1. Introduction
Human behavior recognition refers to the process of using sensors to capture human motion data and automatically identify the action categories or behavior patterns performed by individuals and groups through algorithms [1].
This technology has important application value in the fields of intelligent monitoring, medical rehabilitation, virtual reality, etc. However, due to the influence of complex environments such as light changes, human occlusion, and background interference, the recognition accuracy of traditional single-modal human recognition methods decreases in these complex environments.
In order to improve the robustness of the behavior recognition system, researchers have gradually introduced multimodal perception methods, such as fusing RGB, depth map, skeleton sequence and other data for modeling, to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of the action. For example, H. Oikawa, Y. Tsuruda et al. used RGB and Depth modality fusion to identify mouse behavior in their research, and verified the effectiveness of RGB-D in low light and occluded environments [2]; Chunyan Ma et al. combined RGB-D and Skeleton modalities and proposed a fusion network structure based on LSTM-DGCN for basketball player action recognition [3-4]; Li Tongwei, Qiu Dawei et al. studied and sorted out the dual-modal fusion method of RGB and Skeleton, and pointed out that both can be effectively fused at the feature layer and the decision layer [5].
Different from previous reviews that started from the perspective of network structure or classifier design, this paper focuses on the "perception modality" level and analyzes the characteristics of different modalities and their combination methods. This paper mainly analyzes from the following three perspectives: (1) Introduction and analysis based on the current mainstream perception modalities of human behavior recognition. (2) Analysis of the advantages of multimodality over a single modality. (3) Challenges of human behavior technology, prospects and summary.
2. Analysis of mainstream perceptual modalities: RGB, Depth and Skeleton
This chapter mainly introduces the most basic modalities: RGB, Depth, and Skeleton. The comparison of RGB, Depth, and Skeleton perception modal human recognition shown in Figure 1 can help you better understand the mainstream perception modalities.
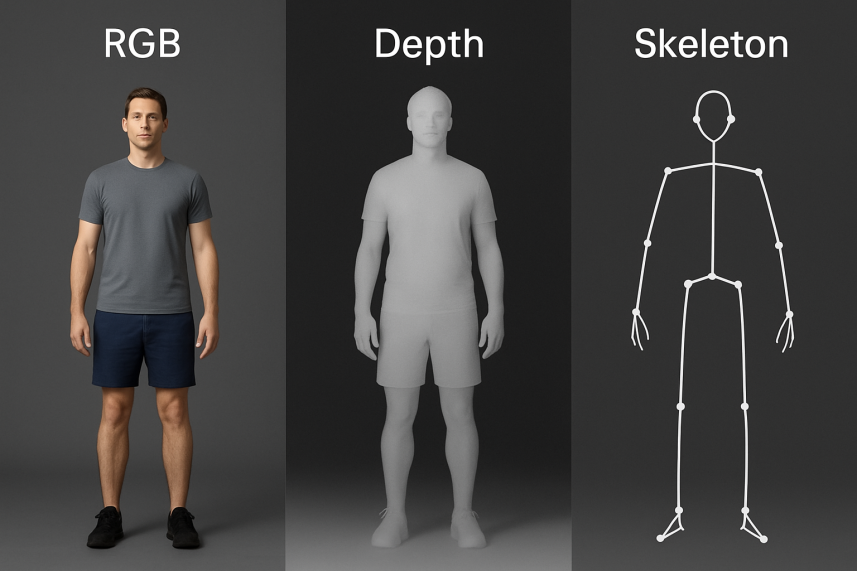
RGB images are currently the most commonly used type of perceptual data. They provide rich information about the color, texture, and posture of objects, and can be efficiently spatially modeled using models such as CNN. The RGB modality is sensitive to lighting, background complexity, and occlusion issues, and has poor robustness when used alone [6-8].
