Volume 4 Issue 2
Published on November 2025
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the total market value of final goods and services produced by a country in a year. This study attempted to find the best-fit Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) model for forecasting China’s GDP over the next five years (2025 to 2029). In this study, we collected historical GDP data for China from 1960 to 2024 from the World Bank. Using the Box-Jenkins approach, we examined the ACF and PACF plots, performed stationarity tests, and tested several models using the AIC criterion. We determined ARIMA(1,2,1) would be the best model to fit the data. We then used the fitted model to forecast the following five years for GDP in China, demonstrating the capabilities of ARIMA as an effective forecasting model.This study provides valuable insights for policymakers and economists in planning sustainable economic strategies for China's future development.

 View pdf
View pdf


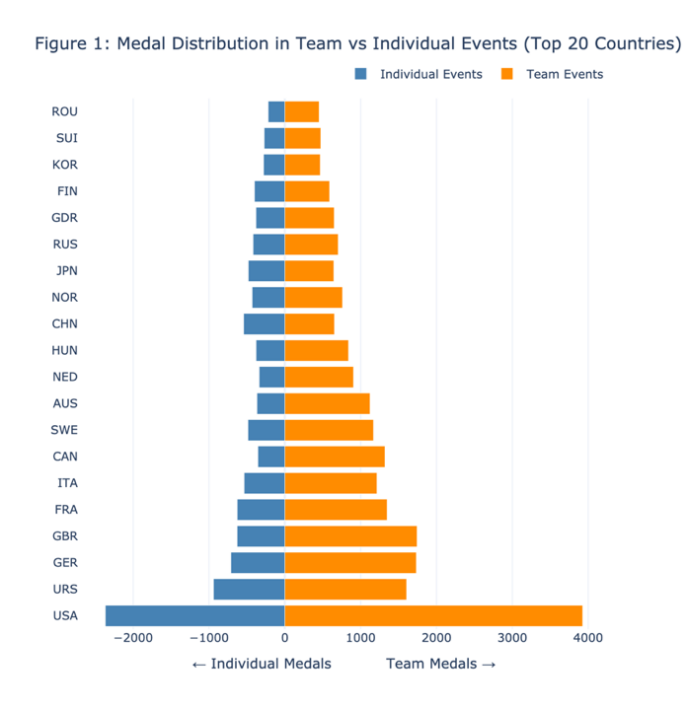
Understanding how countries allocate resources and formulate strategies between team and individual sports in the Olympic Games is crucial for uncovering broader institutional and cultural dynamics. This study, based on a visual analytics framework, explores the structural patterns of Olympic medal distribution over a century. Leveraging a large-scale athlete-event dataset, we construct three interrelated visualizations: 1) a symmetrical bar chart comparing national performance in team and individual sports; 2) a structural clustering model based on medal distribution, combining principal component analysis and K-means clustering to identify pattern types; and 3) a dynamic timeline visualization of the evolution of Australia's performance in team sports. The results reveal systematic differences in national strategic preferences, ranging from "team dominance" to "balanced" performance, and identify four structural archetypes of team sports success. Time series analysis further demonstrates how individual countries adjust their strategic priorities across Olympic cycles. The research suggests that medal structure is not simply a result of competitive performance but is also influenced by long-term strategic planning and institutional configurations. This study offers a new data-driven perspective for cross-national sports comparative analysis and demonstrates the unique value of visual analytics in revealing the underlying structure of global competitive systems.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper proposes an intelligent decision support framework that integrates geographic information system (GIS) and building information modeling (BIM) to optimize supply chain operation in smart building design. This framework uses intelligent algorithms to synchronously balance procurement paths, supplier selection, and construction procedures, thereby minimizing embodied carbon emissions and full life cycle costs. Taking a mid-level office building as an example, under the principle of balancing environmental and economic objectives, this method reduces embodied carbon by 18% and lowers life cycle costs by 12% compared with the traditional plan. Scenario simulation further reveals a controllable balance of carbon costs: up to 25% carbon emission reduction (with a 9% cost increase), or 18% cost savings (with only a 4% carbon emission increase). Stability tests show that when price and emission parameters are perturbed by ±10%, the fluctuation range of the optimization scheme remains at ±2%. The achievements demonstrate the potential of AI-driven spatial analysis technology to guide sustainable procurement, logistics optimization, and material selection. Subsequent research will integrate real-time data streams with renewable energy factors to support dynamic reoptimization.

 View pdf
View pdf


The Boston housing dataset is one of the significant tools used to examine the influencing factors of housing price. Meanwhile, housing price prediction is crucial for government regulation, business decision-making, and individual homebuyers. Existing studies fall short in balancing model interpretability, computational efficiency, and generalization ability. Hence, this study, based on the Boston housing dataset, focuses on the prediction of the median value of owner-occupied homes (MEDV). It constructs three models, including linear regression, decision tree regression, and Bayesian regression, and evaluates their performance using mean squared error (MSE), mean absolute error (MAE), and the coefficient of determination (R2). It examines the effects 13 features, including per capita crime rate by town (CRIM) and average number of rooms per dwelling (RM) on MEDV. Furthermore, it trains and visualizes the results of each model. The results show that decision tree regression achieves the highest R2, effectively capturing nonlinear relationships but being prone to overfitting. Linear regression and Bayesian regression perform better in terms of MSE and MAE; the former is simple in structure and fast to train, while the latter can output probability distributions to assess uncertainty. Each model has its strengths, and the choice should depend on the application scenario. The limitations related to dataset timeliness and the lack of extensive hyperparameter tuning are acknowledged, providing useful insights for housing price prediction research and practice.

