1. Introduction
It can be seen from the literature that Large Language Models (LLMs) can assist doctors in diagnosis and treatment by learning from large volumes of clinical data and Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) knowledge. The TCM-FTP model, for example, uses a pre-trained LLM and is fine-tuned with the DigestDS dataset. It can effectively predict TCM prescriptions and dosages, achieving an F1-score of 0.8031 and a normalized mean square error of 0.0604 in dosage prediction, thereby providing a valuable reference for physicians when prescribing medications [1]. This approach facilitates the integration of TCM theory and clinical practice with modern technology and promotes the modernization of TCM. By constructing TCM knowledge graphs and developing domain-specific models, the efficiency and accuracy of TCM diagnosis and treatment can be improved, allowing TCM to better meet the needs of contemporary society [2]. Furthermore, large-scale models can integrate and analyze a vast amount of TCM literature and empirical data, uncovering the potential value of TCM knowledge and promoting innovation in TCM theory and practice. Through the study of ancient TCM classics and clinical experience, these models can identify new drug combinations and treatment methods, providing new directions for TCM innovation.
2. A “Four Diagnostic Methods” framework
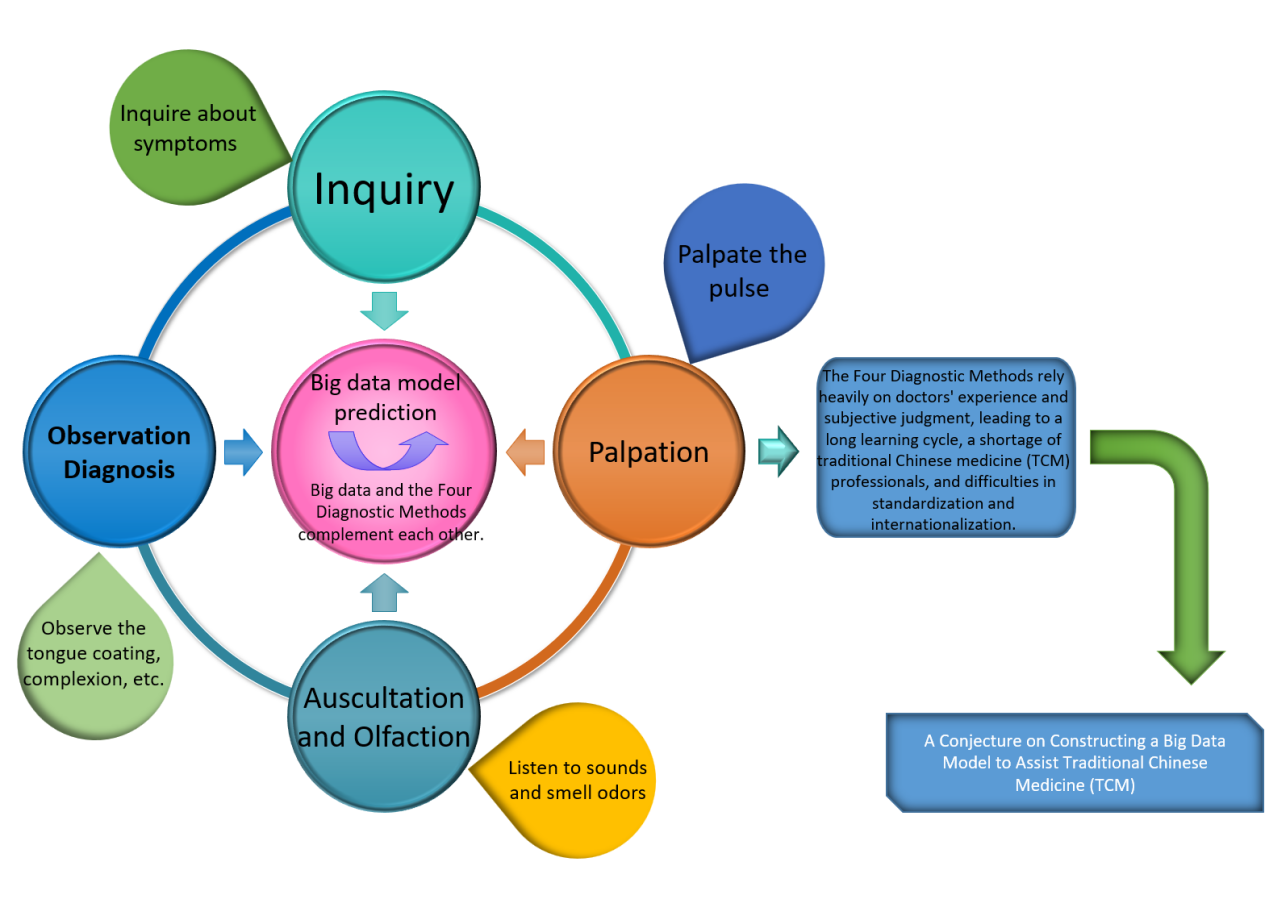
Amid the rapid advancement of modern medicine, the modernization and internationalization of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) have become inevitable trends. The application of large-scale models offers an effective means for TCM to integrate with contemporary technologies, thereby enhancing its scientific rigor and standardization.