Depth provides three-dimensional spatial structural information by measuring the distance between objects in the scene and the camera. Compared with RGB, the depth modality is insensitive to lighting changes and is suitable for modeling behavioral features such as front and back movements and spatial displacement. However, its resolution and semantic density are low, so it cannot provide appearance information and is not suitable for structural modeling [2,9].
The Skeleton modality consists of a set of key human joint coordinates, which can be obtained through a depth camera or a posture estimation algorithm. This modality has a high degree of abstraction and has the advantages of clear structure, strong anti-interference, and low computational cost. It is suitable for modeling using graph neural networks (such as GCN). However, the accuracy of the skeleton depends on the quality of the sensor, lacks fine-grained semantic information, and has limited spatial and appearance perception capabilities [1,7,10].
3. Analysis of multimodal combination and representative methods
With the development of multimodal perception technology, a single modality often has the problem of incomplete information in specific scenarios and is difficult to cope with behavior recognition tasks in complex environments.
Multimodal fusion can make up for the limitations of a single modality by complementary integration of different single modalities to improve the overall modeling capabilities of spatial, appearance and structural features. Therefore, collaborative modeling between different modalities has become an important means to improve the performance of human behavior recognition. Common modal combinations include RGB-D, RGB+Skeleton, and a three-modal structure that combines RGBD+Skeleton. The comparison of RGB-D, RGB+Skeleton and RGBD+Skeleton perception modal human behavior recognition shown in Figure 2 can more clearly understand the advantages of multimodality. The following is an analysis of multimodal fusion.
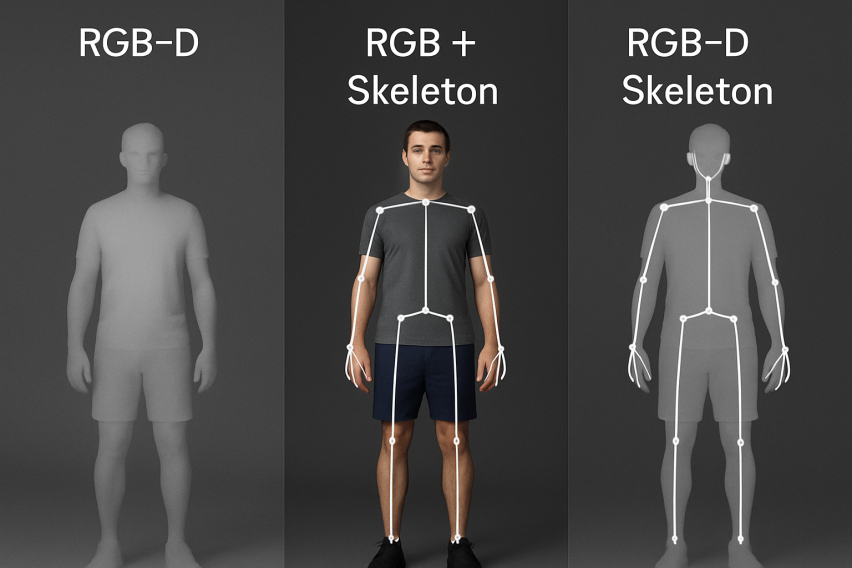
3.1. RGB + Depth fusion analysis
Although the RGB modality provides rich color and texture features and is suitable for capturing appearance details, it is highly sensitive to lighting changes, perspective occlusion, and background noise, and cannot understand real three-dimensional space [5].
As a supplement to structural information, the Depth modality provides the depth value of each pixel in the scene, which can effectively depict geometric features such as the forward and backward movement and spatial distribution of characters, and has strong robustness to weak light and occlusion [2]. For example, in the task of mouse behavior recognition, H. Oikawa et al. combined RGB with Depth and used bottom-view acquisition to significantly improve the recognition accuracy in weak light and occluded scenes, showing the complementarity of RGB-D fusion in perceiving redundant background and capturing spatial behavior [2]. Therefore, the fusion of RGB and Depth not only achieves complementarity in the spatial modeling dimension, but also significantly improves the robustness of the system in complex environments (such as occlusion and weak light), which is impossible to achieve with a single RGB modality [2,5].
