1. Introduction
A perfect highway system is an important measure of a country's national economic development, and also an important condition for achieving inter-regional economic collaboration. According to the Ministry of Transport's 2021 Transport Industry Development Statistics Bulletin data, by the end of 2021, the highway mileage was 169,100 km, an increase of 0.81 million km, and the national highway mileage was 11.70 million km, an increase of 0.4 million km. It can be seen that the development of China's motorways is on a rapid rise, and the demand for construction funds is very large, PPP (public-private partnership) is a new financing mode widely used in China, which is of great significance to the financing of motorways. Many experts and scholars at home and abroad have conducted in-depth research on the application of PPP mode in the field of infrastructure construction, but through extensive reading of literature, the problems that exist in the application of PPP mode in highway construction have not been fully analyzed and the suggestions given are not specific enough. In view of this, this paper summarizes the previous research on the PPP mode and presents other problems that may exist in this mode and gives specific measures to solve them.
2. The Definition of PPP Mode
2.1. Definition Given by Foreign Experts and Scholars
The PPP mode refers to a partnership between the private sector and public institutions through joint operation, information sharing and risk sharing in order to achieve mutual profitability [1]. Some experts and scholars also see the PPP mode as a partnership between private enterprises and local administrative officials to improve local conditions [2]. E.S.Savas considers them to be infrastructure projects of a private nature, with multi-participation by business and government [3]. Additionally, Tony Bovaird believes that the PPP mode is different from a transactional contractual relationship and is a new type of relational contract that should follow the principles associated with relational contracts [4].
2.2. Definition Given by National Experts and Scholars
The PPP mode is a partnership, financing, construction and operational management mode in which the public and private sectors enter into a full life-cycle relational contract for the provision of a public good or service and the realization of the public benefits of a specific public project [5]. Jia et al. argue that it refers to the process of cooperation between government departments and the private sector, enabling the private sector to invest resources to participate in the provision of public goods and services, bringing benefits to private enterprises while fulfilling government functions [6]. According to Zhang et al., PPP refers to an agreement or partnership established when the public sector and private enterprises jointly participate in the production and provision of public goods and services [7].
2.3. Definition Given by Domestic and International Organizations
The concept given by the United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR) is that PPP is an all-in-one institutionalized cooperation approach designed to solve some complex problems on the ground, while the European Commission gives the concept of a ppp mode as a partnership between government departments and private individuals aimed at providing public services that would otherwise be provided by the government. And the PPP mode is defined by China's National Development and Reform Commission as "a relationship of benefit sharing, risk sharing and long-term cooperation between the government and social capital through franchising, service purchase and equity cooperation to enhance the supply capacity and improve the efficiency of public goods and services".
As we can see from the above concepts, no matter foreign scholars, domestic scholars or various organizations, their concepts of PPP mode are not completely unified, but all definitions have some common features, one is the cooperation or contractual relationship between government public sector and private private sector, cooperation is the core of PPP mode; two is to provide public goods and services as the goal, we can regard it as the motivation of PPP mode. The third is the sharing of benefits and risks, which is an important feature of the PPP mode.
3. The Development Status of PPP Mode in the Financing of Highway Projects in China
The concept of PPP was first given by the private sector in Europe to build roads and has since taken shape in the UK [6]. China took the lead in introducing this concept in the 1980s and applied it in the construction of large-scale infrastructure such as railways, highways and waterways. According to the 2022 semi-annual report of the Center for Government and Social Capital Cooperation of the Ministry of Finance, by the end of July 2022, China's PPP management library had a total of 10,354 projects with an investment amount of 16.5 trillion yuan, of which the investment amount in the transportation sector was 585.8 billion yuan, accounting for 35.5%. This shows that the PPP mode is widely used in the field of transportation and the investment amount is huge, which has a very bright application prospect and can be developed with great space.