In this context, we propose a “Four Diagnostic Methods” framework designed to assist physicians in TCM, as illustrated in Figure 1. The components and operational details of the framework are outlined below.
2.1. Observation diagnosis
As the first of the Four Diagnostic Methods in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), observation diagnosis is characterized by strong subjectivity and a high dependence on clinical experience, which has hindered its standardization and broader application. The integration of big data and artificial intelligence technologies offers a new pathway toward the objectification and intelligent development of observation-based diagnostics. We examine the current applications of big data in various subfields of observation diagnosis, including tongue diagnosis, complexion analysis, and eye examination. Key enabling technologies such as standardized data collection, multimodal data fusion, and dynamic feature analysis are also explored in depth. Based on this analysis, we propose several strategies to advance observation diagnosis: the construction of a comprehensive TCM observation diagnosis database, the optimization of deep learning models, and the enhancement of clinical validation efforts. These measures aim to drive the evolution of observation diagnosis toward greater precision and quantification.
2.1.1. Mining tongue and facial features for assisted diagnosis
By leveraging big data and deep learning, it is possible to extract features from a large number of tongue and facial images, providing an objective basis for disease diagnosis. For example, by analyzing features such as the color, shape, and coating of the tongue, and comparing the tongues of patients with different diseases using big data, doctors can be assisted in diagnosing illnesses. A research team has developed an intelligent tongue recognition system based on deep learning, which can quickly and accurately identify pathological features in tongue and facial diagnosis. The system applies the following technologies: YOLOv5s6 is used for regional segmentation of tongue images, such as identifying the boundary of the tongue body. U-Net further optimizes the detailed segmentation of tongue images, focusing on local features such as tongue coating and tooth marks. MobileNetV3 is employed for feature classification to identify pathological features, including tooth marks, ecchymosis, and fissures [3].
2.1.2. The diagnostic information dimension has been expanded
Big data contains a rich and diverse range of information. It not only includes data on tongue appearance and facial features but also encompasses multi-source information such as patients' medical histories, symptoms, and examination results. Integrating this information with data from observation diagnosis can provide a more comprehensive perspective for clinical assessment. Data integration is increasingly emerging as a key approach in medical diagnosis. We propose a “tongue image—pulse condition—symptom” association framework by analyzing tongue images, pulse data, and electronic medical records. Similarly, Li et al. developed an improved U-Net model that uses tongue image segmentation technology to achieve an accuracy rate exceeding 93.33% in identifying features such as tooth marks and cracks, assisting physicians in diagnosing syndromes such as spleen deficiency and blood stasis [4]. By combining patients’ genetic information and lifestyle data with inspection diagnosis results, the risk of diseases can be assessed more accurately. Certain facial features may correlate with specific genetic conditions, and integrating this information with family medical history can improve diagnostic accuracy and reliability. This approach is valuable for the early detection and intervention of diseases.
