1. Introduction
In the age of the Internet, the global communications industry is developing rapidly, and smartphones have become a necessity in people's daily lives. Thanks to advances in communication technology and hardware, its use has long been more than just communication. In the current society, smartphones provide a great convenience for people's study, work, and life. In most work situations, a smartphone can help us to handle all kinds of work events, whether it is reading and sending a text or taking over as a carrier for online meetings. Therefore, with such a popular product market, major manufacturers and distributors are bound to devote many resources to carving up the limited market. In the Chinese domestic market, the competition is fierce, and brands are constantly updating their products in order to enlist users. Huawei, Xiaomi, OPPO, and VIVO, as the representatives of China's domestic mobile phones, are changing their product designs, marketing techniques, and end-user prices at a swift pace in order to adapt to the increasingly competitive market and the increasingly demanding consumer needs. However, due to the COVID-19 effects of globalization, most countries and regions of the world have fallen into a swamp of consumer depression. With the difficulty of ensuring stability in their daily lives, people tend to reduce their spending on non-essential consumer goods, and the renewal of smartphones is one of the weighty categories. According to data, global smartphone shipments fell by 11% in 2022, with loads in the Chinese market down 13.2% year-on-year [1]. Senior analysts at IDC China pointed out that the reasons for such a phenomenon are relatively uniformly known within the industry, including market saturation, longer replacement cycles, insufficient product innovation, and bottlenecks in technology development. The decline in revenue brought about by the epidemic has served to add insult to injury. In addition to the impact of the general environment, Huawei has been restricted by the US ban for 19 years and has lost its chip supply and Google license, causing a considerable loss of users. In the list of smartphone market share in 2022 published by IDC, Huawei has fallen out of the top five, while Glory, which is independent of Huawei, is ranked as high as second [2]. Based on this, this paper takes Huawei as an example and explores its means to improve consumer stickiness and breakthrough during the bottleneck period under the perspective of digital marketing.
The purpose of this paper is, based on the current smartphone industry, the development of bottleneck. This paper combines smartphone enterprise development status to the background and Huawei mobile phone business situation and dilemma for Huawei mobile phone to enhance customer adhesion, break through the development of smartphone bottleneck to provide referenceable practical suggestions. The significance of this paper is that Huawei, as a leading domestic communications company, has been severely hampered in its mobile phone business development by both external and internal environments. Through the research in this paper, it is hoped to help Huawei mobile phones improve their product competitiveness and sustain their growth in an unfavorable environment. This paper uses the review research method to provide a reasonable and effective integration and analysis of the theoretical and practical basis for the article through journal literature, news reports, and official data in order to effectively ensure the rationality and feasibility of the conclusions.
In the next part of the main analysis and discussion, the paper first discusses the current development status of smartphone companies and their business environment. Secondly, the paper discusses the current situation and dilemmas of Huawei mobile phones and finally discusses the means to improve customer stickiness and break through bottlenecks in Huawei mobile phones from the perspective of digital marketing.
2. Analysis of the Current Development of the Smartphone Market and the Business Environment
2.1. Current Smartphone Market Development
Figure 1: Top 5 smartphone vendors in China by market share in 2022.
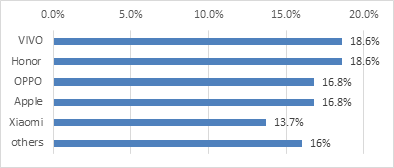
As shown in figure 1 the data shows that the top five mobile phone market shares in China in 2022 are 18.6% for Vivo, 18.6% for Honor, 16.8% for Oppo, 16.8% for Apple, and 13.7% for Xiaomi, in addition to 16% for others [2]. The company's reputation has been gradually built up in the x series and in the high-end product market, and its own Google has made it popular in foreign markets, with a reasonable online and offline layout helping it to take the top spot. Honor also has a good product and user base. Meanwhile, Honor is an independently operated brand, unaffected by the US ban, and its product line has been gradually improved after several years of development. Oppo has been building up its strength in self-research technology, especially in the mid-to low-end market share. Apple is still in fourth place with its heritage as a pioneer in the smartphone field, despite lower-than-expected shipments due to market discontinuation. Xiaomi's Redmi Redmi, a subsidiary of Xiaomi, was the main driver of Xiaomi's market share, with outstanding market performance. Huawei, on the other hand, has now dropped out of the top five in terms of smartphone market share in China due to a shrinking market share.
