1. Introduction
Balanced Homodyne Detection (BHD) is a foundational technique in quantum optics, enabling phase-sensitive signal analysis with exceptional efficacy in characterising quantum noise [1]. By employing a differential configuration, BHD suppresses classical noise components, particularly those arising from the Local Oscillator (LO), by differencing the photocurrents generated by two identical photodiodes. This setup allows for the selective extraction of quadrature-phase information, facilitating measurements that approach the quantum noise limit [2]. As demonstrated in [3], BHD can measure the orthogonal components of any phase. To have precise control on phase we usually apply PZT, EOM or fibre optic delay line [4], which compensates for phase fluctuations.
Thanks to these capabilities, BHD has become integral to a wide range of quantum technologies, including Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution (CV-QKD) [5], squeezed light characterisation, and large-scale applications such as gravitational wave observatories. Notably, the LIGO experiment employs BHD to suppress shot noise interference [6], while CV-QKD systems utilise it to decode quadrature-modulated quantum states transmitted over optical fibres [7].
To support such advanced applications, BHD systems must demonstrate three critical performance metrics: a high signal-to-noise ratio SNR, extensive detection bandwidth, and strong Common-Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR). Achieving all three simultaneously - especially at frequencies approaching 300 MHz - poses substantial technical challenges.
Although numerous advances have addressed specific aspects of BHD design, comprehensive approaches targeting all key performance dimensions remain limited. Therefore, this study proposes the development of a next-generation BHD platform, engineered for enhanced bandwidth, improved signal-to-noise (SNR), and superior CMRR. The proposed system aims to provide robust support for quantum-enhanced measurement tasks involving squeezed states and other non-classical light fields.
2. Theoretical background
2.1. Historical development and current state
By the 1980s, this technique had become a cornerstone of quantum optics research, enabling accurate resolution of quadrature amplitudes and facilitating the earliest experimental verifications of squeezed light states at the quantum noise limit [8].
During the 1990s, BHD contributed significantly to the development of quantum state tomography and the detection of vacuum fluctuations and quantum noise. These advances were supported by the emergence of low-noise Transimpedance Amplifiers (TIAs) and high-precision differential amplifiers with strong CMRR.
The period spanning the 2000s to 2010s marked a transition towards miniaturisation and
photonic integration, which significantly advanced BHD’s use in quantum information processing, coherent optical readout systems, and dynamically adaptive quantum measurement protocols [9-12]. During this time, improvements in analogue front-end design including the integration of low-noise TIAs and amplifiers with enhanced CMRR - greatly refined both the performance and compactness of BHD modules.
Today, BHD remains a foundational technique across a range of cutting-edge domains, including high-precision quantum metrology, broadband optical communications, gravitational wave interferometry, and scalable quantum computing systems.
2.2. BHD working principle