2.2. Auscultation and olfaction
2.2.1. Enhancing the accuracy and objectivity of auscultation and olfaction diagnosis
Traditional auscultation and olfaction diagnosis primarily rely on physicians’ subjective perception, which poses inherent limitations. Big data technologies enable the collection and analysis of large volumes of sound and odor data to develop more accurate diagnostic models. Modern sound collection and analysis devices have been applied to the study of voice diagnosis and related diseases. Machine learning techniques allow for in-depth analysis of differences between pathological and normal sound patterns. For example, research on voice analysis related to five-zang organ diseases, as well as time-domain and frequency-domain detection of respiratory sounds in healthy individuals and patients infected with the novel coronavirus, has demonstrated promising accuracy. Moreover, big data can integrate multi-source information, providing a richer and more comprehensive basis for auscultation and olfaction diagnosis [5].
2.2.2. Expanding the diagnostic scope and depth of auscultation and olfaction
Big data technology can identify additional sound and odor features associated with diseases, thereby broadening the diagnostic scope of auscultation and olfaction. For example, electronic nose technology can detect the specific characteristics of odor molecules. Spectral technologies, leveraging artificial intelligence and other methods to identify and differentiate volatile organic compounds (VOCs), have been applied in the diagnosis of respiratory diseases, breast cancer screening, and the assessment of TCM syndrome characteristics in type 2 diabetes, among other applications [5].
2.3. The innovation and breakthrough of “inquiry” diagnosis
2.3.1. Intelligent information extraction and analysis
Large language models, combined with natural language processing technologies, enable more efficient and accurate extraction of key information from patients’ descriptions. Inquiry diagnosis models based on deep learning—such as the Chinese medicine inquiry-assisted diagnosis algorithm that integrates Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) and graph convolutional neural networks—can simulate the diagnostic reasoning process of physicians. These models accurately extract symptoms, medical history, and other relevant information from patient statements. Compared with traditional inquiry methods, they significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of information extraction [6].
2.3.2. Innovative diagnosis and treatment models
Intelligent inquiry platforms developed with the support of large language models enable remote consultations and real-time diagnoses. Currently, technology-driven facial complexion classification can be applied to assist diagnosis. Similarly, intelligent inquiry platforms can integrate image recognition and other technologies to provide more comprehensive diagnostic capabilities [7].
2.4. Palpation
2.4.1. Assisting in disease prediction and diagnosis
By integrating diverse diagnostic information and patients’ personal data, big data can provide a more comprehensive foundation for disease prediction and diagnosis. In pulse diagnosis, the application of digital intelligence technologies to mine and analyze Traditional Chinese Medicine clinical data facilitates the identification of potential disease patterns and risk factors. Through the comprehensive analysis of pulse data from a large patient cohort, combined with their medical histories, symptoms, examination results, and other relevant information, big data enables the construction of disease prediction models. By analyzing temporal trends in patients’ pulse conditions alongside other factors, it becomes possible to predict disease onset, progression, and prognosis. This approach supports early intervention and treatment, thereby improving the efficiency and accuracy of disease diagnosis [5].
2.4.2. Promoting the inheritance and development of pulse diagnosis in traditional Chinese medicine
Big data technology facilitates the organization and preservation of extensive clinical experience and data related to pulse diagnosis in Traditional Chinese Medicine, thereby supporting the inheritance of pulse diagnosis theory. Through digital processing and analysis of pulse diagnosis data from historical texts and clinical cases, valuable insights and patterns can be uncovered, providing rich resources for the teaching and research of pulse diagnosis in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Moreover, big data can drive the integration of pulse diagnosis with modern medicine. For example, by applying multidimensional data in disease research and combining modern medical findings with big data analytical methods, the theory of pulse diagnosis in Traditional Chinese Medicine can be further validated and refined. This approach helps to explore the scientific relationship between pulse condition changes and the physiological and pathological alterations in the human body, thereby promoting the modernization of pulse diagnosis in Traditional Chinese Medicine [8].
2.5. Construction of BD-TCM model framework
Multi-source data, including traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) ancient books, textbooks, clinical cases, Chinese pharmacopoeias, and public data resources, should be collected. At the same time, standardized information can be obtained from databases such as TCMBank and ETCM v2.0, covering traditional Chinese medicines, ingredients, targets, diseases, and other content, enriching the data dimensions [9]. Annotate the collected data. For example, mark the "four diagnostic methods" information, symptoms, disease types, etc., in TCM diagnosis data. Remove incorrect and duplicate data to ensure data quality. For ambiguous or incomplete data, it can be improved through expert review or data supplementation to make the data more suitable for model training requirements [10]. Select excellent open-source foundation models such as Baichuan2 and LLaMA. These models have certain performance in the general field and can be adapted to TCM tasks through subsequent training [11].