According to data from market research firm Canalys, the global smartphone market fell 12% year-on-year in the first quarter of 2023 due to a decline in revenue caused by the epidemic, resulting in a decline in user purchasing power, including a decline in productivity of some smartphones due to corporate shutdowns and other objective reasons, and is already the fifth consecutive quarter of decline. For the above data, some analysts said that the industry has predicted a decline in the first quarter of 2023, for the actual result is not a surprise. The macroeconomic situation makes it difficult for suppliers to invest and operate, and consumer appetite for purchases remains low, spurred by price cuts and promotions.
The slow pace of global smartphone development does not mean that the mobile phone industry has reached its "ceiling." For example, high-end models are still growing in the Chinese market, and according to market research firm Counterpoint Research, the share of high-end smartphone sales in China (with wholesale prices above RMB 3,500) will increase to over 26% by 2022 [3]. One of the key reasons why users need to replace their smartphones is because their existing devices do not meet their real-world needs, and high-end models often use the most advanced technology available to the brand and are adequate for the consumer's scenario.
2.2. Analysis of the External Business Environment of Smartphone Companies
On the economic front, this year's government work report points out that GDP will grow by 3% for the year 2022, with an average annual growth rate of 5.2% over the past five years and an increase of nearly 70 trillion yuan and an average annual growth rate of 6.2% over the past ten years, achieving medium to high-speed growth and moving towards high-quality development based on a high base. This indicates that the overall economic trend in China is positive. However, due to the epidemic that has hit the country over the last three years, most consumers have become more precise in their grip on consumption. Although the overall economic growth rate at the national level is more impressive, some consumers have adjusted their consumption strategies and placed their focus on investments in necessities or products that retain more value. Mobile phones, in general, are being replaced at a faster rate, and each year's on-time renewal seems to have a specific impact on personal finances. Therefore, both in terms of data and subjective analysis, the shift in national consumption will have an effect on the growth of smartphone manufacturers.
In terms of technology, with the progress of science and technology, by now, we have entered the 5G era, where everything is connected. At the same time, people's demand for communication products is also increasing; functional diversity and stable operation are the necessary conditions for the products. For a long time after the emergence of smartphones, the core components of China's smartphones were controlled by foreigners. In recent years, influenced by the international situation, domestic brands have realised the importance of technological independence and increased investment in scientific research, and the core technology of China's mobile phones have developed rapidly. For example, vivo in x series application of self-research chip v2 and equipped with Xiaolong 8th generation through the architecture upgrade into the power of the new track; in supporting equipment, vivo has the world's first 200w super flash charging, Oppo has also launched self-research chip - Mariana chip, Pantanal system, and the Andes intelligent cloud and so on The European Patent Office (EPO) has published a list of technologies for the year 2022. The European Patent Office has published a list of the top 25 Chinese companies in its 2022 Global Patent Index, with Oppo occupying one of the top 25 spots and ranking second among the four Chinese companies.
In terms of social environment, the 51st "Statistical Report on the Development of the Internet in China" released by CNNIC shows that as of December 2022, the number of Internet users in China reached 1.067 billion, an increase of 35.49 million compared with December 2021, and the Internet penetration rate reached 75.6%. Smartphones have developed to the point where not only are there a vast number of users, but also a wide range of uses, such as entertainment, shopping, payment, study, work, etc. A mobile phone can meet almost all daily needs. In addition, the development of patriotic themes in the school curriculum and the cultivation of national sentiments, as well as the growing recognition and support for national brands and national enterprises that are brave enough to take on social responsibility, have contributed to the development of domestic brands. In the case of Huawei, for example, the patriotism of Chinese consumers reached a corresponding peak due to the long-standing passive technology blockade and the emergence of the company's top management being detained overseas. With the national support for national products, the corresponding Chinese brands and national companies are experiencing an excellent "welfare period" of development.