BHD is designed to measure the expectation value and fluctuations of a specific quadrature in a light field. By interfering with the signal with a strong local oscillator LO, the system enables the detection of the differential signal between two outputs (as shown in Figure 1).
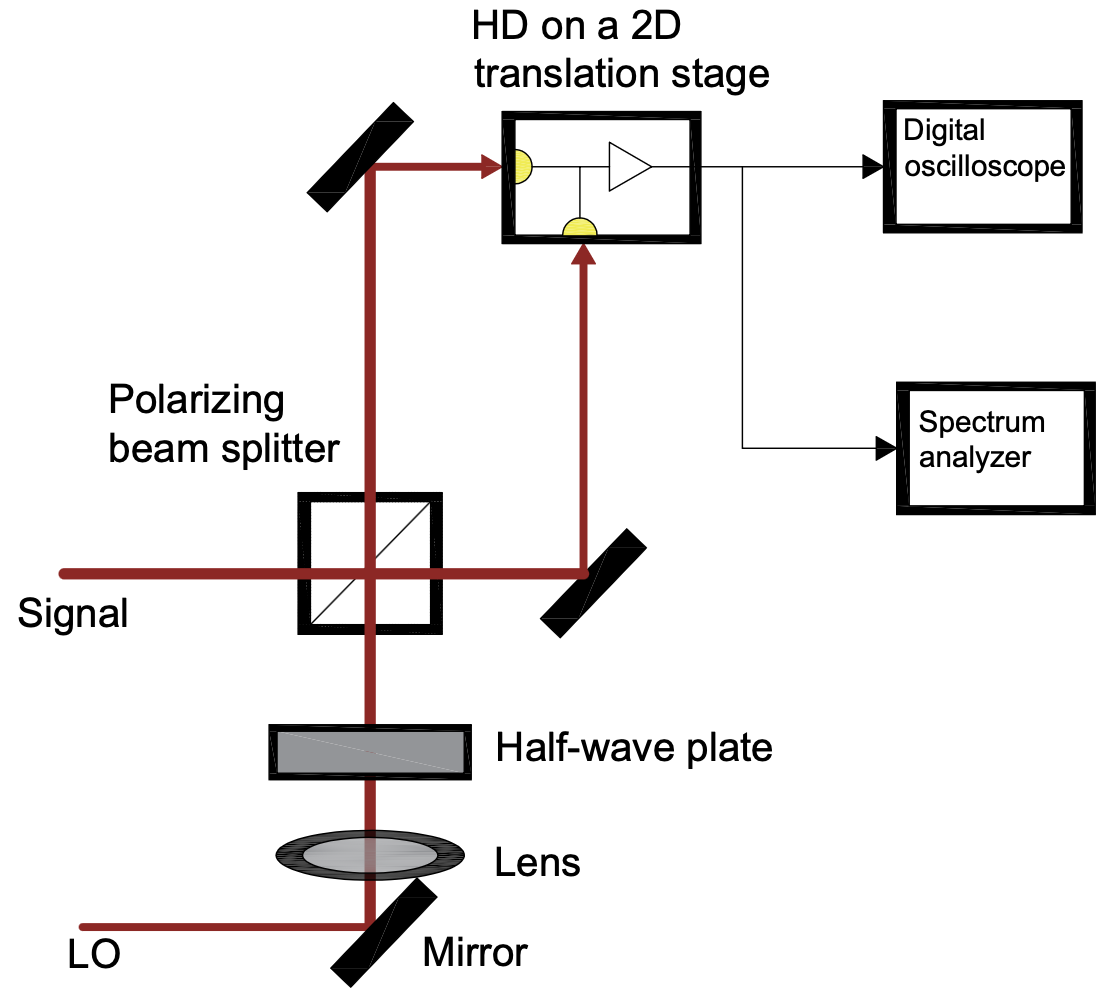
In this setup, the aim is to measure the signal light, which is weak and hard to capture - examples include vacuum states, squeezed states, or weak coherent states. In contrast, the LO serves as a strong reference light with a strong and stable phase, typically output by a laser.
These two beams pass through a 50:50 BS (Beam Splitter), producing two outputs,
and
These two beams are detected by two photodiodes, which convert light into electrical currents. Two outputs by detectors undergo a differential operation. It is known that that:
where
and
We can find
which represents quantum fluctuations of the amplitude of the signal light in the phase
Finally, the result is the current transferred from the signal light, amplified by 1 time.
2.3. Importance
Quantum optics experiments typically involve processing extremely weak optical signals, often significantly weaker than those in classical systems. This sensitivity requirement is especially critical in advanced applications such as quantum radar [13-17] and quantum information systems [18-20], where quantum metrology techniques [19] are poised to revolutionise measurement science.
While conventional photodetectors are limited to measuring optical intensity, many precision experiments require access to the full electromagnetic field information. BHD provides the ability to resolve a specific quadrature of the light’s electric field vector with high fidelity [21].
To enable such measurements in the quantum-noise limited regime, it is essential that the detector’s electronic noise floor remains extremely low. This ensures a sufficiently high SNR, allowing quantum features of the optical field to be observed without significant contamination from technical or thermal noise.
2.4. Innovation
This work introduces three key improvements over conventional designs.
Firstly, the detector supports dual-mode operation, functioning seamlessly under both continuous-wave and pulsed conditions. This enhances compatibility with a wide range of quantum optics experiments.
Secondly, by integrating high bandwidth photodiodes and low-noise, high-speed operational amplifiers, the system achieves strong performance while remaining cost efficient.
Thirdly, the design reaches the 300 MHz bandwidth, while maintaining low electronic noise, achieving a clear separation between shot noise and electronic noise of approximately 10
Compared to earlier systems with limited high-frequency resolution, this implementation significantly extends the frequency range and improves the reliability of quantum noise discrimination.
2.5. Application
BHD is extensively utilised in both quantum optical systems and coherent communication technologies to retrieve detailed phase and amplitude characteristics from low-intensity optical fields. This approach relies on coherently combining a weak signal with a high-power local oscillator to precisely extract one quadrature component of the electromagnetic field. Owing to its ability to suppress classical noise and achieve measurements approaching the shot-noise limit, BHD plays a crucial role in scenarios requiring high sensitivity and quantum-level precision [22].