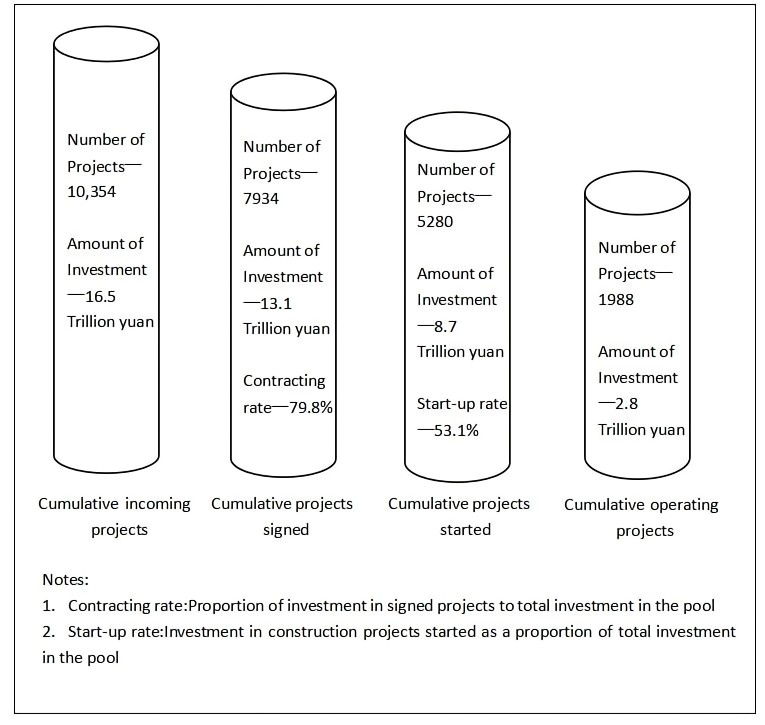
Figure 1: Accumulation of management pool since 2014.

Figure 2: Cumulative investment in projects in pool.
By analysing the data in the project list of the project management database of the Ministry of Finance PPP Centre's national PPP comprehensive information platform, it can be concluded that the investment amount of motorways in the transportation sector is generally large, for example, the three motorway PPP projects in Guangxi Province in November 2021 all reached more than 10 billion yuan, as well as the establishment of a motorway PPP project in Chengde City, Hebei Province in June 2022, with an investment amount of 14.149 billion. We can thus see the importance of the PPP mode for highway financing.
Table 1: List of projects included in the project management pool of the national PPP comprehensive information platform in November 2021.
Project Name | Amount invested | Primary sector | Secondary Sector | Province |
Guangxi Cenxi (Guangdong-Guizhou Border) to Daxin Highway (Nanning to Daxin Section) PPP Project | 144.56 billion yuan | Transportation | Highway | Guangxi |
Guangxi Gouyang (Xianggui Border) to Tian'e (Ha Lao) Highway (Jiang Yong to Guilin (Guangxi Section)) Phase I Project PPP Project | 107.02 billion yuan | Transportation | Highway | Guangxi |
Guangxi Wuzhou - Yulin - Qinzhou Highway (Yulin to Pubei Section) PPP Project | 178.57 billion yuan | Transportation | Highway | Guangxi |
Table 2: List of projects included in the project management pool of the national PPP comprehensive information platform in June 2022.
Project Name | Amount invested | Province | City | District |
Miyun District Rural Sewage Treatment Area 1 PPP Project | 2.42 billion yuan | Beijing | —— | Miyun District |
Miyun District Rural Sewage Treatment Area 2 PPP Project | 3.83 billion yuan | Beijing | —— | Miyun District |
Miyun District Rural Sewage Treatment Area 3 PPP Project | 4.42 billion yuan | Beijing | —— | Miyun District |
South Ring Road and Supporting Infrastructure Upgrading PPP Project in Wanquan District, Zhangjiakou City, Hebei Province | 10.69 billion yuan | Hebei | Zhangjiakou | Wanquan |
Chengde City, Hebei Province, China Danxi Expressway Keshketeng to Chengde Liaison Line (G1611) Jimeng Border to Weichang Section Project | 141.49 billion yuan | Hebei | Chengde | —— |
4. Advantages of PPP Mode in Highway Project Financing
China's highway has the characteristics of quasi-public, that is, it should be provided by the government public sector at the same time does not have the nature of profit, but because of the special nature of the highway project, its preliminary need for a large amount of capital investment to carry out land acquisition and demolition, construction equipment purchase, etc. If only rely on the government's financial input or bank loans, may lead to excessive financial pressure on the government, unstable sources of funding and other unfavorable circumstances in contrast to traditional financing modes, the PPP mode has the following three main advantages:
4.1. Effectively Solve the Problem of Funding Sources for Highway Construction to Ensure Smooth Implementation of the Project
In traditional highway project financing, funds mainly come from bank loans or direct government funding, but as bank loans are easily affected by factors such as national macro-control and increasing government financial pressure, the instability of these two main sources has gradually become greater, so highway projects can easily be forced to stop because of a break in the capital chain. However, the PPP mode is a good way to bring in social capital and provide a channel for highway financing, ensuring that the construction of highways will not be stopped due to a shortage of funds.