 View pdf
View pdf


The intrinsic nonlinearity and non-stationarity of financial time series create major challenges for traditional forecasting approaches. By virtue of its strengths in non-parametric modeling and feature selection, Random Forest (RF) has developed into a key methodology in financial forecasting. Nevertheless, prior research has focused mainly on applications, with limited attention to methodological limitations. This paper explores the application of RF in stock price and volatility prediction, highlighting their strengths and identifying key challenges to facilitate progress in next-generation intelligent financial forecasting systems. Based on a literature review and comparative analysis, it synthesizes the application of RF in feature engineering, task definition, and model optimization, and proposes a “threefold challenge” framework encompassing theoretical memorylessness, applicational static nature, and practical complexity. The results indicate that RF is effective in addressing feature lags and integrating multi-source information like realized and implied volatility, yet it exhibits notable constraints in modeling long-term dependencies, responding to concept drift, and handling the costs of optimization and deployment. Future work may emphasize extending temporal memory through hybrid models with deep learning, enabling adaptive responses to market shifts, and improving transparency and trust with Explainable AI (XAI).

 View pdf
View pdf


In recent years, with the rapid growth of data scale and the increasing complexity of statistical models, traditional parameter estimation methods have encountered new challenges. The continuous development of parameter estimation techniques aims to improve accuracy and computational efficiency to meet practical needs in complex environments. This paper investigates the fundamental theories and major methods of parameter estimation, with particular emphasis on the underlying concepts, evaluation standards, and application frameworks in statistical models. By presenting the three core methods, namely Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE), Method of Moments (MoM), and Bayesian Estimation, this study analyzes their derivation logic, theoretical properties, and applicable scenarios. Furthermore, it explores computational bottlenecks in high-dimensional Bayesian methods, the trade-off between subjective and objective prior selection, and the emerging trend of hybrid approaches based on empirical Bayes and regularization strategies. The results reveal both the commonalities and distinctions among the methods with respect to consistency, efficiency, and computational complexity. Besides, the potential of artificial intelligence to boost computational efficiency and enable more flexible, high-dimensional modeling in parameter estimation is emphasized, providing useful insights for both theoretical research and practical applications.

 View pdf
View pdf


This article explores the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in the field of e-commerce logistics and uses Amazon, a global e-commerce giant, as a case study for analysis. The article analyses the application of AI in various aspects such as warehouse management, logistics distribution, supply chain collaboration, sales forecasting, and inventory optimization. It reveals how Amazon has enhanced its overall operational efficiency through intelligent means. Additionally, it discusses how AI can empower e-commerce platforms, consumers, and third-party sellers through personalized recommendations, virtual try-on, and shopping assistance functions. Using case study methods and secondary analysis of Amazon's public materials, industry reports, and academic literature, this article reviews Amazon's strategies based on AI technology and its achievements, as well as the challenges it has faced, such as issues related to information systems. Finally, this article summarizes the transferability of Amazon's AI technology strategies, analyses the strategic importance of AI, and provides recommendations for the industry and regulation.

 View pdf
View pdf


The pace of AI integration into organisational leadership is revolutionising decision-making around everything from hiring to performance measurement. This transition offers unprecedented efficiency but brings major human and operational challenges. This article examines the key factors obstructing AI adoption to date, including worker struggles with AI explainability, prevalent opacity, and compounded resistance due to hierarchical corporate cultures. Such problems can result in trust issues, ethical questions, and workplace negativity. In this respect, we outline a multi-faceted framework of design solutions which supports responsible and effective AI integration. The strategies include technical approaches such as Explainable AI (XAI) for understanding decision-making, strong communication and training activities, the construction of emotionally supportive AI systems, and the development of a participatory organisational climate. We contend that transcending the limitations of AI deployment will involve more than simply technological remedies, but necessitate a consideration of the deep human and cultural aspects of technological change.