3.2. RGB + Skeleton fusion analysis
Although the RGB modality can provide information about appearance changes during the execution of an action (such as limb shape, clothing texture, etc.), it lacks the ability to model the temporal structure of a person’s posture, especially in scenes with changing lighting or complex backgrounds, where the misrecognition rate is high [6].
The Skeleton modality constructs the human skeleton with key joints, has highly abstract structural features and strong anti-background interference capabilities, and is suitable for representing temporal and posture changes [1]. As described by Li Tongwei et al., in the task of action recognition, the Skeleton modality is used to guide the RGB network to focus on key action areas (such as joints and limbs), which significantly improves the model’s sensitivity to posture details and local actions, and effectively overcomes the problem of the RGB modality’s strong dependence on background [8]. This fusion method is particularly suitable for scenes that focus on structural accuracy, such as medical rehabilitation and posture analysis. It can be seen that by guiding visual feature learning with structured skeleton information, RGB + Skeleton fusion effectively makes up for the limitations of the RGB modality’s weak structural modeling capabilities and sensitivity to background interference, and demonstrates stronger action semantic parsing capabilities [1,6,8].
3.3. RGBD + Skeleton (trimodal) fusion analysis
RGB-D fusion has significant advantages in modeling three-dimensional actions, it still has shortcomings in fine action changes or high-dimensional dynamic modeling.
The Skeleton modality can further provide low-dimensional, structured posture trajectory information to make up for the shortcomings of RGB-D in temporal modeling [9]. In the literature [3], Chunyan Ma et al. proposed an LSTM-DGCN network that integrates RGB-D and skeleton sequences, effectively combining trimodal features: RGB captures appearance details, Depth perceives spatial layout, and Skeleton represents dynamic structure. In the basketball motion recognition task, this model shows excellent classification effects for the habitual actions of different athletes (such as changing direction and passing), and has good recognition robustness even in scenes with multi-person interaction and severe occlusion [3]. Although the backbone of its model is the Skeleton modality, its research background is based on the RGB-D dataset and has trimodal analysis value. Compared with single or dual-modal systems, trimodal fusion can achieve synergistic enhancement in information dimension, modeling depth and semantic level, and shows significant superiority in complex scenarios such as multi-target, rapid changes and privacy constraints [3,9].
3.4. Comparative analysis
Table 1 shows the comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of the perception modalities.
The analysis of the three combinations of RGB + Depth, RGB + Skeleton, and RGBD + Skeleton shows that different combinations have their own advantages in information coverage, system complexity, and applicable scenarios. Bimodal fusion can improve the local action perception ability while ensuring the simplicity of the system; while trimodal fusion integrates multi-dimensional information to show higher recognition accuracy and robustness in complex dynamic environments. Future research will pay more attention to modal coordination mechanisms, adaptive fusion strategies, and lightweight designs to meet the higher requirements for multimodal behavior recognition systems in real application scenarios. Overall, the superiority of multimodal fusion stems from the complementary mechanism between modalities - it systematically improves the performance upper limit of the behavior recognition model in multiple environments and multiple tasks by making up for the shortcomings of a single modality in spatial structure, posture modeling, and dynamic timing.
