1. Introduction
With the rapid development of digital technology, FinTech, as an emerging field, is profoundly transforming the operational models and business environments of traditional financial services. FinTech directly relies on technological innovations such as big data, cloud computing, the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, and blockchain. The application of new technologies promotes the automation, intelligence, and personalization of financial services, significantly reducing transaction and risk costs, fostering transaction mutual trust, and improving financial security [1]. The rise of FinTech not only meets consumer demand for efficient and convenient financial services, but also promotes innovation and competition in global financial markets. In recent years, the scale of the Fintech market has continued to expand, attracting a large amount of investment and becoming an important driving force for economic development.
This study aims to explore the concept, market size, participants, and regional development status of FinTech, with a particular focus on the characteristics and trends in North America, Europe, and Asia. At the same time, the research will also focus on the challenges faced by Fintech in its development process and offer insights into future developments. To achieve these goals, this study adopts a combination of literature review and case analysis to deeply analyze the current status of FinTech development across different regions.
This article will examine the current state of FinTech in various contexts and its role in the global financial system. The significance of this study lies in providing valuable insights for policymakers, industry participants, and academics, helping them understand the dynamic changes in FinTech and offering theoretical support for future innovation and development, ultimately promoting the sustainable development of the financial industry.
2. Concept of Financial Technology
FinTech refers to the industry that utilizes technological means to improve and automate financial services and processes.
It integrates financial services and modern technology, including Internet, mobile devices, blockchain, big data, artificial intelligence, and other technologies, aiming to improve the efficiency of financial services, reduce costs, and enhance user experience. The scope of FinTech applications is extensive, covering multiple fields such as payment, lending, investment, insurance, asset management, among others.
The core concept of fintech is to meet the financial needs of consumers and businesses through innovative technological solutions. For example, mobile payment applications enable consumers to conveniently conduct online and offline transactions, while P2P lending platforms reduce borrowing costs and increase liquidity by directly connecting borrowers and investors. In addition, the introduction of blockchain technology has provided greater transparency and security for financial transactions, which has driven the development of digital currencies and smart contracts. The application of blockchain technology provides a new perspective for small and medium-sized enterprises to overcome financing difficulties. By optimizing blockchain applications in small and medium-sized enterprises, these companies are expected to achieve significant achievements in FinTech, both in China and globally [2].
In recent years, the development of FinTech has significantly accelerated, especially with the continuous expansion of investment and market size worldwide. Fintech not only presents challenges to traditional financial institutions, but also provides enormous opportunities for startups and emerging markets. With continuous technological advancements of and evolving consumer demand, fintech will continue to play an increasingly important role in the global financial system.
The scale of the fintech market has shown a rapid growth trend in recent years. According to reports from industry research institutions, the global fintech market is expected to reach trillions of dollars in the coming years. In the era of FinTech 3.0 (2008 to the present), based on Internet technology, it connects multiple financial scenarios, expands the boundaries of artificial intelligence, blockchain, big data, and inclusive financial services, and accelerates the support and development of digital finance for the real industry [3]. Especially in the fields of payment, lending, and investment, the application of financial technology is significantly changing the market landscape.
The participants in the Fintech ecosystem include startups, traditional financial institutions, technology companies, investors, and regulatory agencies. Start-up companies typically challenge traditional financial institutions with innovative products and services, while the latter adapt to this changing market environment through collaboration and investment.
3. Current situation of regional development
Financial technology (FinTech) is evolving differently across various regions, each showing unique characteristics and trends. The following is an analysis of the current situation in the three major markets: North America, Europe, and Asia.
North America, especially the United States, is a pioneer market for global fintech. In terms of the current situation, numerous fintech startups and mature enterprises have excelled in fields such as payments, lending, and wealth management. For example, companies like PayPal, Square, and Stripe are leading the trend in digital and mobile payments. In addition, many traditional financial institutions actively collaborate with fintech companies to enhance their technological capabilities and service efficiency. In terms of future prospects, the North American fintech market is expected to continue attracting significant investment, particularly in the application of artificial intelligence and blockchain technology. As consumer demand for digital services continues to increase, fintech will further drive innovation and transformation in financial services.
Europe’s FinTech market is also thriving, especially in countries such as the UK, Germany, and France. In terms of current situation, London in the UK is renowned as a global fintech hub with numerous startups and investors. European fintech companies have made significant progress in regulatory technology (RegTech), payment solutions, and digital banking. For example, companies such as Revolut and TransferWise (now Wise) have performed outstandingly in cross-border payments and digital banking services. In the future, with the continuous improvement of digital finance regulations by the European Union, the European market will become more standardized. This will provide a clearer operational framework for fintech companies and may also promote cross-border cooperation and expansion.
Asian is one of the fastest-growing markets for fintech, especially in China and India. In China, mobile payment (such as Alipay and WeChat payment) has been deeply rooted in the hearts of the people, promoting the digital transformation of the whole society. In addition, India's digital payments and financial inclusive services (such as the UPI system) are also rapidly developing. Digital technology is effectively addressing existing industry challenges, reducing search and matching times between financial service providers and consumers, improving service efficiency, effectively reducing financial institution costs, and greatly enhancing the accessibility of financial services [4]. In the future, with the improvement of Internet penetration and the widespread use of smart phones, the Asian FinTech market is expected to continue to grow rapidly. Especially in emerging markets such as Southeast Asia, fintech will provide more financial solutions for underserved populations and promote comprehensive economic development. However, Despite Hong Kong’s position as one of Asia’s leading financial centers and its consistent ranking as the third-largest international financial hub, it still faces a considerable gap compared to the top two financial centers and is increasingly challenged by other emerging international financial centers [5].