2.3. Analysis of the Internal Business Environment
Firstly, Huawei holds a highly competitive brand resource value. Brand image is an intangible asset of a company. Huawei, for example, has a vision and mission to bring the digital world to every person, every family, and every organisation, and to build an intelligent world where everything is connected. Huawei launched the Fertile Ground Programme to provide a platform for the industry to learn and develop. It establishes an image of an open-minded, win-win enterprise to the outside world. In addition, the naming of many of Huawei's self-developed technologies is entirely Chinese, for example, the Hongmeng system, Kunlun glass, Kirin chip, Kunpeng chip, and other naming methods. These naming rules about products resonate more with domestic users than foreign brands [4]. In addition, Huawei, as a traditional enterprise producing telecommunication equipment, has strong strength in this field, and a report released by market research firm Dell'Oro Group shows that Huawei continues to lead the global telecommunication equipment field in 2021 and has a large lead over the second place [5]. Despite the US trade ban from 2019, Huawei's market share in global telecoms infrastructure has increased, partly due to a surge in demand for such facilities due to the New Crown epidemic, and also primarily facilitated by China's policy of accelerating the deployment of 5G networks in the sector [5].
Secondly, Huawei has a strong core competence in China. The core competitiveness of enterprises is reflected in rarity, inimitability, durability, profitability, and irreplaceability. For mobile phone companies, core competitiveness is usually reflected in core technologies such as chips. For Huawei, for example, according to an official report in 2021, R&D expenditure accounted for about 22.4% of annual revenue, and the cumulative R&D expenditure invested in the past ten years exceeded RMB 845 billion. Relying on its strong R&D team, it is a domestic leader in the field of chip R&D with its own system, with about 107,000 Huawei personnel engaged in research and development, accounting for about 54.8% of the company's total workforce as of 2021. As of approximately 31 December 2021, Huawei held a total of more than 45,000 validly granted patents worldwide [6].
3. Huawei Mobile's Business Dilemma and Current Corporate Business Strategy
3.1. Operating Difficulties
In recent years, Huawei was once without chips due to the intensification of trade friction between the US and China and the objective impact of various international situations [7]. Although Huawei has one of the more front-end technological research and development capabilities of any domestic manufacturer, this does not seem to compensate for the lack of access to major monopoly mobile phone parts. Huawei's latest high-end releases are still unable to use 5G mobile signals due to Qualcomm's chip outages. This has even become an irreparable disadvantage after the major manufacturers have launched phones supporting 5G communication in the 5G era. Furthermore, affected by the US ban, Google stopped licensing Huawei phones in 2019, which means that Huawei phones will not be able to use Android, as well as various types of Google ecosystem software. While this does not affect the vast majority of cases at home, the firm reliance on Google in foreign regions means that Huawei will lose a lot of overseas markets. According to market share figures, Huawei's market share in Europe fell to 16%, 16%, 14% and 12% between Q1 and Q4 2020, a year-on-year decline of up to 30%, 27%, 31% and 37%, respectively, and a drop in market ranking from second to fourth [5].
