Volume 4 Issue 3
Published on November 2025A mathematical framework is presented to quantify the relationship between quaternary-structure symmetry, free energy, and catalytic efficiency during the transition from aD2-symmetric tetramer to aC2-symmetric dimer, exemplified with LDHA. The approach constructs explicitD2representations on subunit and interface feature spaces, derives projection operators to decompose operators and data into irreducible-representation components, and computes symmetry-resolved free-energy differences via Gaussian/statistical and harmonic/Hessian methods. Connections to kinetics are made through transition state theory with channel degeneracy. Reproducible algorithms and a workflow for mapping FoldX outputs into irrep-resolved diagnostics and efficiency predictions are provided.

 View pdf
View pdf


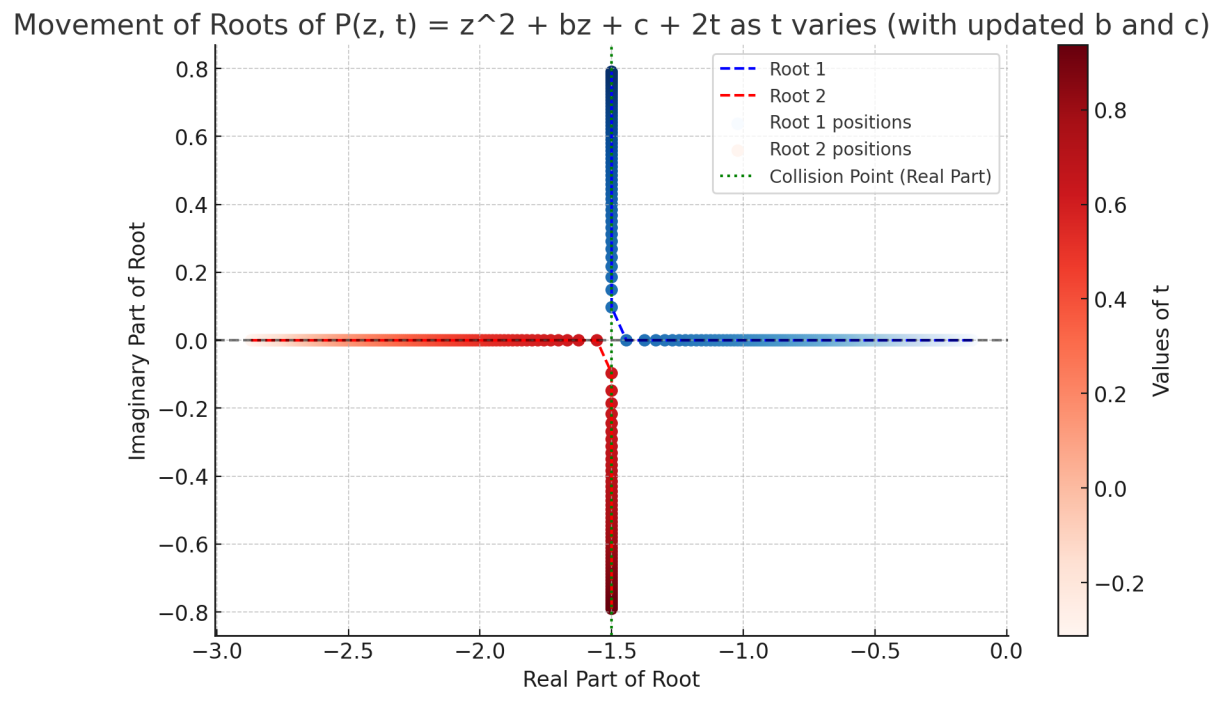
Deformation of polynomials is a kind of operation where we add a new variable to the original polynomial. In our case, suppose P is a monic polynomial of degree n with complex coefficients. We evolve P with respect to time by heat flow, creating a function P(t,z) of two variables with given initial dataP(0,z)=P(z)for which∂tP(t,z)=∂zzP(t,z). In this paper, we focus on the deformed polynomial P(t,z). First, we proved the Taylor series representation of deformed polynomial. Then we apply the results to the classical Hermite polynomials and extend to the case of matrix-valued polynomials. From the inspiration of deformed polynomials’ roots movement, we proved the behavior of Hermite polynomials after heat flow deformation and got an explicit formula. For further work, similar to what we have done in this paper, we want to have an explicit formula for deformed matrix Hermite polynomials and give a proof.