Beyond traditional laboratory setups, BHD has been adopted in practical applications such as CV-QKD, quantum random number generation, and real-time squeezed state monitoring. Its integration with photonic chips and low-noise electronics enables scalable, compact platforms suitable for deployment in fibre-based quantum networks and next-generation optical transceivers. Additionally, BHD supports advanced techniques in quantum metrology and spectral analysis, facilitating the reconstruction of Wigner functions and the direct measurement of quantum noise spectra across a broad frequency range.
Measurement of the amplitude quadrature
Detection of the amplitude quadrature is primarily used in monitoring intensity fluctuations, enabling tasks such as amplitude-squeezed state characterisation, quantum random number generation, and quantum-enhanced imaging, where reduced amplitude noise enhances sensitivity [23]. However, this article does not explore these aspects in depth.
2.6. Challenges
One of the primary engineering challenges in the development of this detector involves simultaneously achieving a high CMRR, maintaining a uniform gain response across the target bandwidth, and suppressing various noise sources. In particular, attaining a high CMRR is essential for minimising the influence of classical noise originating from the local oscillator, which is especially critical under pulsed operating conditions [18].
A flat frequency response is equally important, as it prevents signal distortion and ensures accurate temporal resolution, though implementing such characteristics over a wide bandwidth is technically non-trivial. To mitigate electronic and dark current noise, the design employs low-capacitance, low-dark-current photodiodes and incorporates careful layout strategies to eliminate feedback-induced oscillations.
This project presents a practical and cost-effective solution for constructing a BHD system suited to advanced quantum optics applications. Theoretical modelling conducted within the project further establishes the relationship between detector bandwidth, electronic noise, and their contribution to effective optical loss, offering new insights into performance limits in time-domain quantum measurements.
Potential use cases include quantum state tomography and continuous-variable quantum information processing [19], where the detector’s low noise floor and strong CMRR enable precise discrimination between quantum and classical noise components.
The measurement of