Through the previous analysis, the significance of the model lies in providing a predictive service for the four diagnostic methods of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). We elaborate on the construction of this framework from the following aspects.
2.5.1. Application of mathematical formulas
The loss function used during the continuous pre-training stage is presented in Formula (1).
Explanations of all variables in Formula (1) are provided in Table 1.
|
Variable |
Explanations in detail |
|
Total number of sequences in the pre-training dataset. |
|
|
Number of tokens in each sequence |
|
|
The |
|
|
Model parameters. |
|
|
The probability that the model predicts the (t+1)-th token given the first t tokens. |
Figure 2 presents a visualization of Formula (1) generated using Python code.
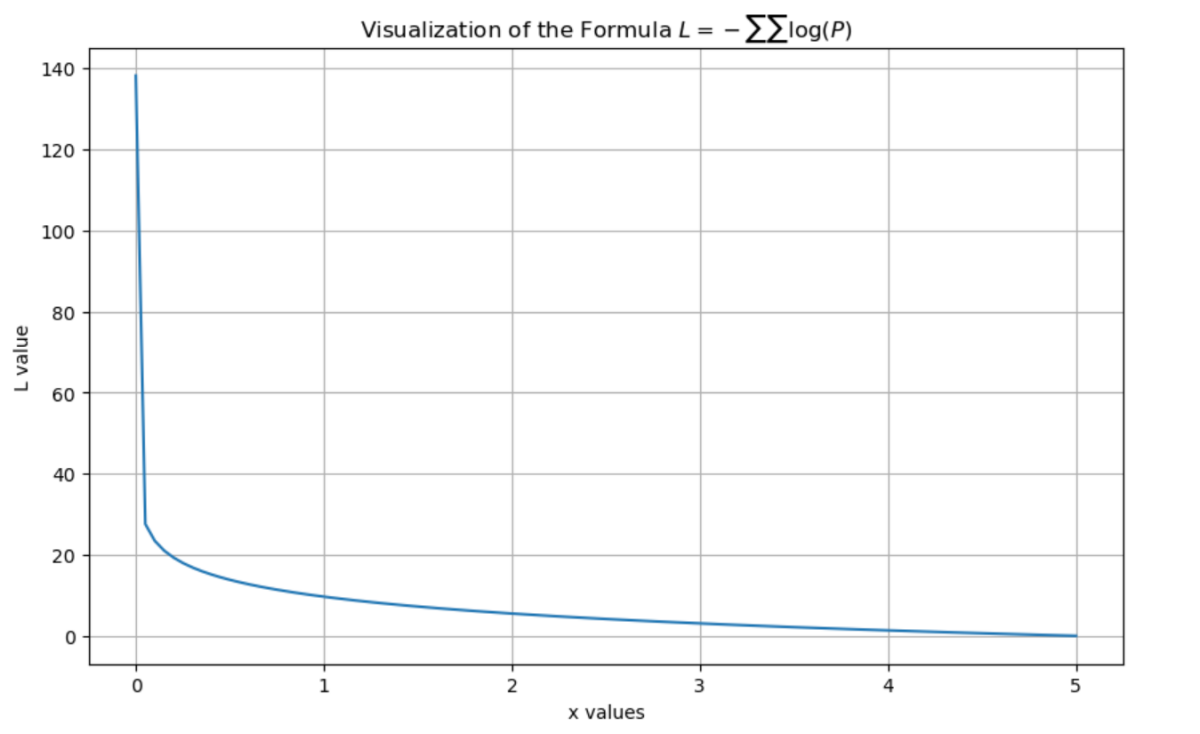
Formula (1) represents the standard cross-entropy loss function used in autoregressive language models. By minimizing this loss, the model learns to predict the probability of the next token, thereby capturing semantic associations and knowledge systems within the Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) corpus. This facilitates foundational learning of TCM theories, syndrome differentiation methods, and related concepts.