4. Challenge
At present, the development of financial technology faces many challenges. In this chapter, I will discuss from four aspects: regulatory compliance, data security and privacy, market competition, and technological risks.
4.1. Regulatory compliance
Fintech companies face complex regulatory environments in different countries and regions. Financial regulatory policies and laws vary among countries, and Fintech companies need to ensure that their products and services comply with local laws and regulations. This compliance not only involves areas such as payment, lending, and investment, but also includes aspects such as data protection and anti-money laundering. The core of the financial regulatory system lies in the allocation of regulatory power, which is directly reflected in the division of authority between central and local governments, and regulatory implementation mechanisms [6]. For startups, compliance costs and complexity may become obstacles to their development. The regulatory sandbox model of FinTech regulation is also important. In May 2020, the People's Bank of China, the Securities Regulatory Commission, the Insurance Regulatory Commission, the SAFE and other four departments jointly issued the Opinions on Financial Support for the Construction of the Guangdong Hong Kong Macao Greater Bay Area, pointing out of the need for a "sandbox" for cross-border financial innovation supervision, and promote the improvement of financial regulatory rules in the innovation field [7].
4.2. Data Security and Privacy
With the popularization of financial technology, data security and user privacy have become important issues. Fintech companies typically handle large amounts of sensitive personal and financial information, and any data breaches or security vulnerabilities can lead to serious consequences, including loss of user trust and legal liability. Therefore, how to protect user data, ensure transaction security, and establish effective network security measures are challenges that fintech companies must face. In addition, a good privacy policy for fintech apps is also important. Figure 1 illustrates the impact of privacy policy on user privacy disclosure through the APCO model. The APCO model was first proposed by Smith in 2011 to explain how privacy affects individual decision-making. The core variable of this model is privacy concern, and a mechanism of "antecedent privacy concern outcome" is constructed. The model also includes a mechanism of "privacy policy trust, and user disclosure privacy" [8].
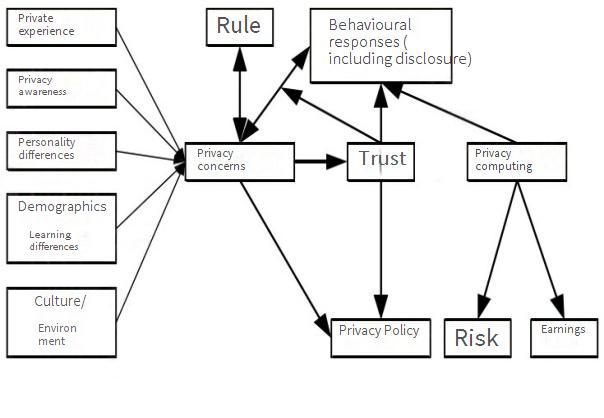
Figure 1: The impact of privacy policy on user privacy disclosure through the APCO model.
4.3. Market Competition
The competition in the fintech industry is exceptionally fierce, especially in areas such as payments, lending, and wealth management. Nowadays, many technology companies have leveraged their strength in other markets to enter the financial market, squeezing out the market share of many traditional financial institutions. If viewed solely from the perspective of traditional financial institutions, this is certainly negative and destructive. But if this destructive behavior can ultimately improve market efficiency as a whole and enhance consumer welfare, it should be viewed as a 'destructive creation' and acknowledged. In this competitive environment, fintech companies need to constantly innovate to maintain competitiveness and market position [9]. At the same time, rapid market changes also require enterprises to have flexible strategies.
4.4. Technical risk
The rapid development of financial technology relies on the continuous advancement of technology. However, rapid technological changes may lead to system instability or failures, affecting the continuity and reliability of services. As technology enables financial enterprises to provide financial services across time, space, and markets, it increases the speed and contagion of financial risks, making wider scope of financial risks [10]. In addition, the complexity of technology may also make it difficult for fintech companies to develop and maintain products, increasing operational risks.
5. Conclusion
Fintech is undeniably reshaping the global financial services industry, fostering industry innovation and substantial transformation. Dispite facing numerous challenges, the sector’s market potential and development prospects remain highly optimistic. As technology advances and market demands evolve, Fintech will consistently offer consumers and businesses more efficient and convenient financial services. A key area for further exploration is the application of blockchain technology. By streamlining cross-border payments, blockchain can immensely improve the efficiency and reduce costs. By enabling peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, blockchain eliminates excessive fees and lengthy settlement times. Additionally, blockchain’s inherent security features, such as data immutability and transparency, help prevent fraud and build trust among participants. Another significant aspect is artificial intelligence (AI) and its role in risk management. Employing machine learning algorithms can revolutionize credit and market risk assessments by analyzing vast amounts of historical data, leading to more accurate credit scores and better-informed lending decisions for financial institutions. Furthermore, AI can facilitate real-time monitoring of market conditions, identifying potential risks and anomalies early on, which can enhance the overall stability of financial systems. Lastly, big data analytics enables personalized financial services tailored to individual needs. By analyzing user behavior and spending patterns, financial institutions can develop customized products and recommendations, thus improving user experience and fostering customer loyalty. In conclusion, Fintech is at a pivotal point, with the potential for significant advancements in how financial services are delivered. Stakeholders must respond proactively to challenges while capitalizing on opportunities for sustainable growth.