4.2. Reduce the Idleness of Social Capital and Facilitate the Flow of Funds Throughout Society
For highways, the capital flow required is very huge, and the traditional financing mode turns away private capital, leading to a large amount of private capital idle, unable to participate in the flow of funds for the whole society, which may further lead to problems such as currency devaluation, etc. Since the PPP mode has the government public sector and social capital as partners, to a certain extent, the risk is lower and a more stable return can be guaranteed, thus the PPP mode is able to attract social capital to join it.
4.3. A Reasonable Balance Between the Quasi-public Nature of Highways and the Profit-seeking Nature of Social Capital
China's highways are quasi-public goods, i.e. the government is responsible for providing them to the public, which is, in a way, one of the basic functions of the government, so it is also decided that highways cannot be profit-oriented, while private capital has the essential attribute of profit-seeking. On the one hand, private capital can provide sufficient financial support for the construction of highways, alleviating the financial pressure on the government and assisting the government in providing public goods; on the other hand, the government can provide financial subsidies and concessions for private capital so that private enterprises can receive more stable capital income, while government departments can exercise their power to supervise and control the higher revenue sections and impose certain restrictions on social investors. At the same time, government departments can exercise their supervisory and regulatory powers on the higher-yielding sections to impose certain restrictions on social investors, so as to avoid monopolistic management behaviour by social investors and thus ensure the quasi-public attributes of highways [8].
5. Major problems with the PPP Mode
5.1. Low Motivation for Social Capital Participation
Generally speaking, a large amount of capital needs to be invested in the early stages of a highway project to prepare for the start of construction, and due to the nature of highway projects as quasi-public goods, these funds can easily become sunk costs, and the opportunity cost loss is greater for social capital. In addition, the contract signed rarely takes into account the discounted income, net present value of the problem, if encountered with inflation, economic instability and other conditions, the investor's income will be difficult to protect, which will discourage private enterprises to participate in the enthusiasm. In addition, for small and medium-sized private enterprises, their risk resistance is poor, coupled with the current imperfection of the relevant laws and regulations. In the event of a breach of contract due to a change of government, etc., the interests of the business cannot be guaranteed, which leads to a low willingness of private enterprises to cooperate with the government. [9].
5.2. The Quality of the Work Cannot Be Guaranteed
Due to the construction unit's tradition of "heavy construction, light operation" and the essential attributes of profit-seeking enterprises, in order to obtain certain profits in PPP projects, they usually do not take strategies in the later operation of the highway, such as the development of a reasonable highway toll policy, but in the early construction to shorten the construction period, jerry-built materials, etc. to sacrifice the quality of the project, speed up the progress of the project in disguise to obtain profits. In addition, there is no corresponding regulatory department and laws and regulations to supervise and rectify, the quality of the highway is sometimes difficult to be guaranteed, which affects the operation of the use of the condition and even greatly increases the cost of maintenance afterwards.
5.3. State-owned Enterprises Make Up the Bulk of the Market, Making It Difficult for Small Private Enterprises to Participate
For government departments leading the construction of highways, the government is more willing to cooperate with large state-owned enterprises due to their more stable funding sources and higher credit ratings, while the national credit rating system for private SMEs is not perfect. But the purpose of this is contrary to the original intention of the PPP mode and cannot really solve the government debt crisis, instead it is just a different way to continue the government's financial pressure.
