1. Introduction
An obvious and shared commonality that could be found among top professionals in different fields is that they all have regular workout habits. Examples of this statement could be easily listed, such as Warren Buffet, Richard Branson, Barack Obama, etc. There are many researchers, scholars and journalists that are always trying to find the common characteristics among successful people, trying to figure out the recipe for success. However, the relationship between exercise and investment chances for entrepreneurs has not been examined. In this study, the definition of success is defined and limited in the venture capital field, which refers to whether the chance of the entrepreneur getting an investment would be high or low.
2. Literature Review
In Goldsby and Kuratko's work, the study investigates the exercise regimes of 366 small business owners, as well as the link between exercise frequency and the company's sales and the entrepreneur's personal goals [1]. This study specifically looks at the association between two forms of exercise—running and weightlifting—and sales volume, extrinsic incentives, and intrinsic pleasures. Running is favorably connected to all three outcome variables, while weightlifting is positively related to extrinsic and intrinsic pleasures but not to sales. The key research question was: Are entrepreneurs who follow a fitness program of strenuous exercise more effective at achieving goals as stated by intrinsic and extrinsic rewards? They believed that investigating the effect of exercise in entrepreneurial success is critical due to the high time restrictions and stressful situations that small business owners face. With personal wealth at stake in the operation of a small business, there may be a trade-off between exercise and time spent operating the firm. Simply said, time spent exercising is time not spent operating the business. Furthermore, bigger companies—the source of samples for previous research on exercise—can afford the luxury of wider coverage of job responsibility, better access to on-site fitness equipment, and more financial resources and corporate relationships for granting access to health club memberships. Smaller entrepreneurial enterprises, on the other hand, are less likely to be able to afford such facilities.
Kim discussed the impact of entrepreneurial fitness, dynamic capabilities, and innovative activities on business success [2]. A survey of small and medium manufacturing enterprises in Korea was conducted and evaluated, yielding the following research results. First, the fitness of entrepreneurship and dynamic capabilities, the fitness of dynamic capabilities and innovation activities, the fitness of entrepreneurship and innovation activities, and the fitness of dynamic capabilities and innovation activities all have a significant impact on business performance. Second, all three factors' fitness have a considerable beneficial influence on performance. Additional route analysis reveals that dynamic capacities and innovative activities play a role in mediating the relationship between entrepreneurship and firm performance. The findings suggest that not only does each of the entrepreneurship, dynamic capacities, and innovation activities have a good influence on business success, but that the three characteristics working together have a synergistic positive effect on business performance.
"With the concern regarding COVID-19 and physical health, I've been directing many of those anxieties into keeping a good workout and food regimen," says Christine Nguyen, Founder and CEO of Limitless Foundation [3]. Working out provides me with a much-needed vacation from screens since I spend anywhere from 7 to 15 hours each day in front of one. I would never find the time to take care of my physical health and work out if I didn't have an exercise program."
In Zoran's practical study, the team began reducing extra fat, gaining muscle mass, sleeping better, and feeling better overall after three months of training. As a result of all of this, experiment participants are more enthusiastic at work and more focused on completing their duties. Also, they progressively transitioned from cheering one another on at the gym while completing workouts to supporting each other while conducting regular duties at work. It was challenging for them at first since it was a lifestyle adjustment. A personal achievement for the researcher is that all of these folks have begun to individually research healthy behaviours and how to incorporate them into their life. Participants have learnt to better manage their time via training, and they are more tenacious in completing things. Sport has also brought individuals from various cities together. All of these folks who have altered their workout routines in the previous few months, from the researcher's perspective, are more proactive at work and in their personal life.
Through the literature review, many commonalities could be found between running business and workout habits. As everyone knows, fitness requires a lot of self-control and persistence. The thing is the same for running businesses.
3. Methodology
Our goal for this study was to test whether sharing sports habits of entrepreneurs promotes the investment intention of the venture capital and do investors with different gender would have a different attitude towards the standpoint.
3.1 Participants
We recruited a sample of 110 Chinese employees working in the financial investment industry. The average age and tenure of them are 29 (SD=3.36) and 5.7(SD=2.44), respectively. Among the participants, 42.7% are female, and 97.28% hold a degree above Bachelor. We provided each participant a 3-dollar incentive for their experimental completion.