3.2. Product Strategy
The P series was born with the release of the Huawei P1 in 2012, and the Ascend Mate, which was released at CES in January 2013, was the start of the Mate series. Nova was released in June 2019. The P series and the Mate series have a more mature and stable design that favours professionals, and the price is relatively high, belonging to the high-end models, against Apple's PRO Series and Samsung's top flagship model of Android. The Nova series is known for its high sex price and youthful and fashionable design, mainly for the student population. The Nova series is known for its high price, youthful and stylish design and is mainly aimed at students [8]. Thanks to Huawei's strong R&D team, Huawei phones have a number of original technologies that greatly enhance the competitiveness of its products. Take Huawei's newly released P60 series as an example. Firstly, it can support sending and receiving BeiDou satellite messages so that it can get in touch with the outside world in the absence of periodic signals, ensuring the maximum communication function of the phone. Secondly, the ability to take pictures is one of the most important factors in attracting users, using its original technology to optimise shots in dark environments, giving the finished film purer colours and more decadent layers. Once again, the screen is durable with new materials that are ten times more resistant than ordinary glass. Finally, the folding screen phone, released at the same time as the P60 series, uses self-developed materials to reduce the weight and size of the body, greatly improving portability.
In addition to mobile phone products, Huawei also focuses on supporting the interconnection of cross-border products. Cross-border products involve the home sector, infiltrating Huawei products into users' daily lives. On top of this, Huawei has also launched more intelligent wearable products, such as the watch series and Talk Band B1. Huawei is in the process of continuous research and development, covering its products in more fields and realising cross-border operations. There is no shortage of people around who buy Huawei phones because they buy Huawei's wearable devices, so this is one of the effective measures to enhance customer stickiness.
3.3. Marketing Strategy
Firstly, Huawei sells products with free software. Specifically, the company offers several free software packages for its electronic products to increase the added value of its products and enhance the customer experience. One representative software is the "Changlian" app, which, in addition to making daily phone calls, relies on Beidou satellite messaging technology to contact the outside world in special situations. In addition, Huawei has gradually broadened its business scope to achieve cross-border connectivity, thereby increasing the brand's influence and awareness. Secondly, in terms of sales channels, Huawei generally adopts three approaches, one, online sales, with the Internet and online e-commerce platform cooperation such as Jingdong, Taobao, Tmall, etc., to give full play to the advantages of the online economy. Second, in offline shop sales, Huawei and a large number of physical shop dealers and large electrical sales mall cooperation; almost all large shopping malls have Huawei shops, and third, "Vmall" is Huawei's e-commerce platform, the platform provides Huawei mobile phones, tablets, accessories and a series of terminal products, for Huawei products to offer a one-stop shopping experience [8]. Based on the current online sales environment, advertising is one of the essential marketing tools. Huawei advertisements can be seen on shopping mall advertising screens, advertising areas in public transportation, TV programs, and other venues, and famous people are invited to endorse the products, effectively expanding brand awareness. [9]
4. Huawei Mobile Bottleneck Breakthrough and Customer Stickiness Enhancement Tools Under Digital Marketing
4.1. Product Optimization
In response to the lack of a 5G chip supply, Huawei launched 5G phone cases; some models with issues can use 5G signal but obviously cannot fundamentally solve the problem of 5G signal. In addition, Huawei has developed Huawei Mobile Services, or Huawei HMS, to replace Google GMS, but due to the short online time and immaturity of the technology, overseas recognition is low, and in the short term, it cannot completely replace or even form a competitive situation.
In the case that the application of 5G and GMS cannot be improved in a short period of time, the existing conditions can be optimised; for example, in terms of after-sales service, the current Huawei mobile phone can be replaced with a new one within 15 days from the date of purchase, and this time limit can be appropriately extended to one month to ensure that users can have a certain amount of time to use it. At present, Apple's mainland policy is 15 days to return the goods. Growth time can also form differentiated marketing and increase product advantages. In addition, in terms of product interconnection, can develop Huawei mobile phones and other brands of mobile phones with computer interconnection functions. Second, enhance product differentiation, such as increasing product segmentation variables, for women's palms are relatively more minor than men's to make adjustments to the phone size and screen layout. It also includes differences with the brand's inter-generational products. The new generation of products needs to make innovations in terms of technology level, hardware quality, and design to attract users to buy them. Thirdly, the price of Huawei's mid- to high-end models does not compare favorably with competitive products of the same type, coupled with the disadvantages of lacking 5G and Android licensing, so it is recommended that Huawei make appropriate adjustments to its prices, such as increasing the means and strength of concessions. Refer to Apple's and Microsoft's educational offers, give certain subsidies to specific groups of people, or use holidays to launch corresponding incentives.