 View pdf
View pdf


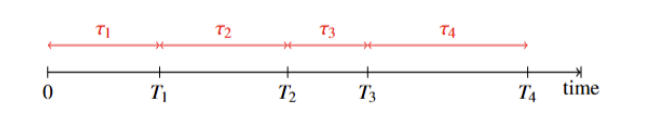
Renewal theory originated from research on component failure and replacement. It has since developed into a key framework for analysing systems of repeated events within applied probability. This paper reviews the key concepts and principal findings in this field, while demonstrating several of its applications. The paper first introduces the Poisson process, highlighting the inter-arrival intervals of the exponential distribution and its 'memorylessness’, thereby introducing the general renewal process. The renewal function, elementary renewal theorem, renewal equation, and key renewal theorem are discussed, with attention to their assumptions, interpretations, and asymptotic conclusions, showing how they can be applied. The paper also presents several practical extensions of the renewal processes, including the delayed renewal process, renewal reward process, alternating renewal process, and age-dependent branching processes. Finally, concise examples illustrate the computation of long-run replacement and success rates, as well as the use of demographic renewal equations. Applications in reliability, service operations, and demography show that renewal models provide transparent asymptotic rates and availability with modest modelling complexity.

 View pdf
View pdf


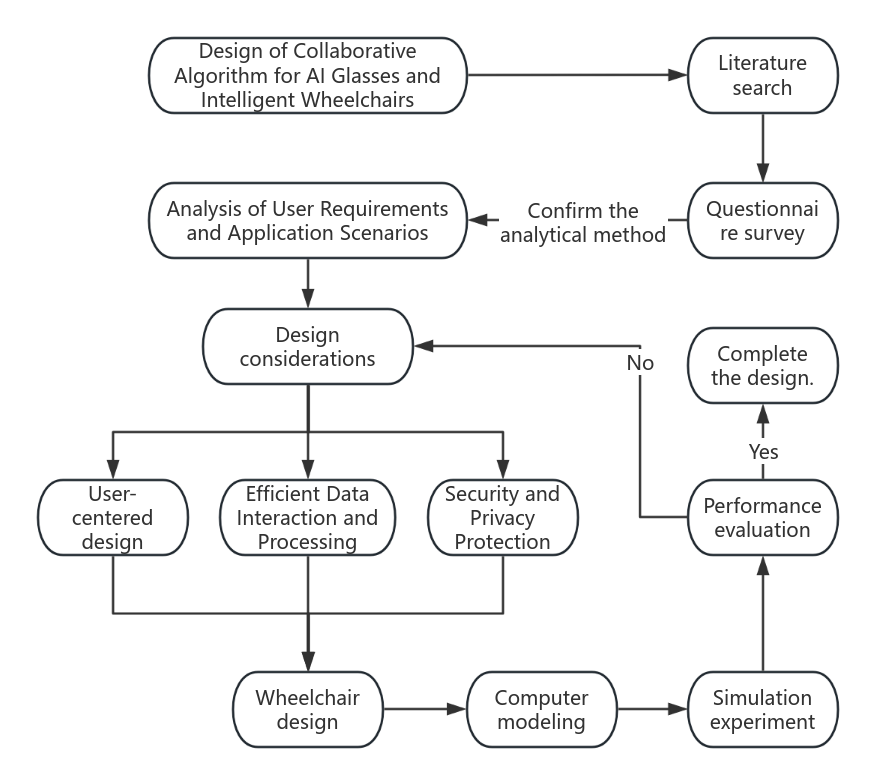
In response to the growing demand for assistive devices under the backdrop of population aging, this paper proposes an innovative collaborative navigation algorithm integrating smart wheelchairs and AI glasses based on multimodal data fusion. The algorithm optimizes a closed-loop interaction among the “environment–user–device” triad. By integrating the wheelchair’s autonomous navigation capabilities with the AI glasses’ advanced environmental perception and real-time interaction functions, it significantly enhances system safety, autonomy, and user experience. The proposed approach employs a hybrid model combining Deep Belief Networks (DBN) and Stacked Autoencoders (SAE) to model and fuse multimodal data. Further integration with Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) enables improved system performance. Experimental comparisons in complex dynamic environments demonstrate that this method outperforms traditional Kalman filter–based fusion techniques. User survey results indicate a high level of acceptance and willingness to adopt this system among the target population. To promote its broader application, future research will focus on algorithm optimization, outdoor performance testing, and the enhancement of data security and privacy protection mechanisms.

 View pdf
View pdf


In recent years, with the significant impact of housing price changes on economic and social stability, scientifically predicting housing price trends can prompt local governments to formulate policies related to housing prices, and investors can make investments based on the corresponding housing prices. At the same time, homebuyers can also make housing purchase plans according to housing prices. Traditional methods for predicting housing prices are primarily based on experience or simple statistical models, which cannot reasonably consider complex factors. This paper investigates the efficacy of machine learning methodologies in the prediction of housing market valuations. Firstly, it discusses the characteristics and value of supervised, unsupervised, and decision tree algorithms in the machine learning field when applied to housing price prediction. Secondly, it explores the reasons affecting housing prices, such as economic characteristics like national income, regional features, and the influence of supply and demand. Then, it applies a public housing price dataset to establish a decision tree for predicting housing prices. Based on basic features, it expands the feature library. It seeks suitable feature combinations to analyze housing prices better and draw conclusions on the value of machine learning methods in housing price prediction. This article summarizes successful experiences from existing application cases and studies the problems and deficiencies in the application process.

 View pdf
View pdf