To address these issues, researchers have introduced advanced stabilisation techniques, low noise circuit design, and high efficiency optical detection systems, essential for achieving quantum-limited performance in BHD systems.
3. Theoretical background
This section will specifically discuss the complete PCB design, including simulation and the experimental schedule for developing a 300 MHz bandwidth BHD, which aims to optimise the detection of weak optical signals at a wavelength of 1550 nm.
The methodology begins with the schematic design of a differential detection architecture, followed by the careful selection of low-capacitance, high-speed
However, a real BHD must be able to measure arbitrary quadrature by precisely adjusting the phase difference introduced by LO and signal. In this paper, we use TINA software to model the system based on a phase difference of
3.1. Introduction to building an MZI
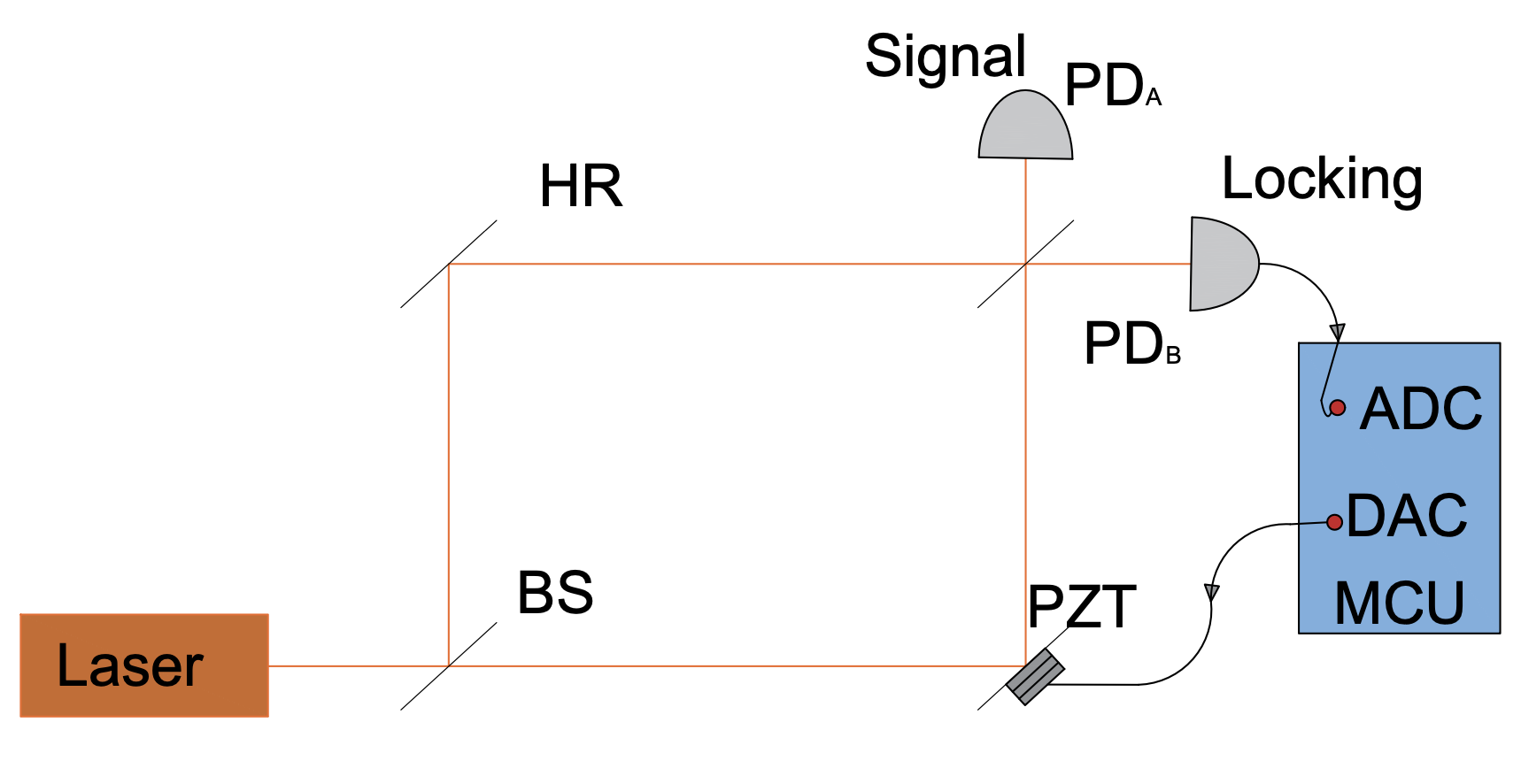
A standard Mach-Zehnder Interferometer (MZI) is composed of two beam splitters and a pair of mirrors that create two distinct optical paths [25], commonly referred to as the interferometer’s arms (see Figure 2).
Upon entering the first beam splitter, the incoming optical signal is coherently divided into two beams, which then propagate along separate routes. Along these paths, the beams may encounter different optical components or experience varying phase delays.
The mirrors reorientate beams towards the second beam splitter, where they are recombined. The interference pattern at the output ports relies on the relative difference of phase between the two optical paths. This interference can be constructive or destructive, depending on the original phase offset. The outputs of the second beam splitter thus encode information about the Optical Path Difference (OPD) between the arms.
To actively control the interference condition, a variable phase shift can be applied commonly using a piezo-driven mirror or a thermo-optic phase modulator. The resulting interference pattern, or fringes, is then monitored by photodetectors placed at the output, providing high sensitivity to phase variations within the system [26].
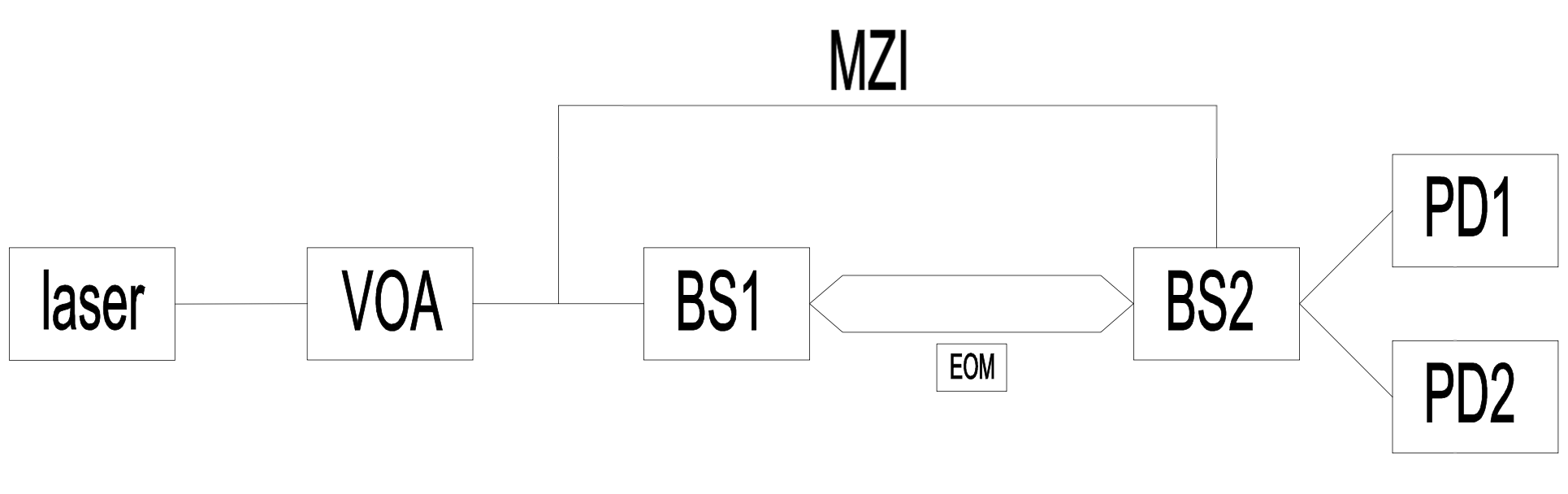
In this experimental setup, a fibre-integrated MZI is employed. The system utilises a Continuous-Wave (CW) laser operating at 1550 nm as the optical signal source. The emitted beam is initially divided into two equal-power paths using a 1×2 fibre optic coupler with a 50:50 splitting ratio. These two optical paths are then routed into the input ports of a 2×2 fibre coupler, forming the core structure of the fibre-based MZI.