TCM terms such as “qi stagnation and blood stasis” require contextual chains that integrate symptoms (e.g., stabbing pain, purple-dark tongue), treatment principles (e.g., promoting blood circulation to remove stasis), and formulas (e.g., Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction). The loss function compels the model to learn these complex, multi-layered associations effectively.
“” by predicting the next word. For example, from “dizziness + aggravation on movement” the model can associate with “qi deficiency,” and further link to herbs like “Astragalus membranaceus” and “Codonopsis pilosula” [12].
2.5.2. Loss function in the supervised fine-tuning stage
Explanations of all variables in Formula (2) are provided in Table 2.
|
Variable |
Explanations in detail |
|
Total number of samples in the fine - tuning dataset. |
|
|
Number of tokens in the response |
|
|
The input prompt of the |
|
|
Model parameters. |
|
|
The |
|
|
The probability that the model predicts the |
Figure 3 presents a visualization of Formula (2) generated using Python code.
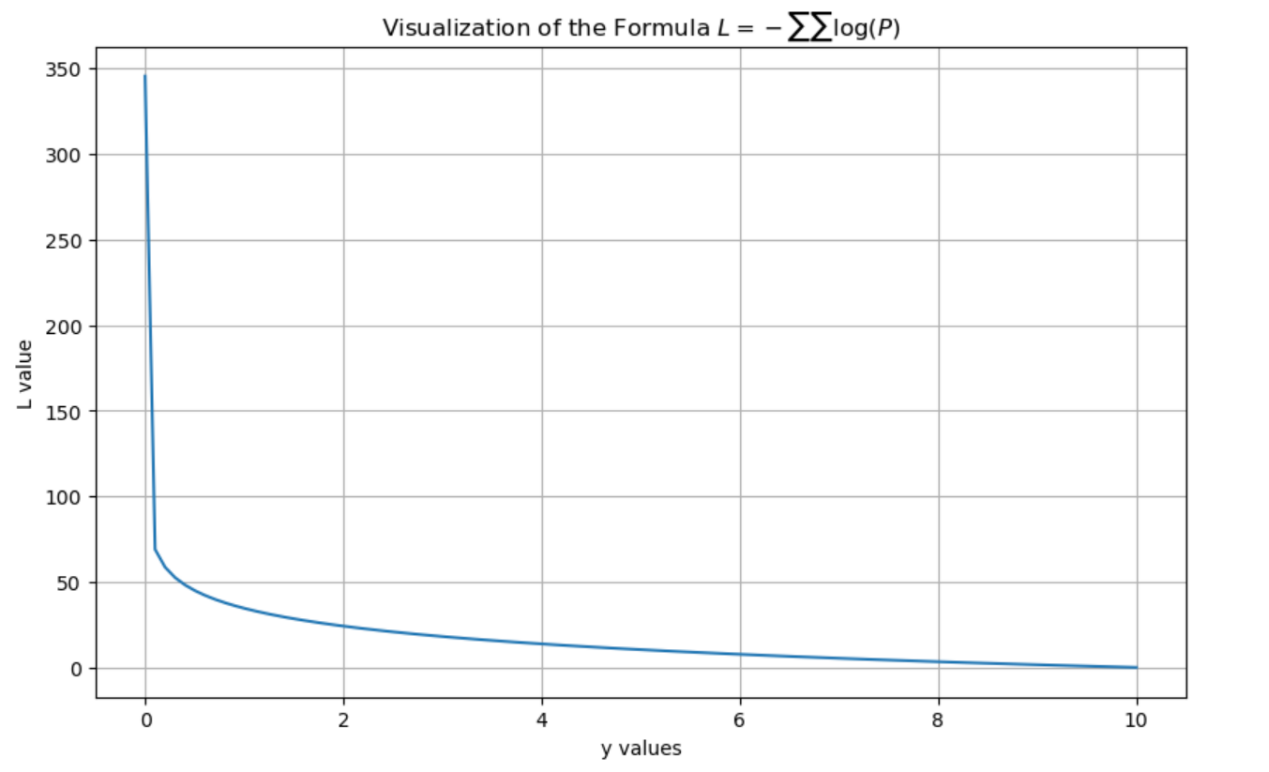
Formula (2) is applied during the supervised fine-tuning phase, aiming to enable the model to generate responses consistent with professional TCM logic—such as consultation dialogues and syndrome differentiation analyses—based on given input prompts. Unlike the pre-training phase, the fine-tuning input includes explicit instructions , and the loss calculation is performed solely on the generation of the response . This design enhances the model’s instruction-following capabilities and its applicability in clinical TCM scenarios.
