has made it difficult to increase the utilization rate of recycled plastics. Therefore, the aim of this paper is to investigate the challenges in the application of recycled materials for packaging suitability. In order to solve the above problems, this study analyzes the advantages and disadvantages of intelligent sorting technology, compares the differences between physical and chemical sorting, and explores the performance defects and modification methods of PCR plastics by comparing different literatures, summarizing case studies and experimental data. It is found that PCR plastic needs technological innovation to break through the bottleneck of sorting and modification, and low-cost and high-precision sorting technology, high-performance modifier and high-efficiency catalysts should be researched and developed in the future, so as to promote its shift from "low-quality recycling" to "high-quality closed-loop", and to provide support for the scale application of sustainable packaging and recycled materials to provide support for sustainable packaging and large-scale application of recycled materials.

 View pdf
View pdf


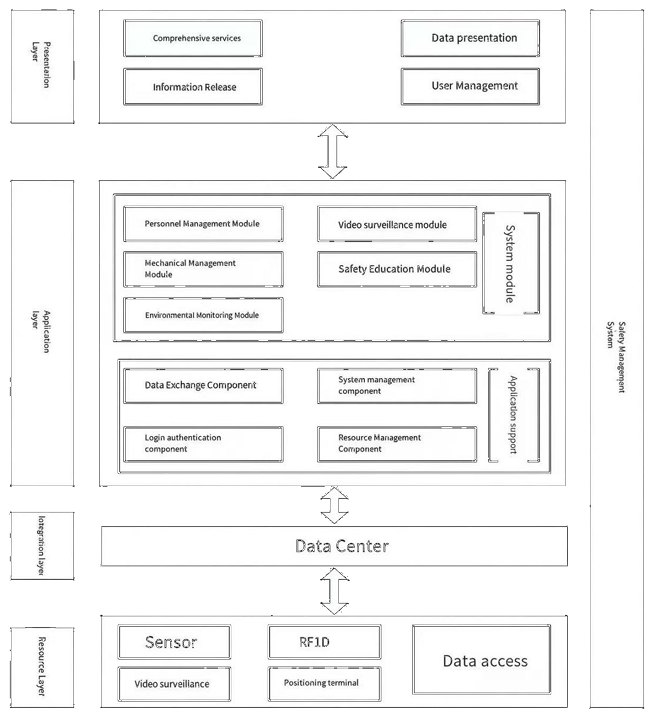
With the rapid advancement of urbanization in China, traditional construction safety management models struggle to adapt to complex environments, leading to frequent accidents. Smart construction sites, centered on IoT, big data, artificial intelligence, and BIM technologies, provide a new path for realizing the digital and intelligentization transformation of engineering safety management. This paper analyzes the research background and current status of smart construction sites, points out their deficiencies in system integration and in-depth Data Analysis, elaborates on key technical supports, and constructs a system framework covering the resources layer, integration layer, application layer, and presentation layer, aiming to improve safety, efficiency, quality, collaboration, and green construction. Case applications show that the system can achieve real-time perception and intelligent early warning, promote the transformation of safety management from post-accident accountability to pre-accident prevention, and reduce the accident rate by more than 30%. Finally, the future development of smart construction sites in terms of technology integration, algorithm optimization, cost control, and standard establishment is prospected. This research provides theoretical reference and practical guidance for the in-depth application of smart construction sites.

 View pdf
View pdf
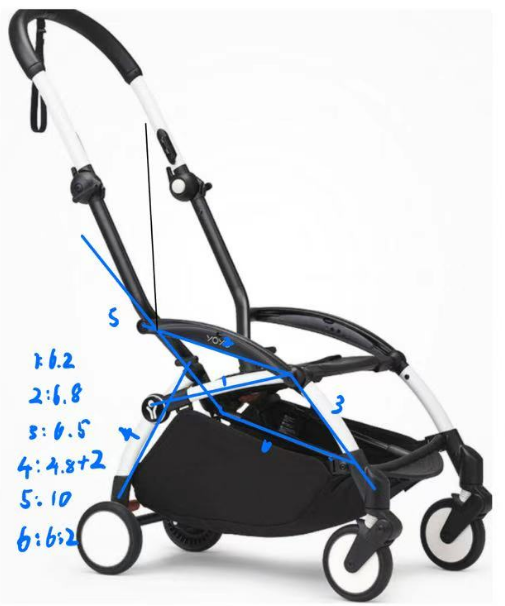



This report outlines the design, analysis, and future prospects of an innovative folding blackboard project inspired by the YOYO stroller mechanism. The project's goal is to make a writing surface that is light, easy to move, and structurally stable for classrooms with limited space. This design employs a single–degree-of-freedom (1-DOF) linkage to achieve compact folding and smooth deployment. We integrate kinematic analysis, SolidWorks simulations, and an initial prototype to connect theory with manufacturability, reporting folding ratio, stability indicators, and key trade-offs observed during iteration.

 View pdf
View pdf