|
Perceptual modality type |
Perceived content |
Advantage |
Disadvantage |
Typical application scenarios |
|
RGB |
Appearance |
Rich in semantics, |
Lack of spatial structure (not as good as Depth) |
Video surveillance, motion detection, image recognition |
|
Vulnerable to the effects of light and shading (not as good as Skeleton and Depth) |
||||
|
Lack of structural modeling (not as good as Skeleton) |
||||
|
Skeleton |
The position of the key points |
Strong anti-background interference ability, |
No visual semantic information (not as good as RGB) |
Posture recognition, rehabilitation training, sports analysis |
|
Lack of deep structure (not as deep as Depth) |
||||
|
Dependent on the accuracy of the sensors and with errors present |
||||
|
Depth |
Distance/Depth |
Resistant to light exposure, |
Lack of visual semantic information (not as good as RGB) |
Fall detection, indoor motion recognition |
|
Lack of action structure (not as good as Skeleton) |
||||
|
Low resolution and blurred edges |
||||
|
RGB + Skeleton |
Appearance + Action Structure |
The synergy between appearance semantics and |
Lack of spatial modeling capability (not as good as RGBD) |
Intelligent sports, training assistance, action recognition |
|
The modal alignment is complex and may be affected by the noise in the skeleton. |
||||
|
RGBD |
Appearance + Spatial Structure |
Spatial perception and appearance recognition |
Lack of dynamic structure modeling for actions (not as good as Skeleton) |
Intelligent security, environmental monitoring, interactive system |
|
The equipment requirements are high, and the integration cost has increased. |
||||
|
RGBD + Skeleton |
Appearance + Spatial Structure + |
The most comprehensive perception, |
The system is complex, with high costs and computational burdens. |
High-precision behavior monitoring, multimodal interaction system |
|
Modal synchronization is the most difficult. |
4. Analysis and prospects of perception challenges in social scenarios
4.1. Challenges in smart security scenarios
In public places such as subways, shopping malls, and campuses, where people are densely populated, traditional RGB single-mode recognition is easily affected by occlusion, lighting changes, and background clutter in such environments, resulting in failure of recognition system perception.
Even multimodal systems that integrate depth information or skeleton information may cause missing skeleton key points or noise in the depth map due to occlusion. To solve this problem, researchers proposed introducing a dynamic mode switching mechanism (such as increasing the depth/skeleton dependency weight when occlusion is severe), using an attention mechanism to focus on key areas, and improving the system's adaptability to occlusion and dynamic changes through multi-person detection and tracking modules, thereby ensuring stable perception performance in complex security scenarios.
4.2. Challenges in medical and health scenarios
In the scenarios of health monitoring and medical assistance for the elderly, the behavior recognition system needs to monitor the user status for a long time and continuously.
Due to the characteristics of small movements and abnormal postures (such as hunchbacks and slow movements) of the elderly, skeleton estimation is prone to missing key points, and the depth mode is also easily affected by occlusion or environmental changes, resulting in incomplete modal information. In addition, the equipment conditions in medical places are limited, and it may not be possible to ensure the long-term and efficient operation of all modal sensors.
4.3. Future outlook: privacy protection in perceptual modalities
The privacy protection issues involved in perceptual modalities are receiving increasing attention.
In particular, the RGB image modality, although it can provide rich semantic information, is also prone to leakage of sensitive information such as user identity and life scenes. Therefore, future perception systems need to take into account privacy protection needs while ensuring recognition accuracy. From the perspective of perceptual modalities, the best approach at present is to use privacy-friendly modalities such as skeletons and depth maps as the main data sources to reduce the direct collection of original images.
5. Conclusion
This paper focuses on the perceptual modality problem in human behavior recognition, systematically analyzes the characteristics and limitations of three commonly used modalities: RGB, Depth, and Skeleton, and summarizes their complementary advantages in multimodal fusion.
RGB is good at appearance expression but is easily disturbed by the environment, Depth is strong in spatial modeling but lacks semantic information, and Skeleton has a clear structure but limited appearance and depth perception capabilities.
Multimodal fusion significantly improves the recognition accuracy, robustness, and generalization capabilities of the system in complex scenarios by integrating these complementary features at the perceptual level. For example, RGB+Depth enhances spatial modeling, RGB+Skeleton strengthens action structure recognition, and the three-modal combination achieves more comprehensive perceptual coverage. Despite this, the current multimodal system still faces challenges such as difficulty in modal alignment, feature redundancy, and high equipment cost. In the future, the system's practicality and deployment capabilities can be further improved from the perspectives of adaptive modal selection, lightweight fusion structure, and privacy-friendly modal modeling.