Both the beam splitting and recombination processes are realised entirely within the fibre infrastructure.
To introduce phase tunability, one arm of the interferometer includes an electrically controlled phase modulation unit, such as a thermo-optic modulator or a piezoelectric fibre stretcher [27]. By adjusting the applied voltage, the local refractive index of the fibre can be varied, enabling precise control over the OPD between the two arms [28].
At the output stage, the recombined beams from the MZI are detected by two photodiodes. These photodetectors serve as the input to a BHD system, where the differential photocurrent is measured. This configuration efficiently suppresses common-mode noise and facilitates high-fidelity extraction of the signal’s quadrature information [29].
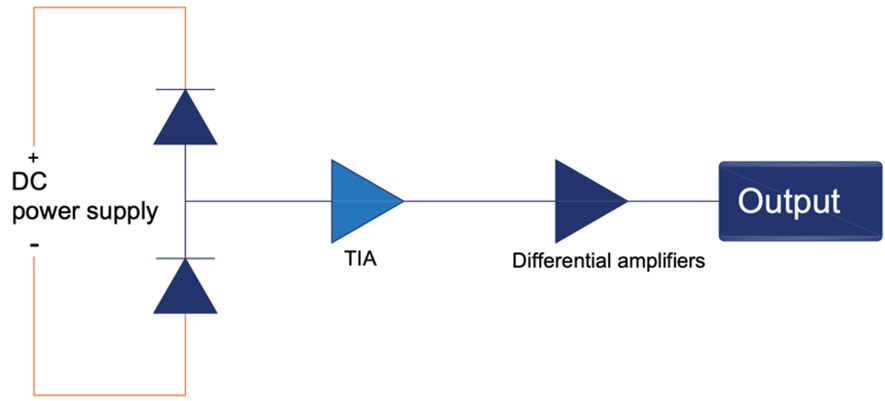
The complete fibre-based BHD system schematic is presented in the following diagram (as shown in Figure 3), which is transferred to an electrical circuit schematic as shown in Figure 4.
The BHD schematic diagrams is shown in Figure 5 below.
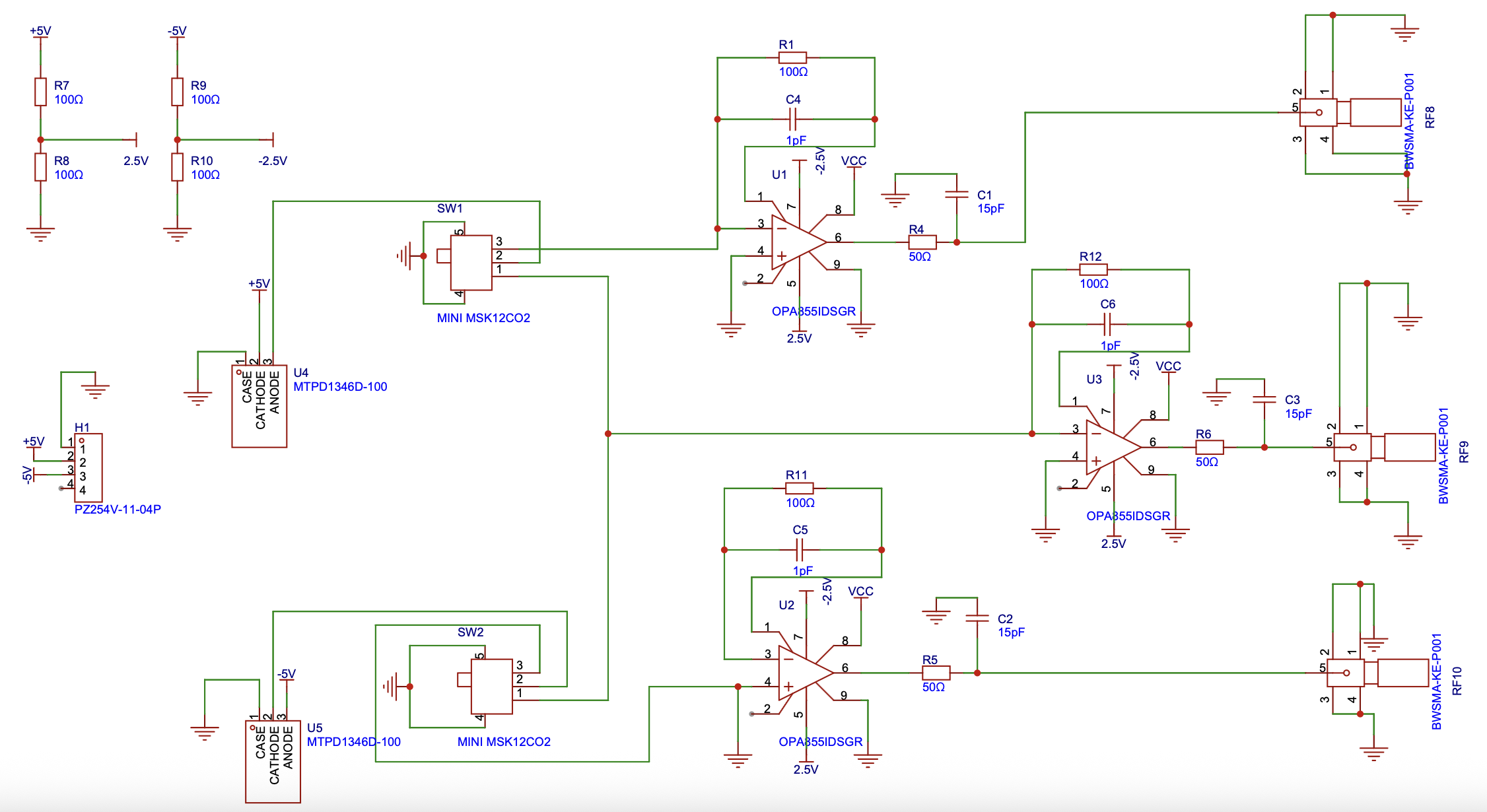
The BHD is designed based on a symmetric architecture consisting of two identical PDs, two TIAs, and a differential amplifier. The system performs homodyne detection by interfering with a weak signal beam and a strong LO beam and converting their intensity difference into a voltage signal. This differential architecture enables high CMRR and improves SNR.
3.2. Devices selection
The selected components for BHD are shown in Table 1.
The photodiode at 1550nm with high responsivity and it enables efficient conversion of photoelectric. High performance TIA OPA855 are selected as high gain bandwidth. The remaining related components are shown in the table 1. below.
|
Components |
Parameters |
Value |
|
Photodiode |
900–1700 nm |
0.9 A/W at 1550 nm |
|
Differential amplifier |
OPA847 |
|
|
TIA |
OPA855 |
GBW: 8GHz |
|
R3 |
100 |
|
|
R4 |
100 |
|
|
C1 |
15pF |
|
|
C4 |
1pF |
|
|
R5 |
50 |
|
|
R6 |
50 |
|
|
Power source |
2.5V DC |
3.3. Simulation results
In addition to the TINA simulation focusing on phase quadrature measurement, MATLAB simulations have also been employed to investigate amplitude quadrature detection scenarios.