 View pdf
View pdf


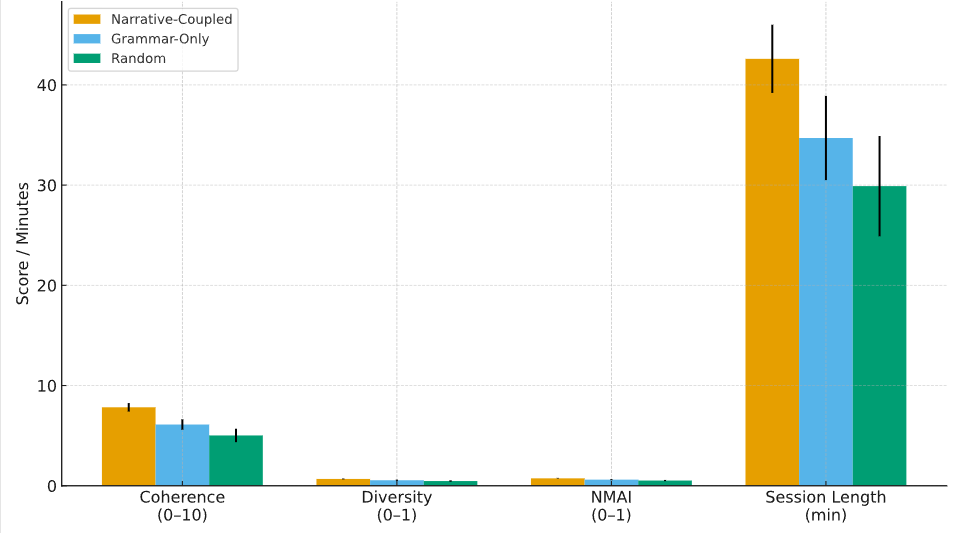
In game design, how to balance narrative coherence and procedural level generation has always been a difficult problem. This paper proposes a method that can automatically extract playable narrative units from story texts and combine them with dynamically generated levels. This method relies on deep semantic parsing, structured segmentation and playability constraints to decompose narrative text into atomic fragments that can be transformed into interactive environments. The system design is divided into two stages: In the first stage, narrative extraction is completed through dependency relationship and discourse analysis; The second stage achieves adaptive level generation by means of constraint-driven grammar and reinforcement feedback. The experiment was based on 124,600 narrative samples from mythological, fantasy and contemporary interactive novels, generating 19,420 independent narrative units and 1,250 levels. Compared with the random concatenation and grammar branch methods, this method significantly improves in narrative coherence, diversity and playability. Specifically, the average coherence score reached 7.83 ± 0.42, which was significantly higher than 6.11 ± 0.51 of the Grammar-driven method. The narrative-mechanism correspondence index reached 0.74 ± 0.03, exceeding the current benchmark. The overall results show that the combination of narrative extraction and procedural generation can not only maintain the integrity of the story but also provide a feasible direction for the flexibility and scalability of the game.

 View pdf
View pdf


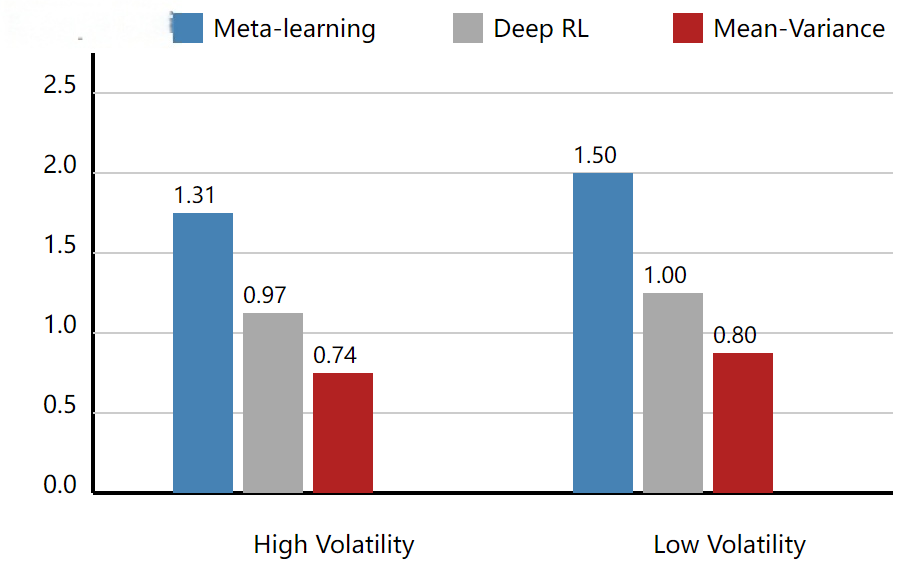
The high-frequency futures market exhibits high volatility and frequent institutional changes, which poses significant challenges for portfolio optimization. Traditional techniques such as the mean-variance model and risk equalization tend to show decreased returns and increased risks in such non-stationary markets. To address this challenge, an online portfolio optimization framework based on meta-learning was proposed. This framework incorporates cross-market and cross-period experiences into parameter adjustments, enabling it to quickly adapt to new institutional environments. Minute-level futures data from the Chicago Mercantile Exchange, New York Mercantile Exchange, and Shanghai Futures Exchange from 2019 to 2024 were used, and the market states were labeled using the Markov switching model through the rolling window method. Comparative experiments were conducted with mean-variance optimization, risk equalization, and deep reinforcement learning benchmarks. Empirical results show that the proposed framework outperforms the benchmarks in terms of excess returns, Sharpe ratio, and maximum drawdown in most cases, and has a faster convergence speed and stronger generalization ability in high-volatility institutional environments. The conclusion drawn from these results is that meta-learning is an effective method for solving portfolio optimization problems in non-stationary markets, providing theoretical support and empirical contributions for high-frequency quantitative trading and asset pricing research.

 View pdf
View pdf