5.4. Revenue Calculation Metric Is Too Static, Making It Difficult for Companies to Secure Revenue
At present, most PPP project contracts often use static indicators to calculate the revenue of private enterprises, failing to take into account the impact of changes in the economic situation, and in the context of the current new epidemic, the global economic situation is on a downward trend, with more and more unstable economic factors, which is difficult for private enterprises to get steady benefits.
5.5. Lack of a Scientific and Rational Supervisory System Makes It Difficult to Carry Out Works Smoothly
Supervision is very necessary for the PPP mode. As the highway project is more professional and involves more processes, it is more complicated than other PPP projects, so there are more problems in carrying out supervision. Generally speaking, the supervision of highway PPP projects is carried out by several departments or institutions respectively, such as local development and reform committees for project creation, bidding, etc., local finance departments. In general, the supervision of highway PPP projects is carried out by several departments or institutions, such as the local development and reform commission for project creation and bidding, the local finance department for the budget of PPP projects, etc., while the quality inspection of the projects is more professional and generally left to third-party institutions. As a result, overstepping and lack of supervision often occur, which affects the normal conduct of the project.
6. Solution
6.1. Improve the Full Cycle of Project Operation and Management to Achieve Sustainable Project Income
For existing highway PPP projects, most of the contracts signed between the social capitalist and the government only cover matters related to pre-construction, and many buildings construction companies then focus on making profits during the construction period, resulting in a profit gap during later operation. In the post-PPP era, the entire project cycle, from construction to operation, should be taken into account in the profitability of the enterprise. For example, the government can take the project's post-operating plan as an important consideration when bidding for the project, so that private enterprises can pay more attention to the post-operating management income, which on the one hand improves the controllability of the whole cycle of the highway project and avoids the unreasonable toll policy after the opening of the highway later, and on the other hand makes the project's income cycle longer and increases the enthusiasm of social capital to join the PPP project.
6.2. Improve the Credit Rating of Small and Medium-sized Private Enterprises and Encourage Cooperation Between Private Enterprises and State-owned Enterprises
An important barrier to cooperation between the government and small and medium-sized private enterprises is the credit risk, as highway projects require a large amount of capital, and once the enterprise it cooperates with has certain risks in credit security and is unable to make continuous investment of funds, the progress of the highway project will be greatly affected. Therefore, on the one hand, professional rating agencies can be introduced to credit rating small and medium-sized private enterprises and use them as reference for project bidding, and on the other hand, the government can take the lead in pairing up private enterprises with state-owned enterprises with good credit ratings, so that they can jointly undertake the PPP project as partners, which can ensure the stability of the project's capital flow.
6.3. Introduce Dynamic Indicators to Measure Corporate Earnings and Ensure the Relative Stability of Corporate Earnings
The government should introduce appropriate dynamic indicators such as net present value in the PPP contracts to reduce this risk and stabilize corporate income, so as to attract more private enterprises to join the highway PPP projects.
6.4. Coordinate the Full Cycle of Project Supervision to Ensure the Smooth Running of the Project
Clarify the subject of the project. For example, for national key construction highways, the National Development and Reform Commission can lead the supervision work, and the relevant provincial and municipal departments can assist in the management. During the whole cycle of supervision, the division of responsibilities should be clearly defined, and the competent department should allocate personnel and coordinate responsibilities for each supervision process before the PPP project starts to ensure the scientific and reasonable nature of the whole project supervision cycle.
7. Conclusion
In summary, the current PPP mode plays a crucial role in China's highway project financing, which is of great significance in reducing the government's financial pressure and revitalising private capital. On the basis of achieving certain results, we should also see some practical problems with the mode, including the low enthusiasm of private capital participation, a certain degree of monopoly of state-owned enterprises and the difficulty of meeting engineering quality standards. Therefore, in the post-PPP era, the highway management unit should address the existing problems and adopt the mode of piloting first and gradually promoting to continuously improve the highway project financing system, so as to realize the steady and efficient development of China's highway construction. This paper lays the foundation for the study of the PPP mode and also provides guidance for the further development of the PPP mode in the financing of highway projects in China.