3.2 Manipulation
We manipulated the entrepreneurs disclosure of their sports habits by randomly presenting one of two entrepreneurial pitch videos. These videos contained three parts- including entrepreneurial motivation, project description, and introduction of the entrepreneurial founder. In the sport habits disclosure condition, the entrepreneurial founder shared he had regular daily exercise habit beyond giving a decent self introduction that involves his previous entrepreneur experiences and his educational background. By contrast, in the control condition, the entrepreneurial founder only gave a decent self introduction that involves his previous entrepreneur experiences and his educational background. All other information about the entrepreneurial founder profiles and projects was equivalent across conditions.
3.3 Measures
Perception of resilience. We measured whether participants thought that the entrepreneur in the video is resilient (1= Strongly disagree; 5 = Strongly agree) from the scale developed by Luthan, F., Avolio, B. J., Avey, J. B., &Norman, S. M. [4]. Items included, “He can handle the difficulties of starting a business”, “He can handle the pressure of starting a business in his stride”, “He will not be overwhelmed by the setbacks of entrepreneurship”, “He is comfortable with the responsibility and pressure of starting a business”, “He will not be discouraged by the difficulties in starting a business”, and “When faced with setbacks in entrepreneurship, he can quickly move on” (α = xxx).
Investment intention. We assessed the investment intention by asking the participants whether they would invest their money to the entrepreneurial project (1= Strongly disagree; 5 = Strongly agree) from the scale developed by Septyanto, D., Sayidah, N., & Assagaf, A. [5]. Items included, “You invest in it out of faith”, “You invest in it for further development”, and “You invest in it for increasing wealth” (α = xxx).
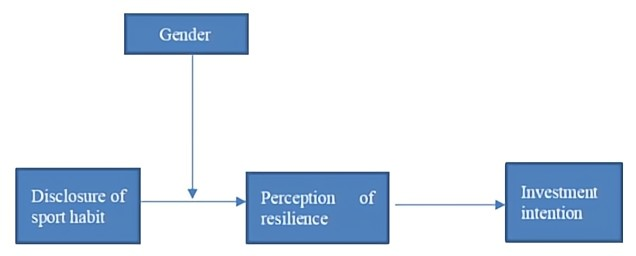
Figure 1: Gender: close to stereotype literature stereotype theory.
3.4 Research Hypothesis
In this study, we constructed the following two types of models:
H1: The exercise behavior of entrepreneur affects the investors' perception of resilience.
H2: The investors' perception of resilience affects their investment intention (Shworth, 2015).
4. Processing of Data
We would divide the data by gender of responders then process the data and review the outcome separately. For each data table, take out the variable sport habit, perception of resilience, and investment intentions. Use SPSS to find the correlation coefficient between the sport habit and perception of resilience, and the correlation coefficient between perception of resilience and investment intention.
4.1 Reliability and Validity Test of Questionnaire
The degree to which random error is excluded from a survey value is known as reliability. The investigation is entirely trustworthy if the random error is zero. The reliability coefficient can be used to illustrate reliability in reliability analysis results. The reliability of the questionnaire increases with the reliability coefficient. When the reliability coefficient is between 0.70 and 0.80, it indicates that the questionnaire we prepared has strong dependability and can more accurately reflect the sample's data. When the reliability coefficient is between.80 and.90, it means that the questionnaire has excellent dependability. The Cronbach's alpha coefficient is used in this case.
The degree to which a measurement tool can accurately measure the trait it is designed to measure is referred to as validity. The more accurately our measurement results reflect the traits we are attempting to gauge, the higher the validity. Here, we use the construct validity test to evaluate the questionnaire that was created. The level of correspondence between a specific structure reflected in the measurement results and the measured value is referred to as construct validity. Factor analysis is the approach used in construct validity analysis.
5. Discussions
5.1 Exercise and Resilience
Understanding resistance to brain illnesses, often known as brain or cognitive reserve, has received more attention. Physical activity has been identified as a significant protective element for the development of resilience. Exercise has been shown to have several beneficial impacts on the brain. As a result, doing exercise is a crucial tool for influencing neurodevelopment and shaping the adult brain to respond to life's difficulties. Exercise intervention has been linked to cognitive enhancement and stress resilience in people and animal models, among other benefits. As a result, an increasing number of studies have shown that exercise not only heals or decreases cognitive deficiencies by increasing neuroplasticity and cognitive reserve, but it also counteracts brain disease [7]. Physical activity has a good impact on resilience since it can elicit favorable physiological and psychological changes, defend against the consequences of stressful situations, and prevent or decrease the effects of numerous neurological illnesses.