For example, as shown in Table 10, through seven rounds of dialogue conducted in “”, the model progressively identifies the syndrome type of “qi and blood deficiency combined with spleen and kidney yang deficiency.” Each response is generated based on the preceding dialogue content, reflecting a logical chain of “consultation— syndrome differentiation—prescription” [12].
2.5.3. Process design
The process can be divided into two main stages. The first stage involves the construction of the core framework, including the Data Input Layer, Feature Fusion Layer, Prediction Layer, and Feedback Layer. The second stage consists of pre-training and fine-tuning the model.
An overview of this process is illustrated in Figure 4.

(1) Data Input Layer
For observation diagnosis, the input includes tongue image feature vectors obtained through tongue body segmentation using YOLOv5s6 and tongue coating feature extraction via U-Net, as well as facial complexion RGB values. In auscultation and olfaction diagnosis, inputs consist of speech spectrum features (e.g., cough frequency, time-domain waveform of breath sounds) and odor molecular concentration data (e.g., detection values from VOC sensors). For inquiry diagnosis, natural language text from patient chief complaints and medical history is encoded into semantic vectors using BERT. Finally, in palpation diagnosis, pulse pressure waveform features are extracted, including frequency components measured at the Cun, Guan, and Chi pulse positions.
(2) Feature Fusion Layer: Detailed Approach: Construct TCM Syndrome Differentiation Vectors. First, concatenate the four diagnostic features into a comprehensive vector
(3) Prediction Layer:Generate Diagnostic Results: Map [features] to the probability distribution of syndrome types
(4) Feedback Layer
If the confidence level of a prediction falls below a predetermined threshold (e.g., <70%), the model automatically generates supplementary inquiry questions (e.g., “Do you experience palpitations?”). After incorporating the updated data from the Four Diagnostic Methods, the model performs a re-prediction. Through a Reinforcement Learning (RL) mechanism, model parameters are subsequently adjusted based on clinical efficacy feedback (such as patient symptom improvement following medication), thereby enhancing long-term prediction accuracy.
(5) Pre-training Stage
The model is trained on extensive TCM corpora, including ancient texts and medical records, to learn fundamental associations among “symptoms-syndrome types-medications” and to develop generalized knowledge representations of TCM. For instance, it captures patterns such as “pale tongue with white coating + thin and weak pulse → qi-blood deficiency,” as described in Diagnostics of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
(6) Fine-tuning Stage
Building upon the pre-trained model, annotated clinical task data—such as consultation dialogues and syndrome differentiation cases—are employed to optimize the model. Explicit instructions are incorporated to guide the model in generating responses that conform to diagnostic procedures. For example, given the prompt, “The patient complains of dizziness and fatigue, which worsens with movement,” the model produces a consultation flow including questions like, “May I ask if there is a sallow complexion? How is the appetite? What about sleep quality?” Ultimately, it outputs the syndrome differentiation result: “Qi deficiency syndrome, treated by replenishing qi and blood with Guipi Tang (Decoction for Spleen and Heart Nourishment).”
3. Discussion
Although Large Language Models (LLMs) currently exhibit limitations compared to human doctors—particularly in diagnostic accuracy, clinical reasoning, managing complex cases, ethical decision-making, and real-time responsiveness—they nonetheless hold substantial potential to assist medical practice. LLMs can provide valuable knowledge support and effectively handle routine tasks. Looking ahead, these models are poised to serve as auxiliary tools that collaborate synergistically with physicians, enhancing overall healthcare delivery.