3.3.1. Phase quadrature
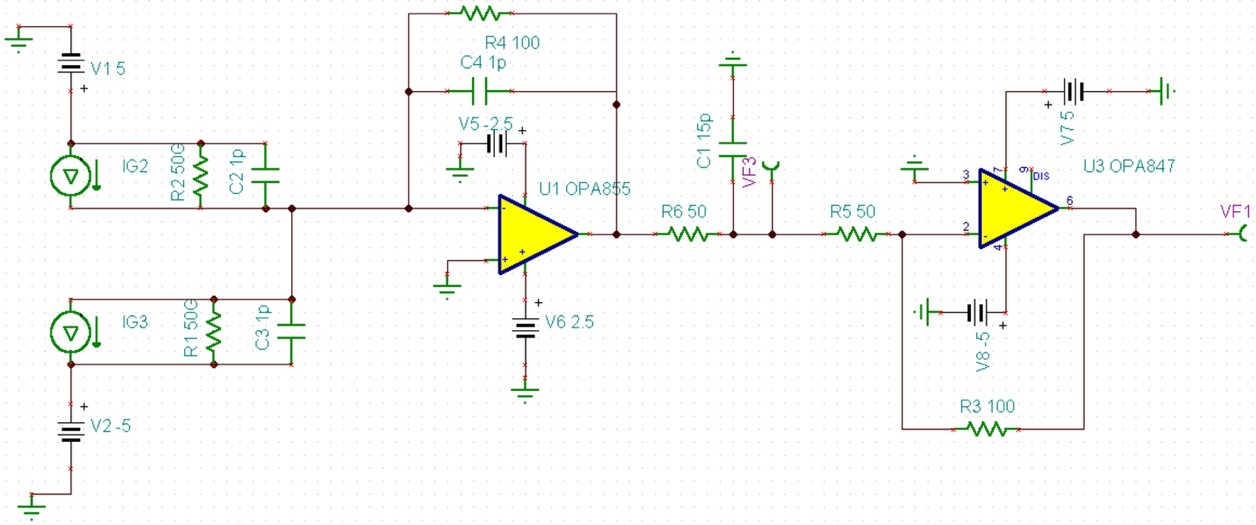
This simulation circuit (see Figure 6), implemented using TINA, demonstrates a Balanced Homodyne Detection (BHD) amplifier setup. Two ideal current sources (I1 and I2), each generating a 550 µA current at 300 MHz with a 90° phase difference, are used to emulate the photocurrents typically produced by photodiodes under optical interference conditions. These signals represent the output of a balanced detector receiving phase-shifted optical fields.
The two current signals are separately converted into voltage signals by two ideal transimpedance amplifiers (OPAMP 3T VIRTUAL, labelled as LTC6269 Channel A and Channel B). These voltage outputs are subsequently processed by a differential amplifier based on the AD8008AR operational amplifier, resulting in a differential output signal observed through the virtual oscilloscope (XSC1).
Components such as resistors (R1, R2, R3, R4, R5) and capacitors (C1, C3, C4) are carefully selected to achieve appropriate gain, bandwidth, and impedance matching, thus ensuring the circuit operates effectively at the target frequency of 300 MHz.
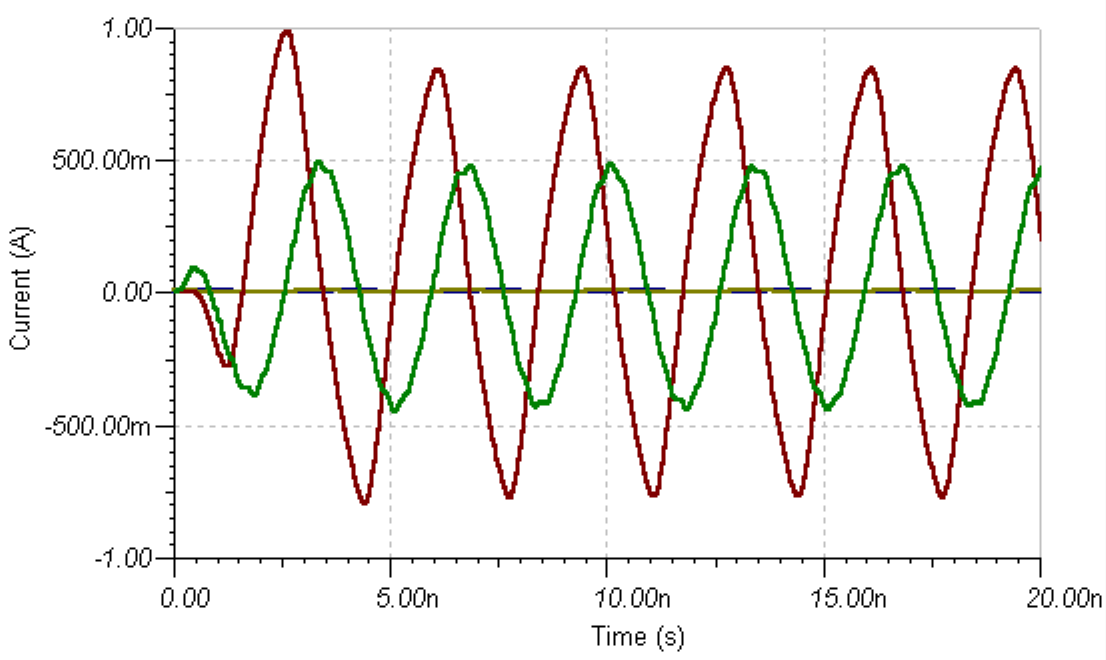
The provided oscilloscope screenshot in Figure 7 (Oscilloscope-XSC1) illustrates the simulated output signals from the differential amplification circuit using TINA:
VF3: Output of the first-stage TIA (green curve)
This waveform represents the output after processing by the OPA855 TIA. It exhibits a clear sinusoidal signal with a stable amplitude around 500mV, indicating successful amplification of the differential input signals.