5.2 Benefits of Workout
Regular exercise practice has benefits that extend beyond physical well-being. Fitness and mental health are inextricably linked, and exercise frequently increases energy, attention, motivation, and general happiness. There are several scientific publications that demonstrate how many benefits physical exercise and sports provide to the human body. A sound mind in a sound body. Exercise increases happiness while decreasing worry and stress. Primarily because it induces the production of the chemicals serotonin and norepinephrine, which help to alleviate sadness and create a sense of well-being. Exercise develops the brain and increases memory and thinking abilities. It increases life expectancy, improves skin health, strengthens muscles and bones, improves sleep quality, boosts metabolism, and boosts team spirit.
There are many benefits brought by doing exercises regularly. Firstly, exercise increases energy levels. When doing exercises, the body releases endorphins, serotonin and dopamine, which are usually referred to as happiness hormones. Exercise improves blood circulation and strengthens the heart muscle. This makes it easy for the body to produce energy. Besides, exercising boosts creativity and concentration. People could use exercise as a detachment strategy which allows them to separate themselves from daily troubles and focus on something entirely different for a short period of time, and that is something one could sense is striving to improve oneself. Another advantage of exercising is that persons who exercise tend to have fewer sick days and experience fewer injuries in everyday life. Employees who participate in some sport have a 14% increase in net value for firms when compared to employees who do not participate in any sport. People who exercise frequently - on average three times per week - have more self-confidence and are happier with themselves, which means they are often more focused at work.
5.3 Resilience and Investment
Being resilient may be required to display in an entrepreneurial attitude. Several studies have found that resilient people are more likely to start new firms, take over existing ones, and pivot their operations amid a crisis like the COVID-19 epidemic [8]. Psychological resilience is also linked to a variety of positive outcomes, including business success [9]. Resilient entrepreneurs have better mental health because psychological resilience helps cushion them from the daily stresses of business. Resilient entrepreneurs are also more likely to learn, innovate, demonstrate transformative leadership, and be happier than those who lack psychological resilience. Resilience is also linked to objective and subjective evaluations of corporate success. One study discovered that portraying personal resilience in crowdfunding campaigns leads to improved financial success, while another discovered that psychological resilience increases the likelihood of venture survival substantially [10].
Any free-market economy relies on entrepreneurship. Globally, small and medium-sized firms account for nearly 90% of all businesses and employ more than 50% of the workforce. They also provide around 45% of the gross domestic output (GDP) [11]. However, entrepreneurs confront several threats to their existence, including financial insecurity and market uncertainty. Surprisingly, about half of all new businesses fail within the first five years [12]. In a difficult environment, entrepreneurs' psychological resilience is a particularly critical personal resource and competitive edge. Hence, from the discussions above, no wonder investors pay special attention to entrepreneurs' potential resilience and count this character as one of the key considerations of whether to make the investment.
What most entrepreneurs don't realize is that maintaining mental health is like filling up your car with gas. Too many entrepreneurs wait until their cars are full of smoke before stopping to fill up. The problem with this is that the car stalls if it encounters an unexpected curve or roadblock. Worse, it could permanently damage the engine. The coronavirus pandemic has had a long-lasting impact on economic conditions around the world. The mental health of entrepreneurs is not only for their own business but also for the business to survive the crisis and move to long-term prosperity. Research shows that 72 percent of entrepreneurs will face mental health problems, and almost the same percentage are not currently receiving treatment. In situations of prolonged uncertainty, mental health distress at the founder level can lead to instability and a lack of trust in leadership. Leaders often fail to create community Spaces, belonging and play Spaces -- critical to individual and company resilience. This obsession at the top has a negative impact on morale, retention, incentives, performance, productivity, and output.
6. Conclusion
The study starts with two roadshow videos and by watching either one of the videos, participants are going to answer a questionnaire based on the impressions that the entrepreneur provided during the roadshow video. After statistical analysis of 110 respondents, it could be found that whether an entrepreneur has regular workout habit provide different impressions for investors in the venture capital field. The chance of having a better impression is related to having regular workout habits. Also, female investors tend to have higher sensitivity in this correlation, which means that female investors tend to provide funds for workout-habit owners higher probability of investment chances. The study is confined to sample size and future study is expected to provide more findings and information.