3.1. The issue of “replacing” doctors by LLMs
First, large language models are accurate in providing "diagnosis and treatment recommendations." Specifically, in some medical scenarios, large language models like GPT-01 can exhibit high diagnostic accuracy. In diagnosing acute diseases, its diagnostic accuracy for ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI) can exceed 95% in certain cases. It can also provide treatment recommendations based on clinical guidelines and performs remarkably well in chronic disease management. The 01 model, as mentioned, also demonstrates its advantages in diagnostic tasks when tested on multiple medical datasets. There is a significant increase in diagnostic accuracy in clinical benchmark tests such as DxBench and NEJMQA [13].
Secondly, large language models lack the capacity for ethical judgment and emotional understanding. Medical decision-making encompasses not only clinical knowledge but also ethical considerations and emotional sensitivity. In interactions with patients and in the formulation of treatment plans, physicians must respect patient autonomy, honor their preferences, and address their emotional needs by providing compassionate, humanistic care. While large language models may demonstrate some sensitivity to ethical issues, they are currently unable to navigate the complex emotions and nuanced circumstances that arise in real-world medical practice. Particularly in situations such as end-of-life care, the communication and decision-making processes between physicians, patients, and their families involve profound emotional exchange and empathy—elements that cannot presently be replicated by artificial intelligence.
Large language models can function effectively as assistive tools to enhance physicians’ work efficiency. In the future, the optimal application of large language models lies in their collaboration with doctors, capitalizing on the complementary strengths of both. Physicians can leverage the rapid data-processing capabilities and extensive knowledge base of large language models to generate more diverse diagnostic hypotheses and treatment options, thereby enriching clinical decision-making.
3.2. Risk of professional competence degradation of doctors
Large language models have certain limitations in medical applications. Research has found that large language models perform inconsistently when faced with semantically varied questions, have difficulty identifying false presuppositions, and exhibit limitations in their medical assessment capabilities, with their answers potentially being incorrect [14] . Large language models also face challenges such as fairness, privacy protection, and reliability. They may produce biases, leak privacy, and perform poorly in complex situations. Moreover, large language models lack clinical experience and the ability to directly observe patients, and thus cannot conduct comprehensive diagnosis and treatment in the same way as doctors [15]. When using large language models, doctors can leverage the reference information they provide to further verify their own judgments, thereby improving diagnostic accuracy. At the same time, large language models can assist doctors in medical education and training, enhancing their professional knowledge and skills. However, if doctors rely too heavily on large language models, it may lead to a weakening of their clinical skills and critical thinking abilities. Over-reliance on ChatGPT, for example, may affect the development of clinical reasoning skills and contextual understanding. Nonetheless, as long as doctors correctly view large language models and use them as auxiliary tools rather than replacements for their own professional judgment, these problems can be avoided [16].
3.3. Issue of liability attribution
Big data comes from a wide range of sources, has a complex structure, and its quality varies greatly. Biases in training data can cause large language models to produce biased output results [17]. In the field of traditional Chinese medicine, if the data used for training contains incorrect information or sample biases, it may lead to errors in diagnoses and treatment recommendations.
A more specific example is the “model hallucination phenomenon” [18]. During the process of assisting in traditional Chinese medicine diagnosis, if the model provides incorrect diagnostic advice or treatment plans, it is difficult to determine where the responsibility lies. Model developers may attribute the error to data issues, while data providers may shift the blame to the model algorithm. From the user's perspective, if traditional Chinese medicine doctors rely too heavily on model recommendations and implement treatments without careful judgment, they also bear certain responsibilities. In actual medical disputes, all parties often shift blame onto each other, making the determination of responsibility extremely complex.
4. Conclusion
This study addresses the longstanding challenge in Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) wherein the “Four Diagnostic Methods” heavily rely on physicians’ professional expertise, resulting in prolonged training periods and limited human resources. To mitigate this issue, we propose a Large Language Model (LLM)-based framework aimed at enhancing diagnostic prediction capabilities. The framework is theoretically grounded in mathematically defined loss functions for both the pre-training and supervised fine-tuning stages. A preliminary predictive model was constructed and implemented using Python, incorporating auxiliary techniques such as cluster analysis, principal component analysis, and factor analysis to support model performance. Finally, we discuss the ethical considerations associated with the deployment of such models, including the potential for replacing human doctors, the risk of professional competence degradation, and the complex issue of liability attribution.