Folding screen phones are an important direction of innovation for mobile phone manufacturers. Compared to traditional straight phones, folding screen phones have larger screens to meet the needs of consumers for large-screen phones. At present, Huawei is developing rapidly in the field of folding screen mobile phones, not only relying on self-research materials to make folding screen mobile phones that the straight phone is thinner and lighter, large screen taking into account the portability in terms of market share is far ahead. The article also points out that nowadays, the hardware configuration and functional experience of straight smartphones are in a bottleneck, and folding screens will become a new opportunity point for the development of the smartphone industry. Therefore, Huawei can continue to develop in the field of folding-screen mobile phones in the future [10].
4.2. Enriching the Means of Promoting Product Characteristics
Relying on the short video platforms that are prevalent today, the Huawei P60, for example, has advanced photography technology as one of its key selling points, but just listing professional data is not attractive to a wide range of users, and it is important to show users how to turn data into high-quality finished films in different environments. For example, inviting a famous director or photographer to shoot a short film with the P60, inviting a celebrity to participate in the shoot, using social media platforms to show the outside world that the product can be used to produce such excellent work, and inviting professionals to record instructional videos on how to operate in dark environments and other extreme environments. This is not only a break with the traditional celebrity endorsement approach but also transforms the data into more intuitive and vivid works, significantly increasing the appeal to users.
4.3. Promote Offline Experiences
In addition to online publicity, inviting users to the offline experience is also an effective means of publicity. Open an offline experience shop. The experience can include the interconnection function between Huawei devices, wearable devices trial, smart home display, and new technology experience. And encourage users to carry out reasonable forms of publicity online. When buying Huawei products can be given certain discounts or gifts. Not only can you achieve the purpose of publicity and promote the joint purchase of Huawei devices, but also make the users get the benefits, achieving a win-win situation for both sellers and buyers.
4.4. Enforcing Strict Channel Price Controls
In the domestic mobile phone market, there is a widespread phenomenon of opaque prices for all types of channels, except for direct shops and official online shops with fixed prices, while the prices of secondary dealers vary, adversely affecting the brand image and reputation of Huawei mobile phones. In response to this phenomenon, it is recommended that Huawei should strictly assess the channels and dealers, sign agreements, and divide the price difference between different platforms and regions with different promotional products or concessions to avoid consumer buying habits caused by price differences as much as possible.
5. Conclusion
Based on the current global smartphone market environment, this study provides recommendations for Huawei to improve customer stickiness and break through the bottleneck in three areas: product optimization, marketing enrichment, and promotion of offline experiences. Product optimization includes improving after-sales service, enhancing product differentiation and improving price concessions, while marketing enrichment is reflected in the use of social media platforms to showcase product advantages more intuitively and achieve promotional purposes.
The shortcomings of this paper are mainly the following two points. Firstly, this paper uses Huawei as an example to start the research and has less reference to other enterprises in the industry, which may lack the feasibility of the conclusions. Secondly, due to the limited access to industry and enterprise data and the relatively shallow knowledge of the industry, most of the recommendations made in this paper are qualitative in nature and not specific enough in practice.
In future research, firstly, it is recommended that the relevant background and data of major manufacturers be integrated to provide richer and more effective support for the conclusions. Second, enrich the research methods, such as adding interview methods and questionnaires and conducting interviews and exchanges with internal personnel of enterprises to obtain more comprehensive information and data. Thirdly, on the basis of enhancing professionalism and industry knowledge, the conclusion section should be expanded to improve the feasibility of the conclusions and provide more specific and accurate decision-making recommendations for enterprises.