VF1: Final output after second-stage amplification (Red curve)
This waveform represents the differential output signal after the second-stage amplification. Its amplitude remains close to zero (approximately 1V), confirming the effective common-mode noise suppression and proper differential operation of the circuit.
4. Results and discussion
4.1. Discussion for phase quadrature measurement
This section will present the quantitative analysis of phase quadrature
The analysis is based on the result of the TINA circuit simulation; SNR and CMRR are calculated to evaluate the performance of the system under ideal conditions. The following subsections provide detailed calculations for determining the transimpedance output, and effective voltage amplitude.
From the simulation results in TINA (Figure 4), we calculate an SNR of approximately 70dB.
The CMRR, which measures the ability of the differential amplification system to suppress common-mode signals, is around 60dB.
The experimental results presented in an ideal mode were obtained through simulations conducted using TINA software. The simulated circuit achieved a CMRR of 70 dB and an SNR of 60 dB, indicating its capability for effective noise suppression and reliable signal amplification. These performance metrics confirm that the proposed design is suitable for practical quantum optics applications, including CV-QKD, squeezed state detection, Wigner function reconstruction, and quantum noise spectrum analysis [26].
5. Process implementation
While the current experiment effectively demonstrates the circuit performance through TINA simulations, there remain several practical improvements to be addressed in future work. Specifically, the construction of the physical PCB layout requires careful attention to detail, including ensuring symmetry and proper routing of differential signal traces.
During PCB fabrication, special care should be taken to maintain balanced and symmetrical lines, avoid unnecessary intersections or overlaps, and minimise potential signal interference or distortion. These precautions are crucial for preserving circuit integrity and achieving the expected experimental results in practical quantum optics applications.
6. Process implementation
BHD remains a foundational technique in the field of quantum science and high-precision optical metrology. It plays a crucial role in quantum optics applications such as reconstructing quantum states, detecting squeezed light, and probing quantum level noise [29].
In practical systems, BHD enables secure communication through CV-QKD and enhances signal sensitivity in large-scale experiments like gravitational wave detection.
With ongoing advances in integrated photonic circuits and low-noise electronic components, the future of BHD points toward more compact, power-efficient, and scalable architectures [30]. These developments are expected to significantly broaden its utility across quantum computing, ultra-fast optical networks, and emerging quantum metrology systems, positioning BHD as a cornerstone of next-generation quantum technologies.
Furthermore, targeted measurement of different quadrature components using BHD has opened specialised application pathways. Amplitude quadrature (
7. Conclusions
This project presents the design of a 300 MHz bandwidth BHD optimised for weak optical signals at 1550 nm. Through circuit design modelling and simulation in TINA, it demonstrates key performance parameters including CMRR of 70 dB and an SNR of 60 dB. These results verify the capability of the circuit design for effective noise suppression and signal amplification in quantum optics scenarios. The system employs InGaAs photodiodes and is equipped with low-noise TIAs, and a high-speed differential amplifier.
Although all results were obtained from idealised simulations, the circuit architecture shows strong potential for real-world implementation.
The next stage of this project will focus on the physical implementation of the BHD system through PCB fabrication. A major challenge in this stage is optimising the PCB layout to ensure that the circuit retains its simulated performance in a real environment. Special attention must be given to the symmetry of the circuit topology, particularly in the routing of differential signal paths from the photodiodes through the TIAs and into the differential amplifier. Maintaining symmetrical and impedance-matched paths is important for minimising timing mismatches and enhancing CMRR.
In addition, we need to further investigate the selection of passive and active components. This includes choosing low-noise resistors, precision capacitors with low parasitic inductance, and alternative amplifier models with superior CMRR and gain bandwidth characteristics. Following this, we will discuss the integration of feedback control loops, aiming to actively suppress low-frequency noise and stabilise gain under different signal conditions.
Overall, the proposed BHD design provides a viable platform for quantum-enhanced tasks including CV-QKD, squeezed state analysis, and time-domain quantum measurements. With further refinement, it is expected to make a significant contribution to scalable quantum sensing and integrated photonics system.



